Cheat Sheet: Light: Reflection and Refraction | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Properties of Light |

|
| Reflection of Light |

|
| Spherical Mirrors |

|
| Concave Mirror Image Formation |

|
| Sign Convention |

|
| Mirror Formula |

|
| Magnification |

|
| Refraction of Light |

|
| Lenses |

|
Properties of Light
Light is a form of electromagnetic energy that enables vision.
It shows both wave-like and particle-like behaviour.
It travels in straight lines and does not require a medium.
Its maximum speed is in vacuum, about 3 × 10⁸ m/s and slightly less in air.
It is responsible for phenomena such as image formation, twinkling of stars, rainbows, and bending of light.
When light strikes a surface, it may be reflected, refracted, or absorbed.
Reflection of Light
Definition: Light bounces off a surface, changing direction.
Laws of Reflection
- Angle of incidence (∠i) = Angle of reflection (∠r).
- Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal lie in the same plane.
Images
- Real Image: Formed where light rays actually meet.
- Virtual Image: Formed where light rays appear to meet.
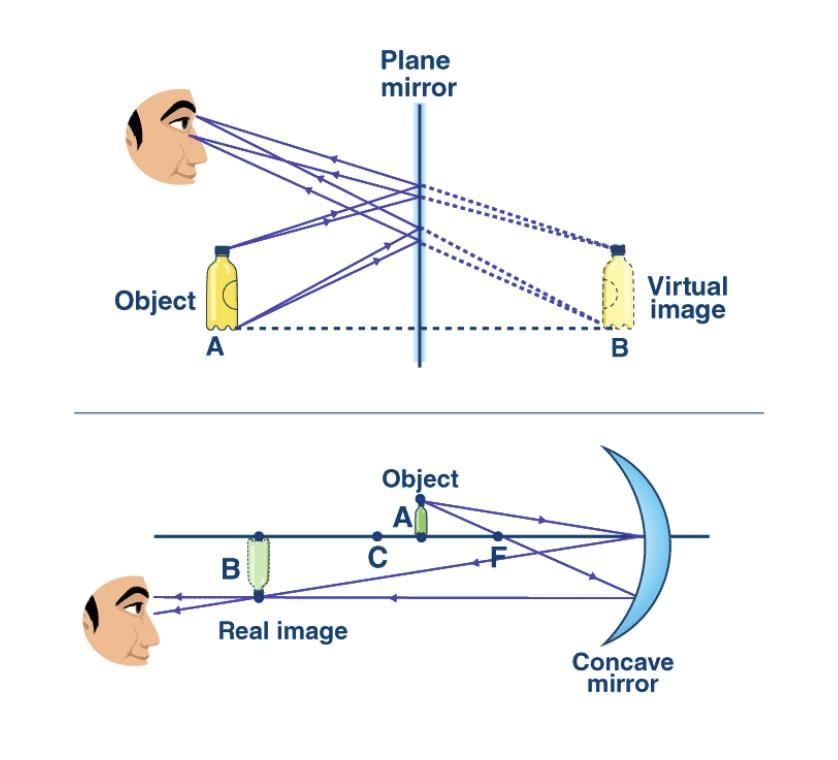
- Plane Mirror Characteristics:
- Virtual, erect, same size as object.
- Image distance equals object distance.
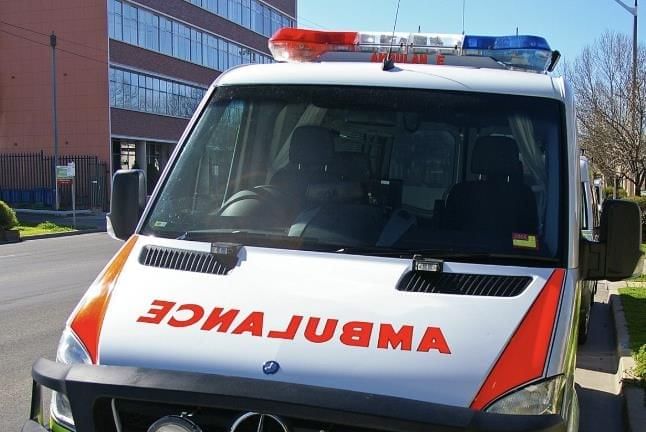
- Laterally inverted (right appears left, vice versa).
- Application: AMBULANCE written reversed for correct rearview mirror reading.

