NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Physiology > Mind Map: Cell Physiology and Membrane Potential
Mind Map: Cell Physiology and Membrane Potential | Physiology - NEET PG PDF Download
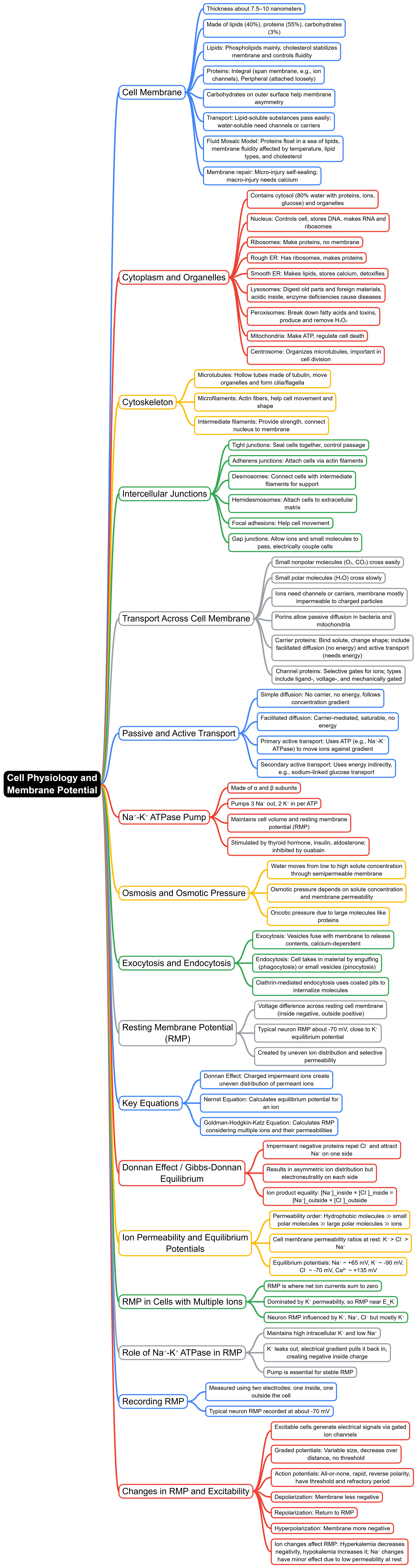
The document Mind Map: Cell Physiology and Membrane Potential | Physiology - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Physiology.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Cell Physiology and Membrane Potential - Physiology - NEET PG
| 1. What is membrane potential and how is it established in cells? |  |
Ans. Membrane potential, also known as membrane voltage, is the electrical potential difference across a cell's plasma membrane. It is established primarily by the distribution of ions, particularly Na⁺, K⁺, Cl⁻, and Ca²⁺, across the membrane. The sodium-potassium pump (Na⁺/K⁺ ATPase) plays a crucial role by actively transporting Na⁺ out of the cell and K⁺ into the cell, creating a negative charge inside relative to the outside. This difference in ion concentration leads to a resting membrane potential typically around -70 mV in neurons.
| 2. What role do ion channels play in generating action potentials? |  |
Ans. Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that allow specific ions to flow across the plasma membrane. During an action potential, voltage-gated Na⁺ channels open in response to depolarization, allowing Na⁺ to rush into the cell, making the inside more positive. This is followed by the opening of voltage-gated K⁺ channels, which allow K⁺ to exit the cell, repolarizing the membrane. The rapid opening and closing of these channels are essential for the propagation of action potentials along neurons.
| 3. How do changes in membrane potential affect cellular signaling? |  |
Ans. Changes in membrane potential, such as depolarization and hyperpolarization, are critical for cellular signaling. Depolarization can lead to the generation of action potentials in excitable cells, such as neurons and muscle cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular events. Hyperpolarization, on the other hand, can inhibit action potentials and reduce cellular excitability. These variations in membrane potential allow for the transmission of signals, communication between cells, and the coordination of physiological processes.
| 4. What is the significance of the Nernst equation in understanding membrane potential? |  |
Ans. The Nernst equation calculates the equilibrium potential for a particular ion based on its concentration gradient across the membrane. It helps to understand how the concentration of ions like K⁺ and Na⁺ influences membrane potential. The equation is given by E_ion = (RT/zF) * ln([ion]outside/[ion]inside), where R is the universal gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, z is the ion's charge, and F is Faraday's constant. This understanding is essential for predicting how changes in ion concentrations can affect the overall membrane potential and cellular excitability.
| 5. What are the differences between graded potentials and action potentials? |  |
Ans. Graded potentials are changes in membrane potential that vary in magnitude and can occur in any part of the neuron. They are typically localized and diminish with distance from the stimulus. In contrast, action potentials are all-or-nothing events that occur when a threshold is reached, leading to a rapid rise and fall in membrane potential that travels along the axon. Action potentials maintain their strength over distance due to the regenerative opening of voltage-gated ion channels, while graded potentials decrease in amplitude and are not capable of propagating over long distances.
Related Searches















