Cheat Sheet: Our Environment | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Ecosystem - What Are Its Components? |

|
| Biotic Components and Their Roles |

|
| Food Chains and Webs |

|
| How Do Our Activities Affect the Environment? |

|
| Summary Points |

|
Ecosystem - What Are Its Components?
A system of interactions between living (biotic) and non-living (abiotic) components, functioning as a unified whole.
Types:
- Natural Ecosystem: Forests, lakes, oceans (exist independently).
- Artificial Ecosystem: Crop fields, aquariums, gardens (human-made).
Components:
- Abiotic: Non-living elements (air, water, land, light, temperature).
- Biotic: Living organisms (plants, animals, bacteria, fungi).
Biotic Components and Their Roles
1. Producers
Green plants, blue-green algae; produce food via photosynthesis using abiotic components.
2. Consumers
Herbivores: Eat plants (e.g., goat, deer).
Carnivores: Eat flesh (e.g., tiger, crocodile).
Omnivores: Eat plants and animals (e.g., humans).
Parasites: Live on hosts, taking food (e.g., lice, cascuta).
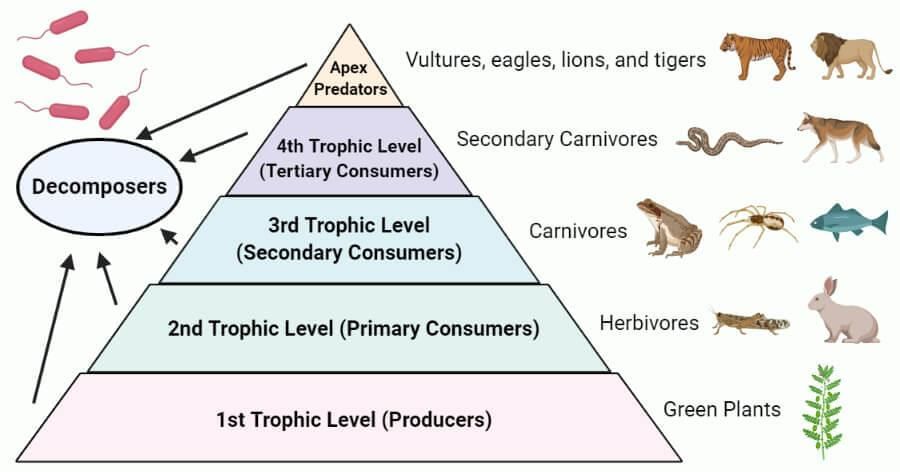
3. Decomposers
Break down dead plants/animals (e.g., bacteria, fungi), replenishing natural resources.
Food Chains and Webs
1. Food Chain
Linear sequence of organisms where one eats another (e.g., Grass → Deer → Lion).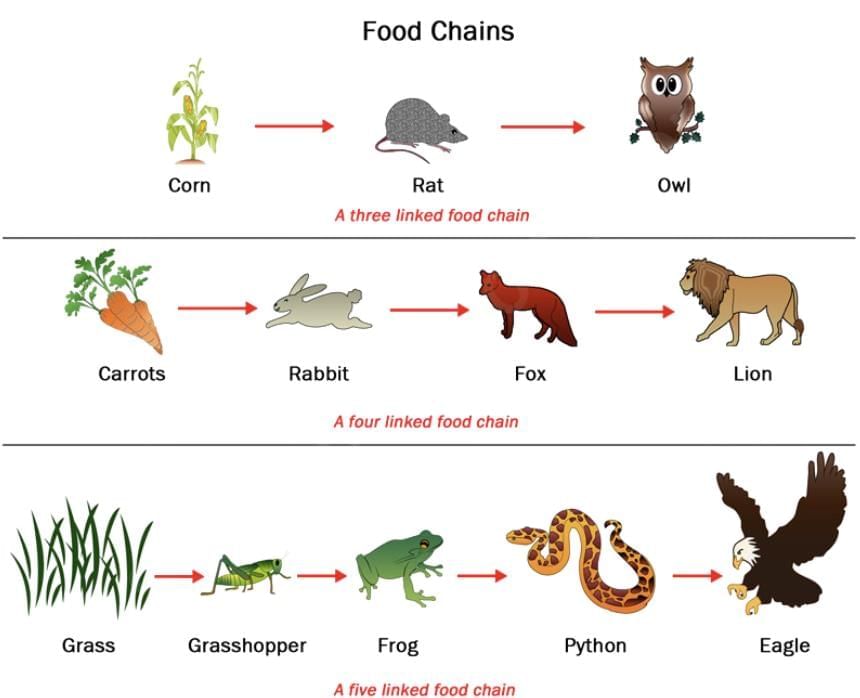
2. Trophic Levels
First: Producers (autotrophs, e.g., green plants) capture solar energy.
Second: Herbivores (primary consumers, e.g., deer).
