Cheat Sheet: Heredity | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction |

|
| Heredity |

|
| Rules for Inheritance - Mendel’s Contributions |

|
| How Traits Get Expressed |

|
| Sex Determination |

|
| Summary Points |

|
Accumulation of Variation During Reproduction
Variations
Reproductive processes produce individuals with similarities but subtle differences.
- Asexual Reproduction: Minimal variation due to small inaccuracies in DNA copying (e.g., bacteria division).
- Sexual Reproduction: Greater diversity due to the combination of genetic material from two parents.
- Mechanism: Each generation inherits a common body design with subtle changes from the previous generation, creating diversity over time.
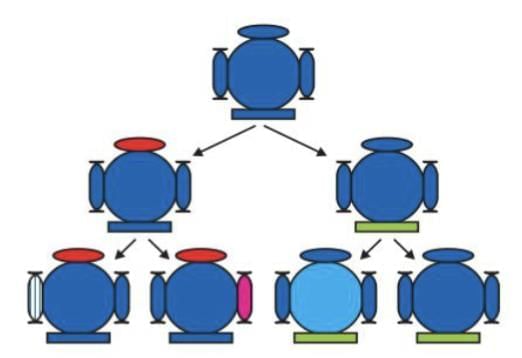
- Survival Advantage: Variations provide different advantages; environmental factors select variants (e.g., heat-resistant bacteria survive heat waves)
Heredity
Heredity is the process by which traits and characteristics are reliably passed from parents to offspring.
Inherited Traits: Children share basic human features but show variations (e.g., earlobe types - free or attached,).
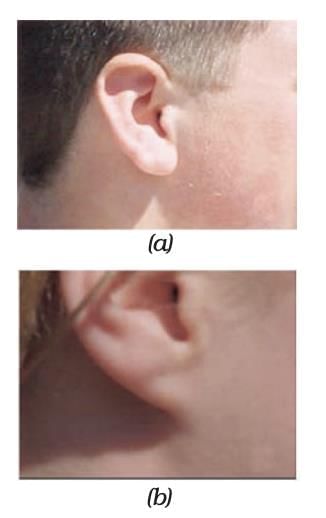 (a) free earlobes (b) attached earlobes
(a) free earlobes (b) attached earlobes
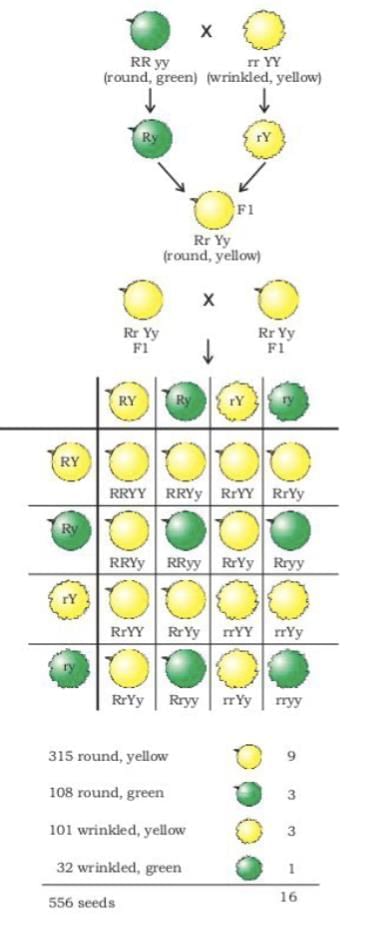
Rules for Inheritance - Mendel’s Contributions
Gregor Mendel (1822–1884): Studied inheritance using pea plants, blending science and mathematics to formulate laws of inheritance.
Experiments:
Used contrasting traits (e.g., tall/short plants, round/wrinkled seeds).
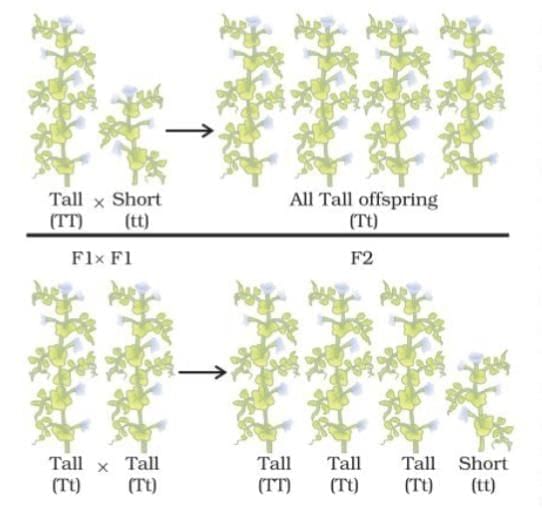
F1 Generation: Crossed tall (TT) and short (tt) plants; all progeny were tall (Tt), showing no intermediate traits.
F2 Generation: Self-pollination of F1 plants (Tt x Tt) resulted in a 1:2:1 ratio (TT:Tt:tt), with 25% short plants (tt).
Conclusion: Traits are controlled by two gene copies (alleles). Dominant traits (e.g., T for tallness) express with one copy; recessive traits (e.g., t for shortness) need two copies.