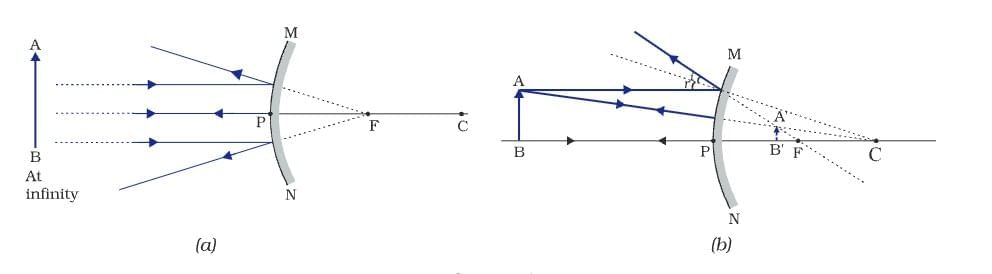
Spherical Mirrors
- Concave: Reflecting surface curved inward (converging).
- Convex: Reflecting surface curved outward (diverging).
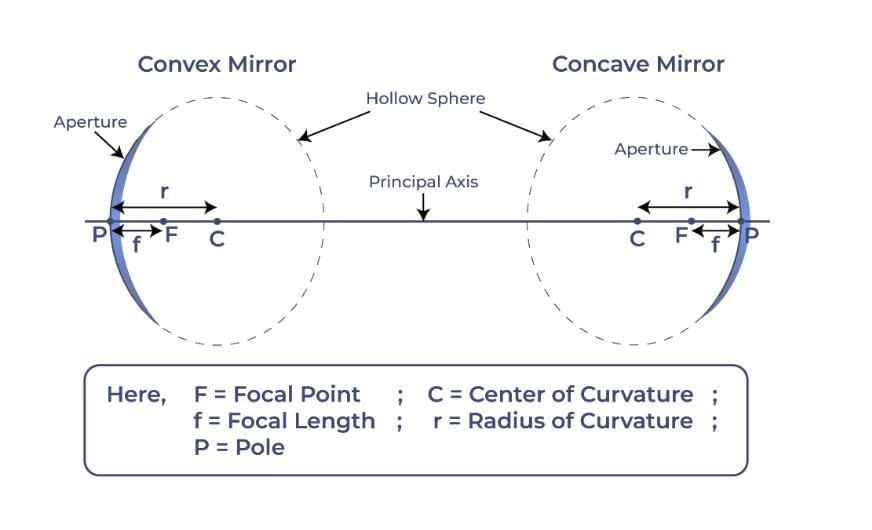
- Principal Axis: Line joining pole and center of curvature.
- Pole (P): Center of the mirror.
- Center of Curvature (C): Center of the sphere forming the mirror.
- Radius of Curvature (R): Distance from pole to center of curvature.
- Focus (F): Point where parallel rays converge (concave) or appear to diverge (convex).
- Focal Length (f): Distance from pole to focus (f = R/2).
- Ray parallel to principal axis: Passes through focus (concave) or appears to diverge from focus (convex).
- Ray through focus: Becomes parallel to principal axis after reflection.
- Ray through center of curvature: Reflects back along the same path.
- Ray incident at pole: Reflects obeying laws of reflection.