Third: Small carnivores (secondary consumers, e.g., fox).
Fourth: Large carnivores (tertiary consumers, e.g., lion).
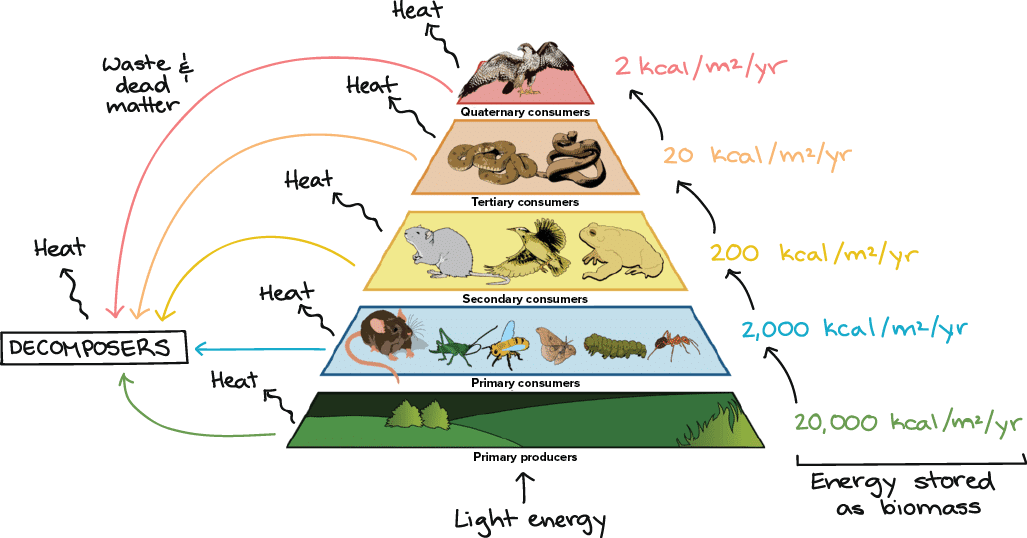
3. Energy Flow
Unidirectional: From autotrophs to heterotrophs/decomposers; energy doesn’t revert to previous levels.
10% Rule: ~10% of energy transfers to the next trophic level; rest lost as heat/metabolic waste.
Green plants capture ~1% of sunlight; herbivores incorporate ~10% of consumed plant energy.
Food chains typically have 3–4 levels due to energy loss.
4. Food Web
Complex network of interconnected food chains, as organisms are eaten by multiple others.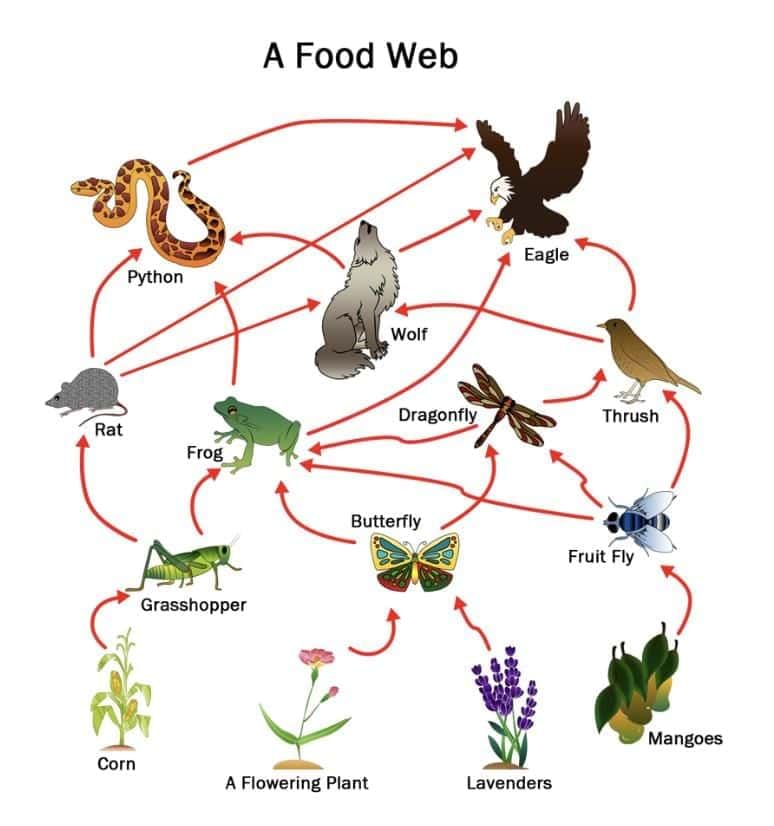
5. Pesticide Impact
Harmful chemicals (e.g., pesticides) accumulate through food chains, reaching humans at higher trophic levels; residues persist in grains, vegetables, fruits, meat.
How Do Our Activities Affect the Environment?
1. Human Impact
Activities like pollution and deforestation disrupt ecosystems.
2. Ozone Layer
Role: Protective layer absorbing harmful UV radiation, preventing health issues (e.g., skin cancer, cataracts) and plant damage.
Composition: Ozone (O₃) formed from molecular oxygen (O₂) in the atmosphere: O₂ →(UV) 2O, O + O₂ → O₃.
Depletion: Caused by synthetic chemicals like chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) used in refrigerants/fire extinguishers; significant decline since the 1980s.
Response: 1987 UNEP agreement froze CFC production at 1986 levels; CFC-free refrigerators now mandatory.
3. Waste Management