Dominant vs. Recessive
Dominant traits (e.g., tallness, round seeds) express over recessive traits (e.g., shortness, wrinkled seeds).
Independent Inheritance
Traits like seed shape and color are inherited independently, producing new combinations in F2 (e.g., tall with wrinkled seeds, short with round seeds).
How Traits Get Expressed
- DNA segments (genes) code for proteins that control traits.
- Plant height depends on a hormone. Efficient enzyme (controlled by a gene) produces more hormone (tall plant); less efficient enzyme results in less hormone (short plant).
- Both parents contribute one gene copy per trait, forming two sets in the progeny. Germ cells have one gene set, ensuring equal contribution.
Sex Determination
Human Chromosomes: 22 paired chromosomes + 1 pair of sex chromosomes (XX in females, XY in males).
Mechanism:
All children inherit an X from the mother.
The father’s contribution (X or Y) determines sex: X = girl (XX), Y = boy (XY).
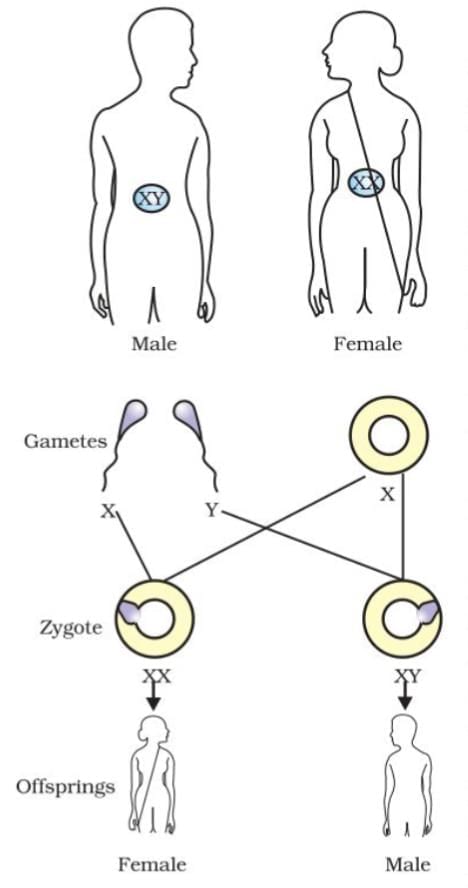
Note: Other Species: Sex determination varies (e.g., temperature in reptiles, sex change in snails).
Summary Points
Variations are inherited and enhance survival.
Sexual reproduction generates greater diversity than asexual reproduction.
Mendel’s laws: Traits are controlled by two gene copies; dominant traits express over recessive ones; traits inherit independently.
Genes code for proteins that control traits (e.g., hormones for plant height).
Human sex is determined by the father’s X or Y chromosome.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Heredity - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the role of heredity in the accumulation of variation during reproduction? |  |
| 2. How do mutations contribute to genetic variation? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of reproduction and their effects on variation? |  |
| 4. Why is genetic variation important for the survival of species? |  |
| 5. How do environmental factors influence genetic variation? |  |