UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography for UPSC CSE > Map: Types of Soil in India
Map: Types of Soil in India | Geography for UPSC CSE PDF Download
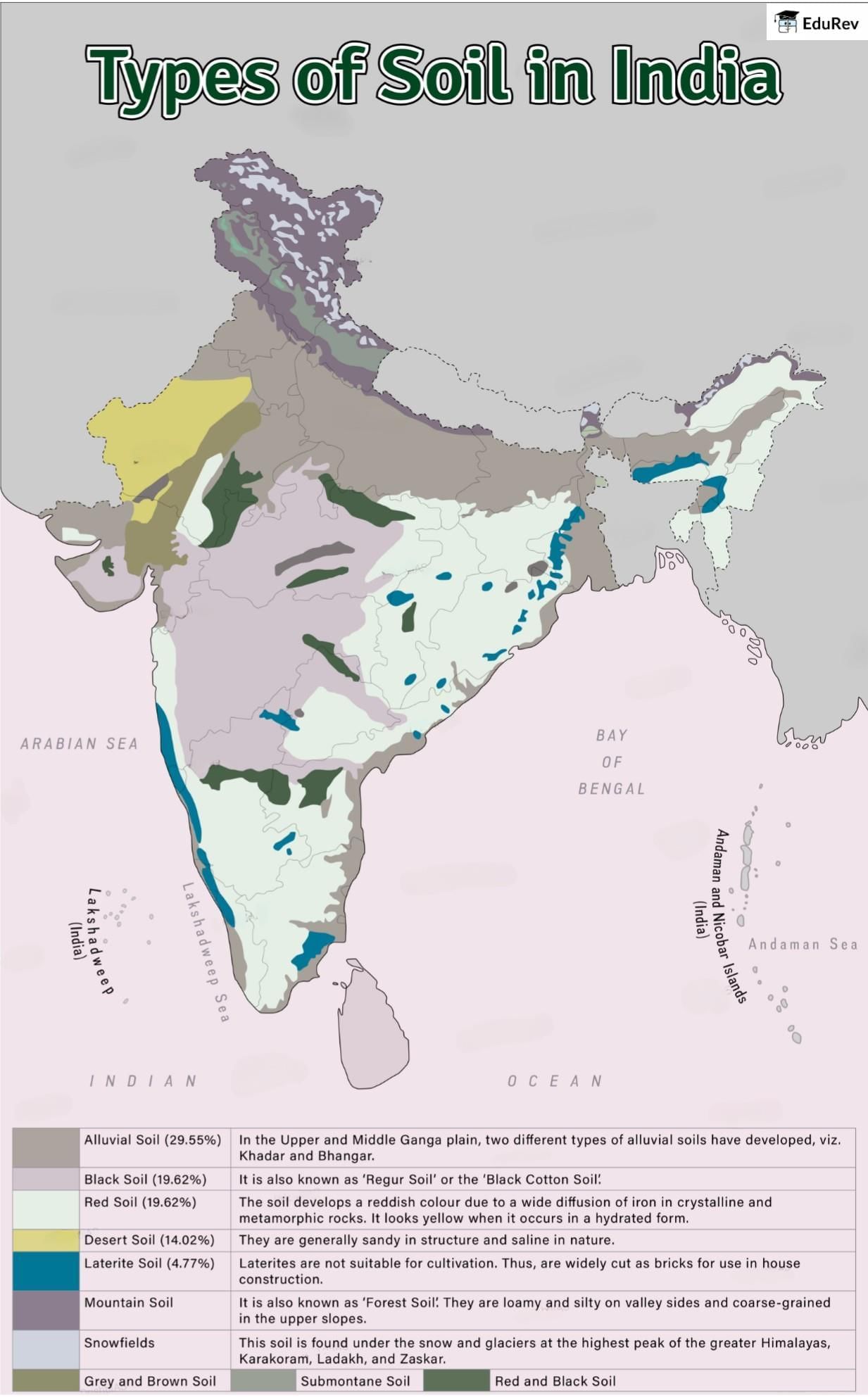
The document Map: Types of Soil in India | Geography for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Geography for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
175 videos|619 docs|192 tests
|
FAQs on Map: Types of Soil in India - Geography for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the major types of soil found in India? |  |
Ans. India has a diverse range of soil types, primarily categorized into the following:
1. Alluvial Soil: Found in river basins and plains, it is fertile and supports agriculture.
2. Black Soil: Known for its moisture-retaining capacity, it is suitable for cotton cultivation.
3. Red Soil: Rich in iron, it is found in southern and eastern India and supports various crops.
4. Laterite Soil: Formed in tropical regions, it is often used for brick-making and supports limited vegetation.
5. Desert Soil: Found in arid regions, it has low fertility and is characterized by sandy textures.
| 2. How do different soil types in India affect agricultural practices? |  |
Ans. The variety of soil types in India influences agricultural practices significantly. For example, alluvial soil is highly fertile, making it ideal for growing rice, wheat, and pulses. Black soil, with its moisture retention ability, is perfect for cotton, while red soil supports crops like millet and groundnut. Laterite soil is less fertile and often requires fertilizers for successful cultivation. Desert soil, due to its low organic content, presents challenges for agriculture but can support drought-resistant crops with proper irrigation.
| 3. What are the characteristics of Black Soil, and why is it important for agriculture? |  |
Ans. Black Soil, also known as Regur soil, is characterized by its clayey texture, moisture retention capacity, and rich mineral content, particularly lime, iron, calcium, and magnesium. It is important for agriculture as it is highly suitable for cotton cultivation, which is why it is often referred to as "cotton soil." The soil's ability to expand and contract helps in moisture retention, making it a valuable resource, especially in regions with low rainfall.
| 4. What role do soil types play in the ecosystem and biodiversity of India? |  |
Ans. Soil types play a crucial role in supporting ecosystems and biodiversity in India. Each soil type provides a unique habitat for various plant and animal species. For instance, alluvial soil supports diverse agricultural ecosystems, while forest soils are essential for sustaining forest biodiversity. The nutrient composition and drainage properties of different soils directly impact vegetation types and wildlife. Healthy soils contribute to ecosystem services such as water filtration, carbon storage, and habitat provision.
| 5. How does soil erosion affect soil types and agricultural productivity in India? |  |
Ans. Soil erosion poses a significant threat to various soil types in India, leading to the loss of fertile topsoil, which is crucial for agricultural productivity. Erosion can be caused by factors such as deforestation, overgrazing, and improper agricultural practices. It reduces soil fertility, decreases crop yields, and can lead to desertification in severe cases. Sustainable land management practices, such as contour farming and reforestation, are essential to combat soil erosion and preserve soil health for future agricultural sustainability.
Related Searches
