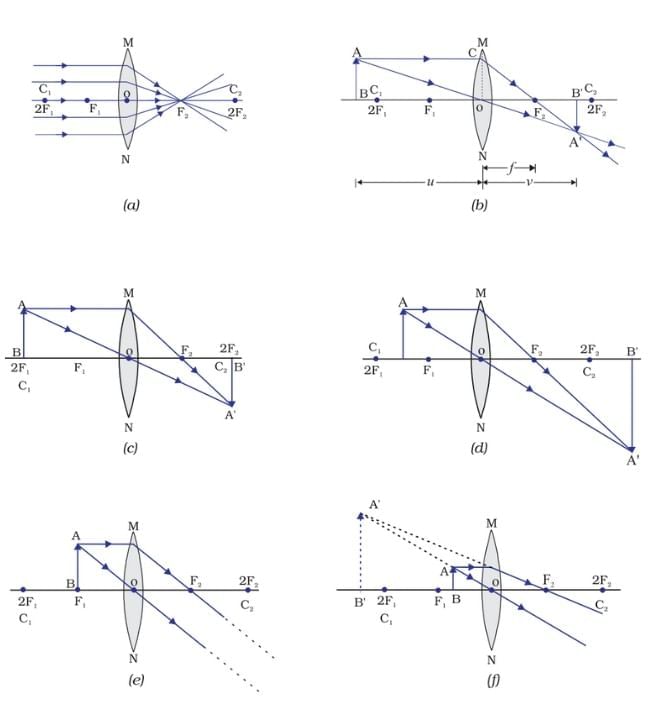
Concave Mirror Image Formation
- Image formation by a concave mirror for different positions of the object
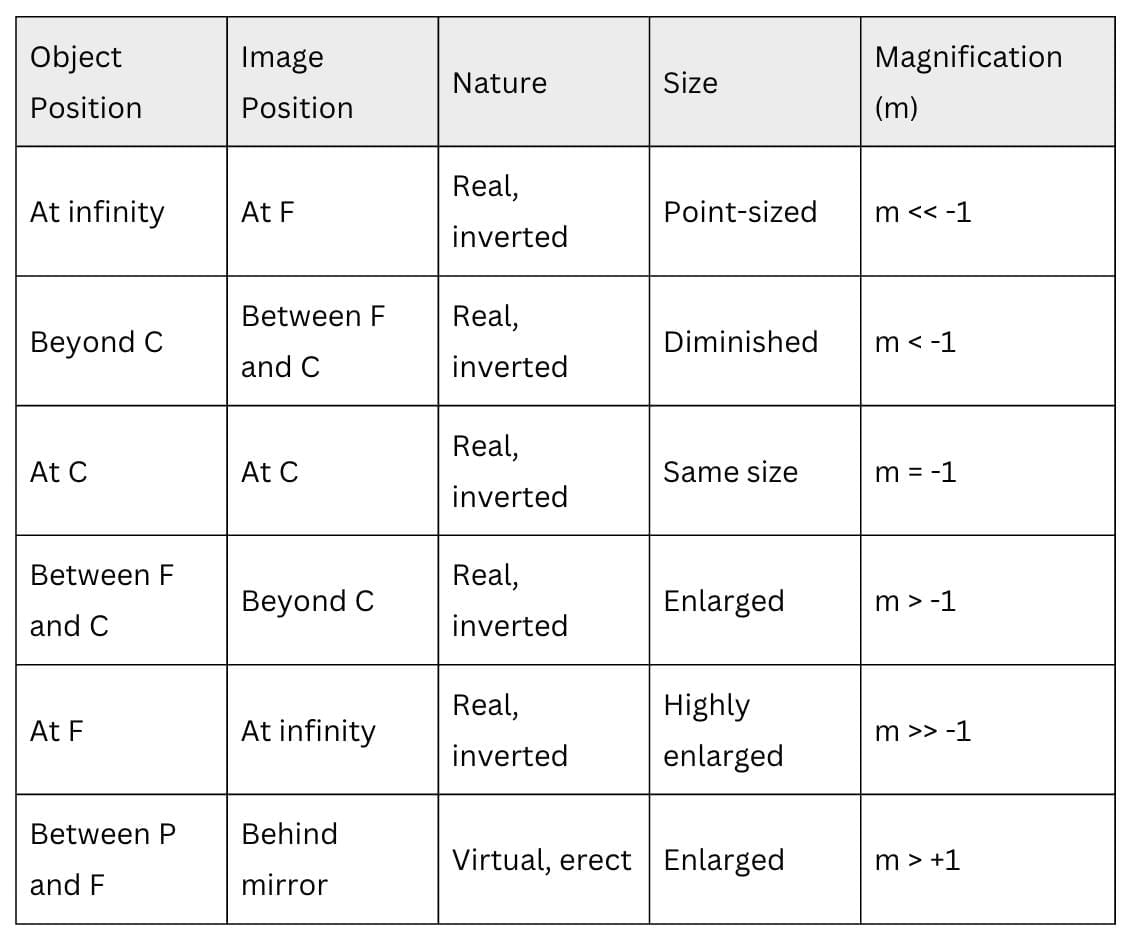
- Ray diagrams for the image formation by a concave mirror
