Mnemonics: Acids, Bases and Salts | Science Class 10 PDF Download
1. Nature of Acids
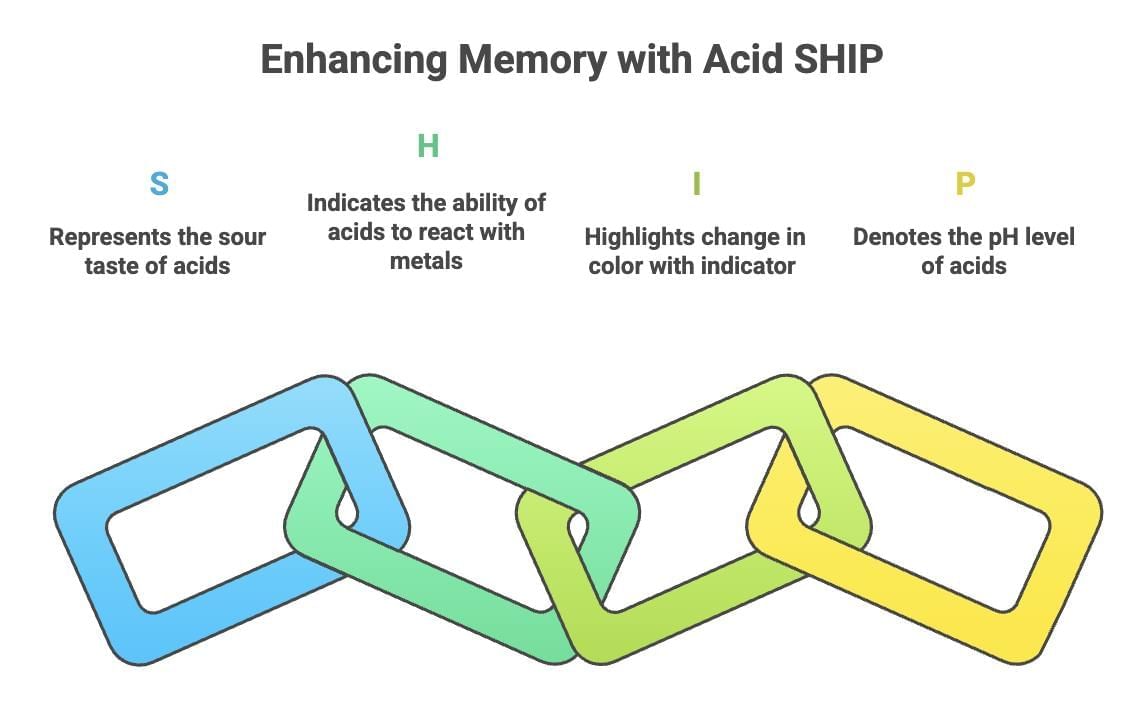
Mnemonic: Acid SHIP
- S – Sour taste (acids have a characteristic sour taste, e.g., citric acid in lemons).
- H – H⁺ donor (acids release hydrogen ions in solution, per the Arrhenius definition).
- I – Indicator change (acids turn blue litmus red and affect other pH indicators).
- P – pH (pH below 7).
2. Nature of Bases
Mnemonic: Base BASH
B – Bitter taste (bases have a characteristic bitter taste, e.g., in baking soda solutions).
A – Alkaline pH (bases increase pH in aqueous solutions, typically above 7).
S – Slippery feel (bases feel slippery or soapy, e.g., soap solutions).
H – Hydroxide or H⁺ acceptor (bases often release OH⁻ ions in water or accept H⁺, per Arrhenius or Brønsted-Lowry definitions).
3. Types of Acids and Examples
Mnemonic: Strong HNS" vs "Weak COLA
Strong HNS (Strong acids- all inorganic acids)
- Strong – Strong Acid
- H – Hydrochloric acid (HCl)
- N – Nitric acid (HNO₃)
- S – Sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄)
Weak COLA (Weak acids- all organic acids)
- Weak – Weak Acid
- C – Citric acid
- O – Oxalic acid
- L – Lactic acid
- A – Acetic acid
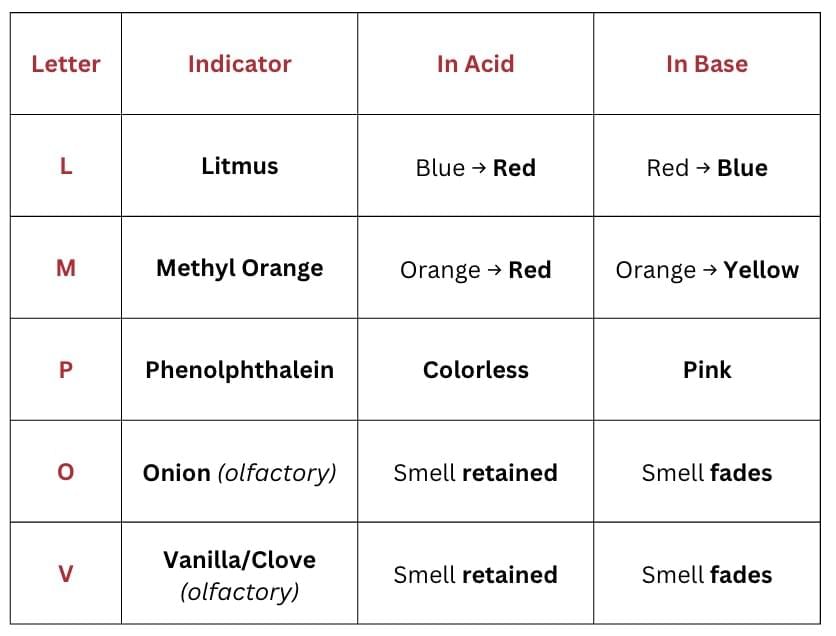
4. Indicators Mnemonic
Mnemonic: Let Me Paint On Van
L – Litmus (red/blue)
M – Methyl orange
P – Phenolphthalein
O – Onion (olfactory indicator)
V – Vanilla/clove (olfactory indicators)
5. Neutralization Reaction
Mnemonic: Neutral Nation: Acid Meets Base = Salt + Splash
Sour acids and soapy bases combine to give salt and water. It’s a classic neutralization reaction, used in antacids and stings.
