NEET PG Exam > NEET PG Notes > Physiology > Mind Map: Male and Female Reproductive Physiology
Mind Map: Male and Female Reproductive Physiology | Physiology - NEET PG PDF Download
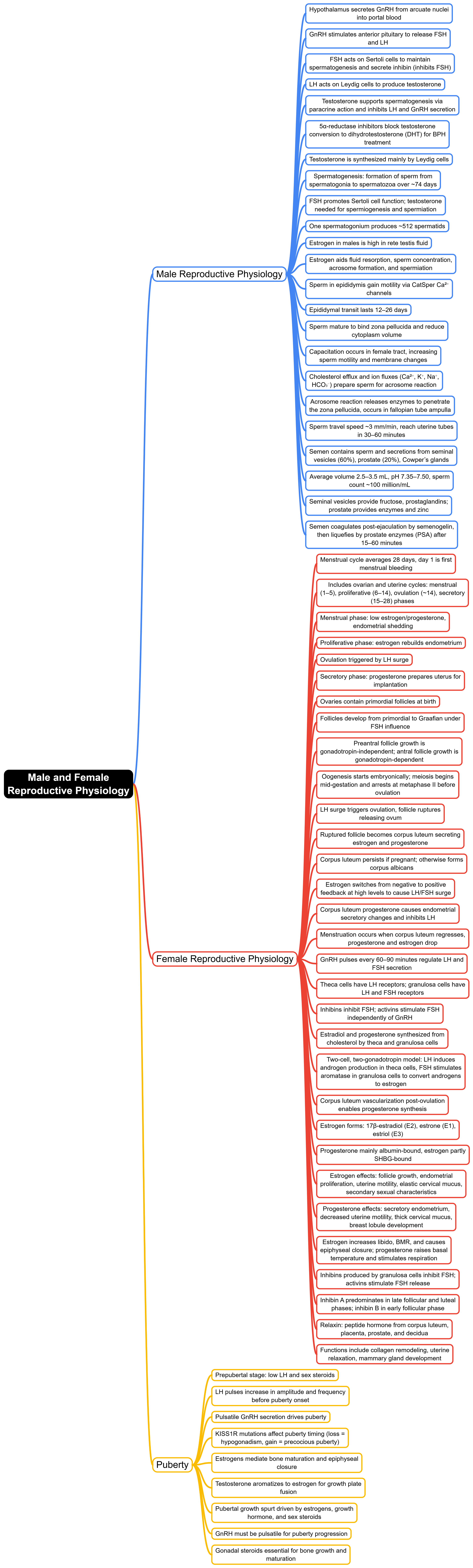
The document Mind Map: Male and Female Reproductive Physiology | Physiology - NEET PG is a part of the NEET PG Course Physiology.
All you need of NEET PG at this link: NEET PG
|
40 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on Mind Map: Male and Female Reproductive Physiology - Physiology - NEET PG
| 1. What are the key differences between male and female reproductive physiology? |  |
Ans. The male and female reproductive systems have distinct structures and functions. In males, the primary organs include the testes, which produce sperm and testosterone, and the penis, which delivers sperm. The male reproductive system also includes accessory glands such as the prostate and seminal vesicles that contribute to seminal fluid. In females, the ovaries produce ova (eggs) and hormones like estrogen and progesterone. The female reproductive system includes the uterus, where fertilization occurs, and the fallopian tubes, which transport the egg. Men typically have continuous sperm production, while females have a cyclical ovulation process.
| 2. How does hormonal regulation differ in male and female reproductive physiology? |  |
Ans. Hormonal regulation in males primarily revolves around testosterone, which is produced by the Leydig cells in the testes and regulates sperm production and secondary sexual characteristics. In contrast, females have a more complex hormonal cycle involving estrogen and progesterone, which are produced by the ovaries. This cycle regulates ovulation, the menstrual cycle, and prepares the uterus for potential implantation of a fertilized egg. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland play crucial roles in both systems by releasing gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) and gonadotropins (LH and FSH) that control these processes.
| 3. What is the role of the menstrual cycle in female reproductive physiology? |  |
Ans. The menstrual cycle is a monthly series of changes that prepare the female body for potential pregnancy. It typically lasts about 28 days and is divided into phases: the follicular phase, ovulation, the luteal phase, and menstruation. During the follicular phase, FSH stimulates the growth of ovarian follicles, leading to estrogen production. Ovulation occurs when a mature follicle releases an egg. The luteal phase involves the formation of the corpus luteum, which secretes progesterone to maintain the uterine lining. If fertilization does not occur, hormone levels drop, leading to menstruation and the start of a new cycle.
| 4. What are common disorders related to male and female reproductive physiology? |  |
Ans. Common disorders in male reproductive physiology include erectile dysfunction, infertility due to low sperm count, and conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) and prostate cancer. In females, common disorders include polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and menstrual irregularities. These conditions can significantly impact reproductive health and may require medical intervention, lifestyle changes, or surgical options.
| 5. How does fertilization occur in human reproduction? |  |
Ans. Fertilization in human reproduction occurs when a sperm cell successfully penetrates an ovum (egg). This typically takes place in the fallopian tube after ovulation. Sperm undergo capacitation, a process that enhances their ability to fertilize the egg. Once a sperm enters the egg, it triggers a series of reactions that prevent other sperm from entering and initiates the development of a zygote. The zygote then undergoes cell division as it travels to the uterus, where it may implant into the uterine lining, leading to pregnancy.
Related Searches