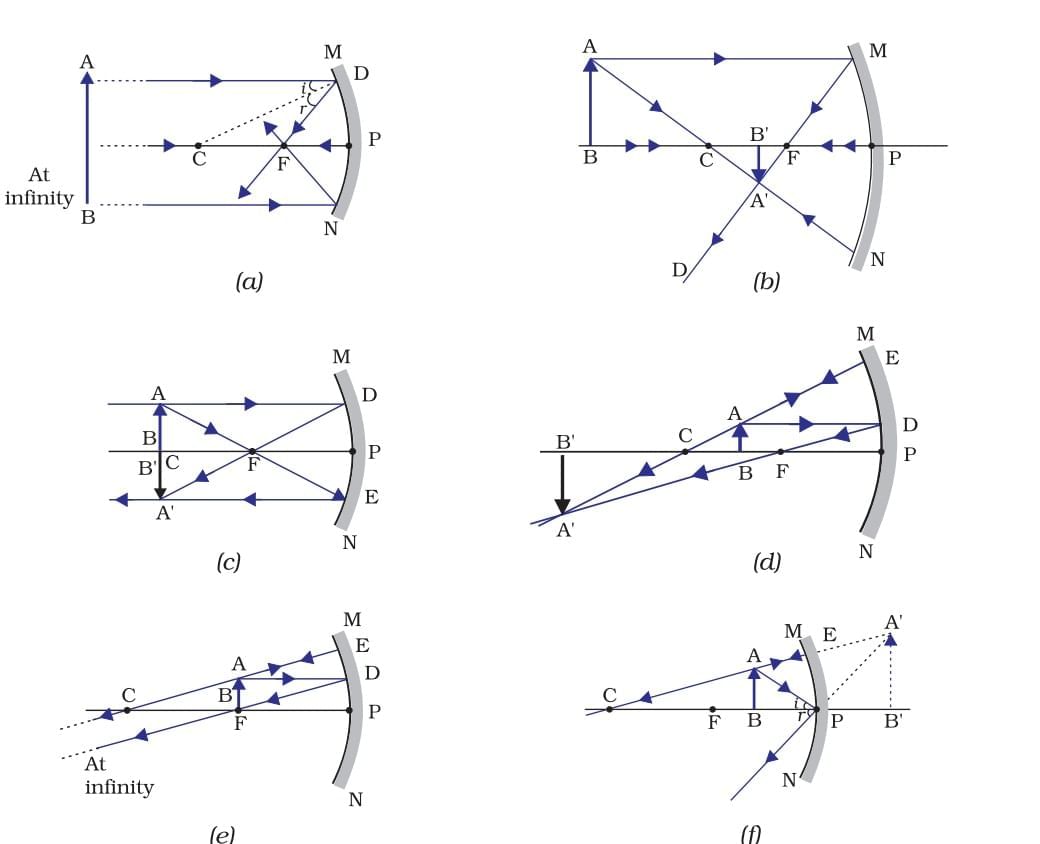
Concave Mirror Image Formation
Nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex mirror
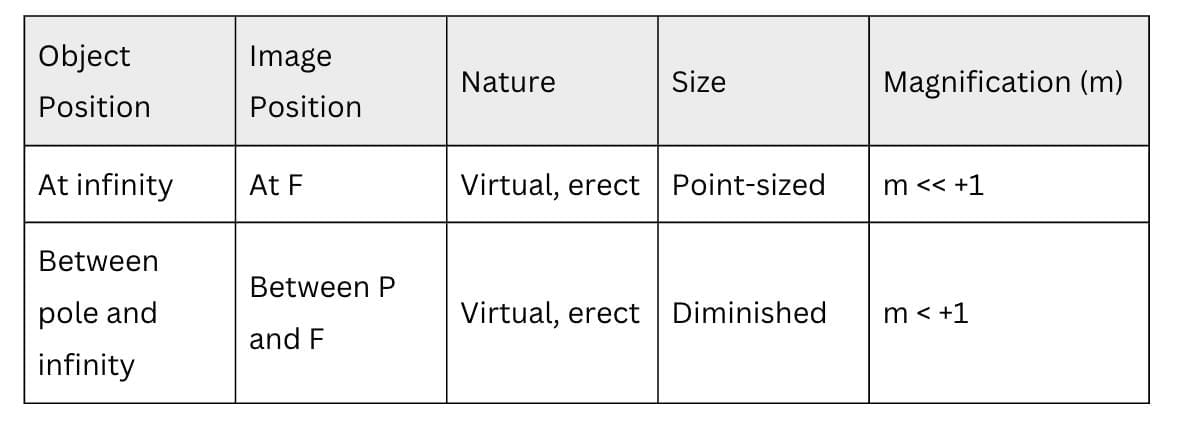
Uses
- Concave: Torches, headlights, dentist mirrors, shaving mirrors, solar furnaces.
