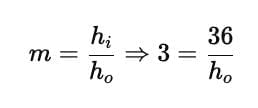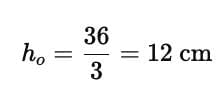Unit Test (Solutions): Light - Reflection and Refraction | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Time: 1 Hour
Maximum Marks: 30
Instructions:
Attempt all questions.
Question numbers 1 to 5 carry 1 mark each .
Question numbers 6 to 8 carry 2 marks each.
Question numbers 9 to 11 carry 3 marks each.
Question numbers 12 and 13 carry 5 marks each.
Q1: Which statement is true for the reflection of light? (1 mark)
(a) The angle of incidence and reflection are equal.
(b) The reflected light is less bright than the incident light.
(c) The sum of the angle of incidence and reflection is always greater than 900.
(d) The beams of the incident light, after reflection, diverge at unequal angles.
Ans: (a)
Q2: The focal length of a plane mirror is
(a) 0
(b) infinite
(c) 25 cm
(d) -25 cm
Ans: (b)
Q3: The image shows the path of incident rays to a concave mirror.
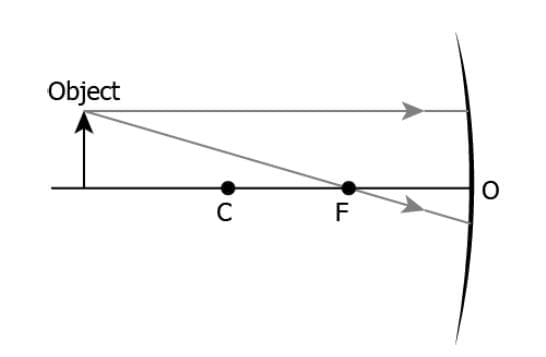
Where would the reflected rays meet for the image formation to take place?
(a) Behind the mirror
(b) Between F and O
(c) Between C and F
(d) Beyond C
Ans: (c)
Q4: A beam of light incident on a plane mirror forms a real image on reflection. The incident beam is:
(a) parallel
(b) convergent
(c) divergent
(d) not certain
Ans: (b)
Q5: Image formed by a convex spherical mirror is:
(a) virtual
(b) real
(c) enlarged
(d) inverted
Ans: (a)
Q6: An image of an object produced on a screen which is about 36 cm using a convex lens. The image produced is about 3 times the size of the object. What is the size of the object? (2 marks)
Ans:
Q7: Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the path of the reflected ray corresponding to an incident ray of light parallel to the principal axis of a convex mirror. Mark the angle of incidence and angle of reflection on it. (2 marks)
Ans: 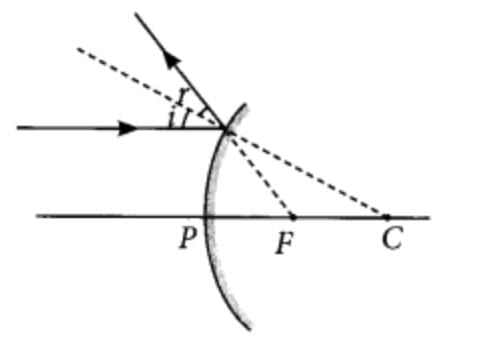
Q8: An object is placed at a distance of 12 cm in front of a concave mirror of radius of curvature 30 cm. List four characteristics of the image formed by the mirror. (2 marks)
Ans: Radius of curvature (R) = 30 cm, object distance is 12 cm in front of the mirror. Thus we can say that object is placed between focus and pole. Four characteristics of the image formed by die given concave mirror when object is placed between pole and focus are:
(i) Virtual
(ii) Erect
(iii) Enlarged
(iv) Image is formed behind the mirror
Q9: An object 4 cm in height, is placed at 15 cm in front of a concave mirror of focal length 10 cm. At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed to obtain a sharp image of the object. Calculate the height of the image. (3 marks)
Ans: Given : object distance, u = -15 cm,
object height, h = 4 cm, focal length f = -10 cm;
Image distance, v = ?
Using mirror formula,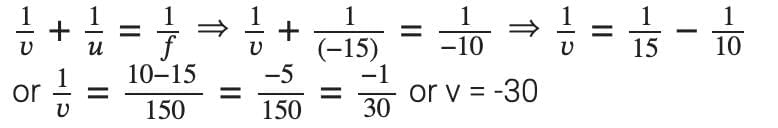
In order to obtain a sharp image of the object on the screen, screen should be placed at a distance of 30 cm in front of the mirror.
Also, magnification,
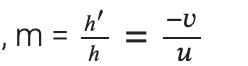
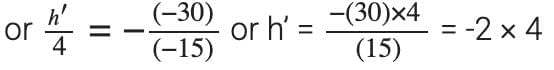
or h’ = -8 cm
Thus, the height of the image is 8 cm
Q10: A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification -1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror.
(i) Write type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror? (3 marks)
Ans: (i) This is a concave mirror.
(ii) The image is real and inverted and of same size.
(iii) As m = – 1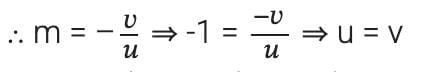
Hence, object is located at centre of curvature i.e., at distance of 40 cm from the pole of the mirror,
Q11: A student wants to project the image of a candle flame on a screen 48 cm in front of a mirror by keeping the flame at a distance of 12 cm from its pole.
(a) Suggest the type of mirror he should use.
(b) Find the linear magnification of the image produced.
(c) How far is the image from its object?