Biodegradable Wastes: Decomposed by microorganisms (e.g., fruit peels, paper, cotton, dung).

Non-Biodegradable Wastes: Not decomposed (e.g., plastics, metals, pesticides, radioactive wastes), persist in environment.

Challenges: Lifestyle changes, disposable products, and non-biodegradable packaging increase waste, causing environmental issues.
Summary Points
- Ecosystems: Interconnected biotic (plants, animals, microorganisms) and abiotic (air, water, temperature) components maintaining balance.
- Producers (e.g., plants) use sunlight for photosynthesis; energy flows unidirectionally to consumers and decomposers, with ~10% transferred per trophic level.
- Food chains (3–4 levels) and food webs show energy transfer; pesticides accumulate through chains, impacting humans.
- Human activities (pollution, deforestation) harm ecosystems; CFCs deplete ozone layer, increasing UV-related risks.
- Biodegradable wastes (e.g., peels, paper) decompose; non-biodegradable wastes (e.g., plastics) persist, exacerbating environmental problems.
- Ozone layer
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Our Environment - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main components of an ecosystem? |  |
| 2. How do biotic components interact within an ecosystem? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of food chains and food webs in an ecosystem? |  |
| 4. In what ways do human activities impact the environment? |  |
| 5. How can we summarize the key points regarding our environment? |  |





