- Convex: Rearview mirrors, security mirrors, blind turn visibility.
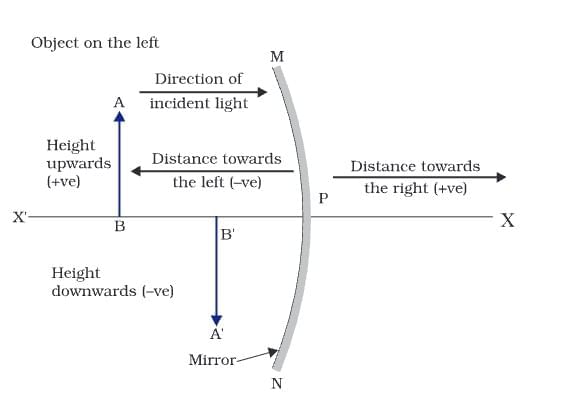
Sign Convention
- Object on left: Object distance (u) always negative.
- Distances along incident ray: Positive.
- Distances against incident ray: Negative.
- Above principal axis: Positive; below: Negative.
- Focal length: Negative for concave, positive for convex.
Mirror Formula
1/v + 1/u = 1/f
v = Image distance, u = Object distance, f = Focal length.
Magnification
m = hᵢ/hₒ = -v/u
- m negative: Real image.
- m positive: Virtual image.
- m = 1: Same size (plane mirror).
- m > 1: Enlarged.
- m < 1: Diminished.
Refraction of Light
Definition: Bending of light as it passes between media due to change in velocity.
Velocity: Maximum in vacuum/air (3 × 10⁸ m/s), lower in denser media.
Laws of Refraction
- Incident ray, refracted ray, and normal lie in the same plane.
- Snell’s Law: n₁ sin(θ₁) = n₂ sin(θ₂).
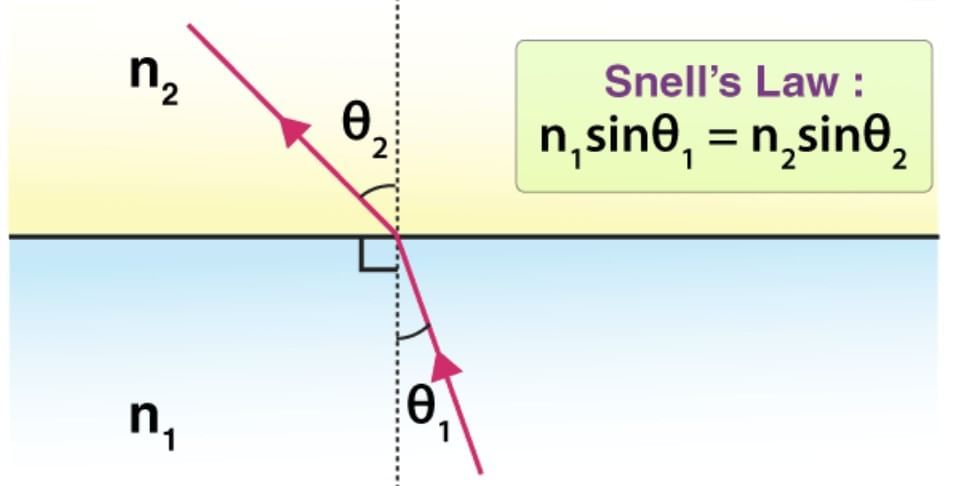
Bending Behavior
- Rarer to Denser: Ray bends toward normal (∠i > ∠r).
- Denser to Rarer: Ray bends away from normal (∠i < ∠r).