(d) Draw ray diagram to show the image formation in this case. (3 marks)
Ans: (a) Concave mirror
(b) Linear magnification,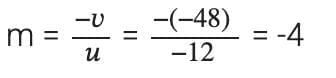
(c) The distance between the image and the object
= 48 – 12 = 36 cm
(d)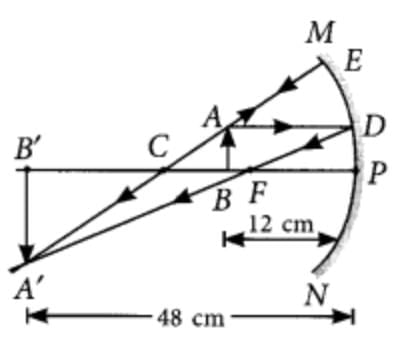
Q12: Read and answer the following questions: (5 marks)
A lens is a piece of any transparent material bounded by two curved surfaces. There are two types of lenses: convex lens and concave lens. Convex lens is made up of a transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces such that it is thicker at the middle and thinner at the edges. Concave lens is also made up of a transparent medium such that it is thicker at the edges and thinner at the middle. The midpoint of the lens is called the optical center.
Convex lens is made up of a transparent medium bounded by two spherical surfaces such that it is thicker at the middle and thinner at the edges. Concave lens is also made up of a transparent medium such that it is thicker at the edges and thinner at the middle. The midpoint of the lens is called the optical center.
A point on the principal axis, where the incident parallel rays meet or appear to come out after refraction, is called the focus.
A convex lens converges a parallel beam of light to the other side, whereas a concave lens spreads out light.
(i) Which of the following lenses would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary. (1 mark)
(a) A convex lens of focal length 50 cm
(b) A concave lens of focal length 50 cm
(c) A convex lens of focal length 5 cm
(d) A concave lens of focal length 5 cm
(ii) Which type of lenses are shown in given figure (i) and (ii)? (1 mark)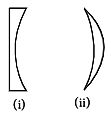 (a) Plano concave, concavo convex
(a) Plano concave, concavo convex
(b) Plano convex, convexo concave
(c) Double concave, concave convex
(d) Convexo concave, double convex
(iii) A small bulb is placed at the focal point of a converging lens. When the bulb is switched on, the lens produces (1 mark)
(a) a convergent beam of light
(b) a divergent beam of light
(c) a parallel beam of light
(d) a patch of coloured light
(iv) The part of the lens through which the refraction takes place is called (1 mark)
(a) aperture
(b) centre of curvature
(c) principal axis
(d) focus
(v) A water drop acts as a (1 mark)
(a) convex lens
(b) concave lens
(c) double concave lens
(d) none of these
Ans:
i. (c) Convex lens is used as a magnifying glass. For better performance, its focal length should be small.
ii. (a)
iii. (c)
iv. (a): An aperture is the area of the lens available for refraction.
v. (a): Water droplets behave like a convex lens only as refraction takes place on the outer surface.
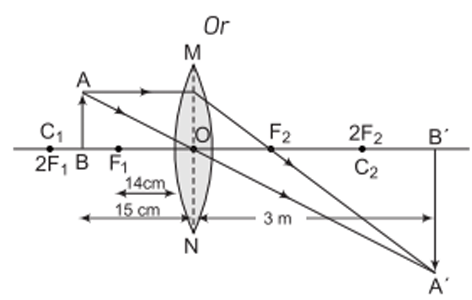
Q13: Read the paragraph and answer the following questions: (5 marks)
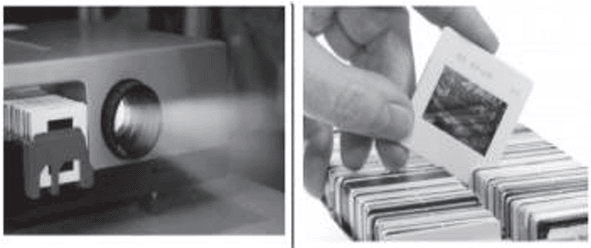 The above images are that of a specialised slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection, since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray. To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced a 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
The above images are that of a specialised slide projector. Slides are small transparencies mounted in sturdy frames ideally suited to magnification and projection, since they have a very high resolution and a high image quality. There is a tray where the slides are to be put into a particular orientation so that the viewers can see the enlarged erect images of the transparent slides. This means that the slides will have to be inserted upside down in the projector tray. To show her students the images of insects that she investigated in the lab, Mrs. Iyer brought a slide projector. Her slide projector produced a 500 times enlarged and inverted image of a slide on a screen 10 m away.
i. Based on the text and data given in the above paragraph, What kind of lens must the slide projector have?
ii. If v is the symbol used for image distance and u for object distance, then with one reason, state what will be the sign for in the given case?
iii. A slide projector has a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. The slide is placed upside down 21 cm from the lens. How far away should the screen be placed from the slide projector's lens so that the slide is in focus? Or When a slide is placed 15 cm behind the lens in the projector, an image is formed 3 m in front of the lens. If the focal length of the lens is 14 cm, draw a ray diagram to show image formation.
Ans:
i. Convex lens
ii. Negative as the image is real and inverted.
iii. 1/f = 1/v-1/-21
= 1/20 = 1/v-1/u
= 1/v = 1/20-1/21
=(21-20)/420 = 1/420
v = 420 cm
|
80 videos|662 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Unit Test (Solutions): Light - Reflection and Refraction - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the law of reflection and how does it apply to mirrors? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of mirrors and their uses? |  |
| 3. How does refraction occur and what factors affect it? |  |
| 4. What is total internal reflection and where is it observed? |  |
| 5. Can you explain the concept of the critical angle and how it is determined? |  |