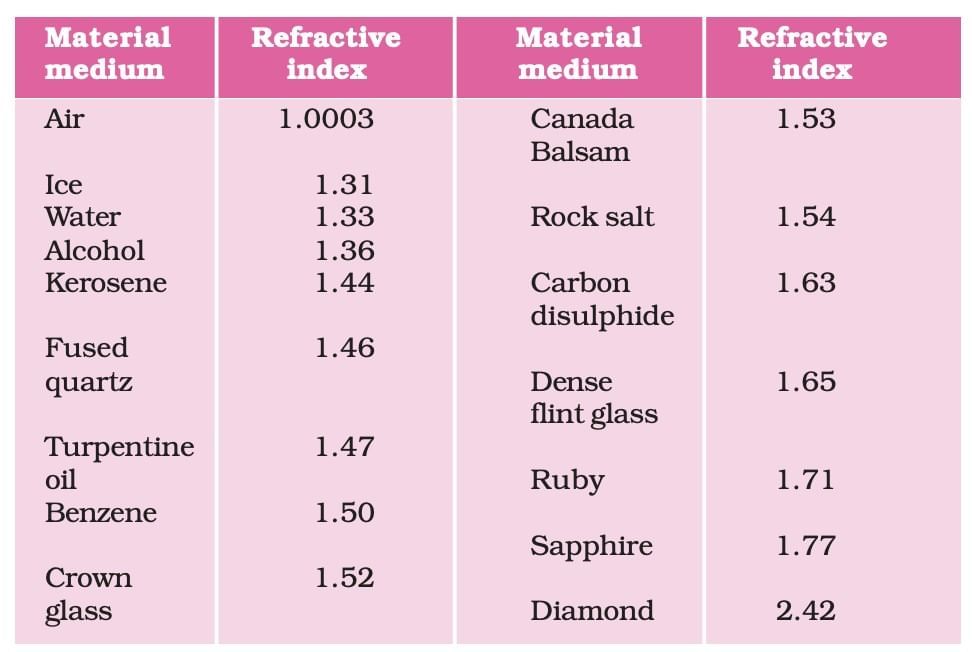
- Refractive Index (n): n = c/v (c = speed in vacuum, v = speed in medium).
- Higher n for denser media; maximum for violet, minimum for red.
Relative Refractive Index
Refraction: When a ray of light travels obliquely from one transparent medium to another, it changes direction due to a change in speed. This phenomenon is called refraction.
Behaviour of Light:
- From rarer to denser medium: Light slows down, bends toward the normal.
- From denser to rarer medium: Light speeds up, bends away from the normal.
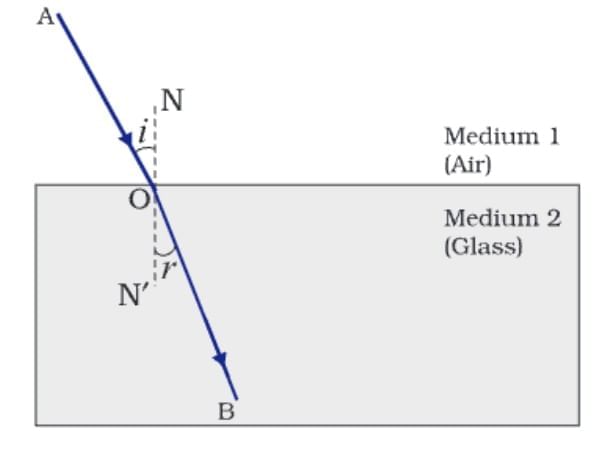
Refractive Index (n):
- It quantifies the extent of change in direction of light when passing from one medium to another.
- For two media, the refractive index of medium 2 with respect to medium 1 is:

- Similarly, for medium 1 with respect to medium 2:

Absolute Refractive Index:
- If medium 1 is vacuum or air, the refractive index of medium 2 is called the absolute refractive index:
 Speed of light in vacuum: 3×108m/s.
Speed of light in vacuum: 3×108m/s.- In air, speed is slightly less; in denser media like glass or water, it reduces significantly.
Optical Density:
- Optical density refers to a medium’s ability to refract light, not its mass density.
- A medium with a higher refractive index is optically denser; light slows down and bends toward the normal.
- A medium with a lower refractive index is optically rarer; light speeds up and bends away from the normal.
Key Observations:
- Light travels fastest in a vacuum, slower in air, and much slower in glass or water.
- An optically denser medium may not have higher mass density (e.g., kerosene has a higher refractive index than water but lower mass density).
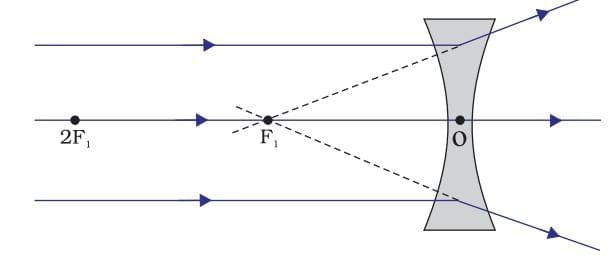
Lenses
Definition: Transparent material with two curved surfaces or one curved and one plane.
Types:
- Convex (Converging): Thicker at center.
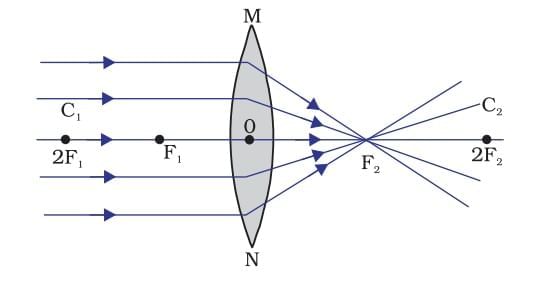
- Concave (Diverging): Thinner at center.
Key Terms
- Optical Center (O): Ray passes undeviated.
- Principal Axis: Line through optical center, perpendicular to lens.
- Principal Focus: Point where parallel rays converge (convex) or appear to diverge (concave).
- Focal Length (f): Distance from optical center to focus.
Ray Diagram Rules
- Ray through optical center: Passes undeviated.
- Ray through first focus (convex) or toward it (concave): Becomes parallel after refraction.
- Ray parallel to principal axis: Passes through second focus (convex) or appears to diverge from it (concave).
Convex Lens Image Formation
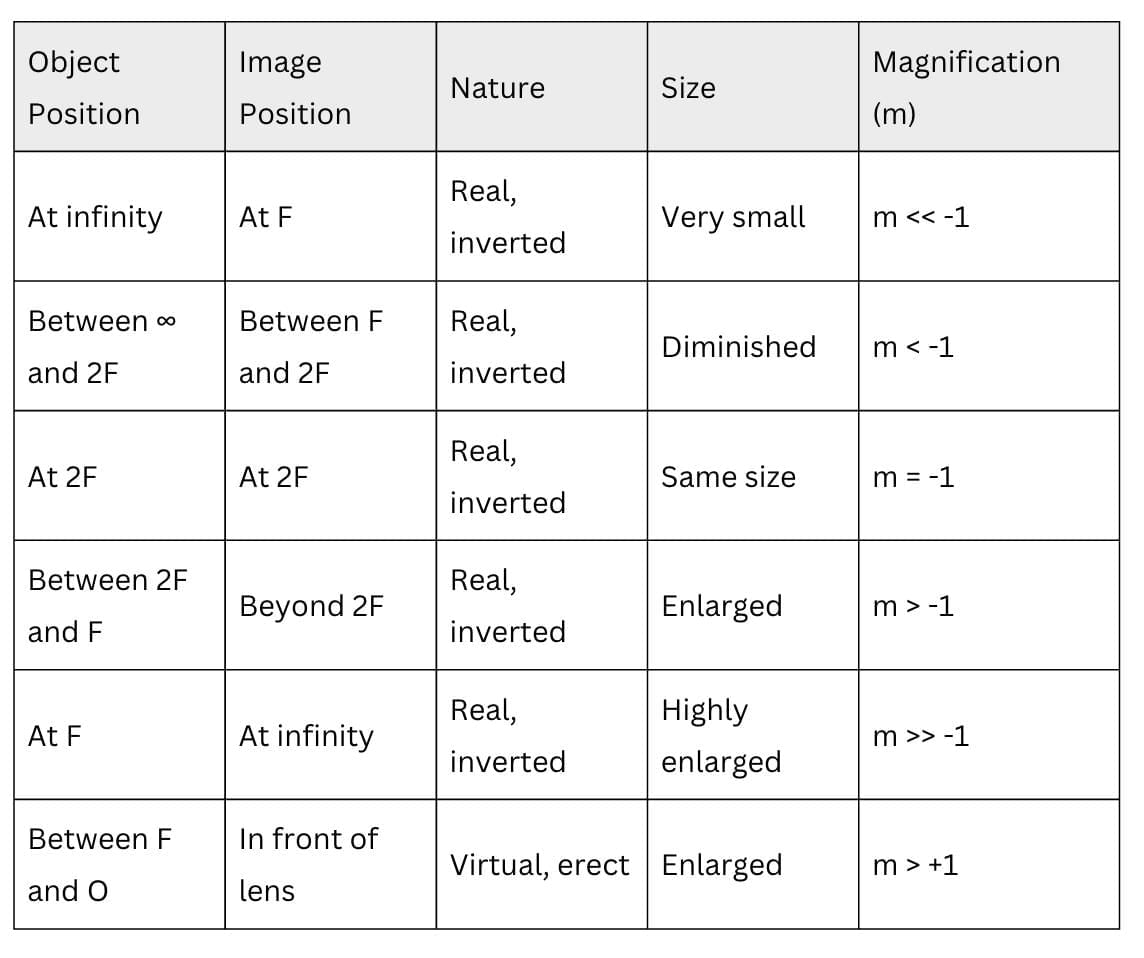
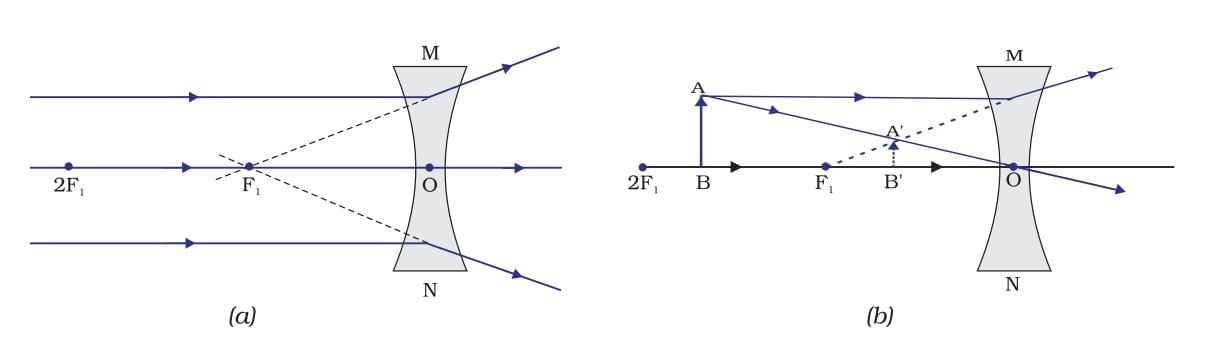
Concave Lens Image Formation
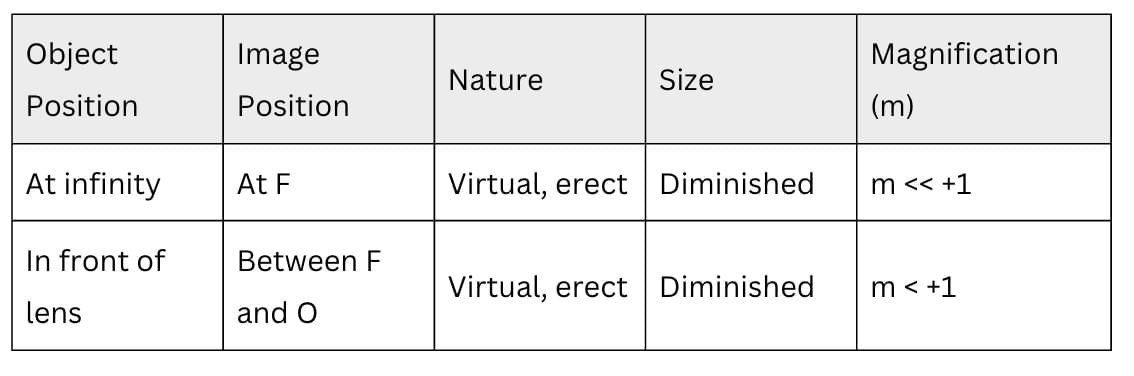
Lens Formula
1/f = 1/v - 1/u
f = Focal length, v = Image distance, u = Object distance.
Sign Convention
- u: Always negative.
- v: Positive for real, negative for virtual.
- f: Positive for convex, negative for concave.
Power of Lens
P = 1/f (f in meters).
Unit: Diopter (D).
Sign: Positive for convex, negative for concave.
Magnification
M = hᵢ/hₒ = v/u
- M negative: Real image.
- M positive: Virtual image.
- M = 1: Same size.
- M > 1: Enlarged.
- M < 1: Diminished.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Light: Reflection and Refraction - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the fundamental properties of light? |  |
| 2. How does reflection of light work, and what are the laws governing it? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between concave and convex mirrors? |  |
| 4. What is refraction of light, and how does it occur? |  |
| 5. How are reflection and refraction applied in daily life? |  |