6. Types of Salts formed by Neutralization Reaction
Mnemonic: Same Strength Neutralizes othewise Strong Wins Always
Same Strength Neutralizes
Strong Acid + Strong Base = Neutral SaltStrong Wins Always
Strong Acid + Weak = Acidic Salt
Strong Base + Weak Acid = Basic Salt
7. Acid-Metal Reactions
Mnemonic: Acids Melt Metals, Spark Hydrogen
Acids react with metals like Zn to form salt and release hydrogen gas, which sparks with a pop when tested with a flame.
Acids Melt: Acids react with metals.
Metals: Like Zn, produce salt (e.g., ZnCl₂).
Spark Hydrogen: Release H₂ gas (pops with flame).
8. Acid-Carbonate Reactions
Mnemonic: Carbonates Acidify, Spit CO₂
Carbonates react with acids to form salt, water, and carbon dioxide, which turns lime water milky, confirming the presence of CO₂.
Carbonates: Metal carbonates/hydrogencarbonates.
Acidify: React with acids to form salt.
Spit CO₂: Produce CO₂ (milky lime water test) and water.
9. Common Salt Derivatives – "Sweet Boys Bake Warm Cakes"
Mnemonic: Sweet Boys Bake Warm Sweets (from NaCl)
Easy recall of 3 key derivatives of common salt (NaCl).
S – Sodium hydroxide (caustic soda)
B – Bleaching powder
B – Baking soda
W– Washing soda
10. Testing for Gases – “Pop for H₂, Milk for CO₂”
Mnemonic: Pop for H₂, Milk for CO₂
Pop sound – Hydrogen test with burning candle
Milkiness – CO₂ test using limewater turning milky

11. Chlor-Alkali Process
Mnemonic: Salty Water Gives Cool Hot Soda
S – Salty = Salt water (Sodium chloride solution a.k.a brine)
W – Water = Electrolysis of brine + water
G – Gives = Produces
C – Cool = Chlorine gas at Anode
H – Hot = Hydrogen gas at Cathode
S – Soda = Sodium Hydroxide (NaOH) remains in solution
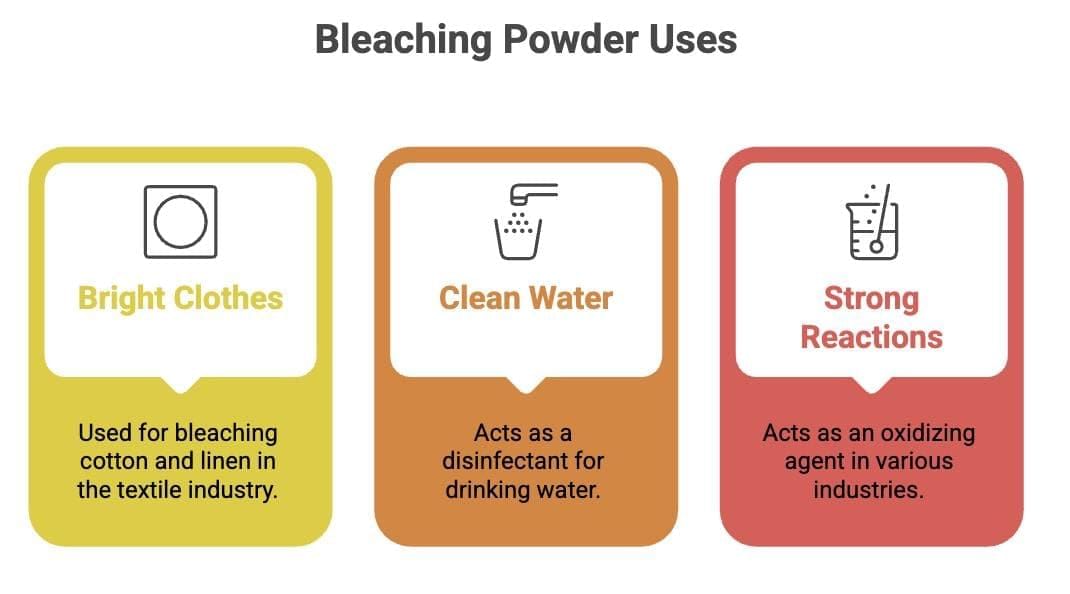
12. Uses of Bleaching Powder
Mnemonic: Bright Clothes, Clean Water, Strong Reactions
B – Bright Clothes → Used for bleaching cotton & linen (textile industry)
C – Clean Water → Disinfectant for drinking water
S – Strong Reactions → Acts as an oxidizing agent in industries
13. Uses of Baking Soda
Mnemonic: Rise, Relief, Rescue or RRR
Summarizes the 3 main uses of baking soda.
R - Rise → Used in baking to produce CO₂ that helps cakes/bread rise
R - Relief → Acts as an antacid to give relief from acidity
R - Rescue → Used in fire extinguishers to help rescue by releasing CO₂
14. Uses of Washing Soda
Mnemonic: Glass Soaps Cleans Hardness
G → Used in the glass industry
S → Used in soap and paper industries
C → Acts as a cleaning agent for household use
H → Removes permanent hardness of water
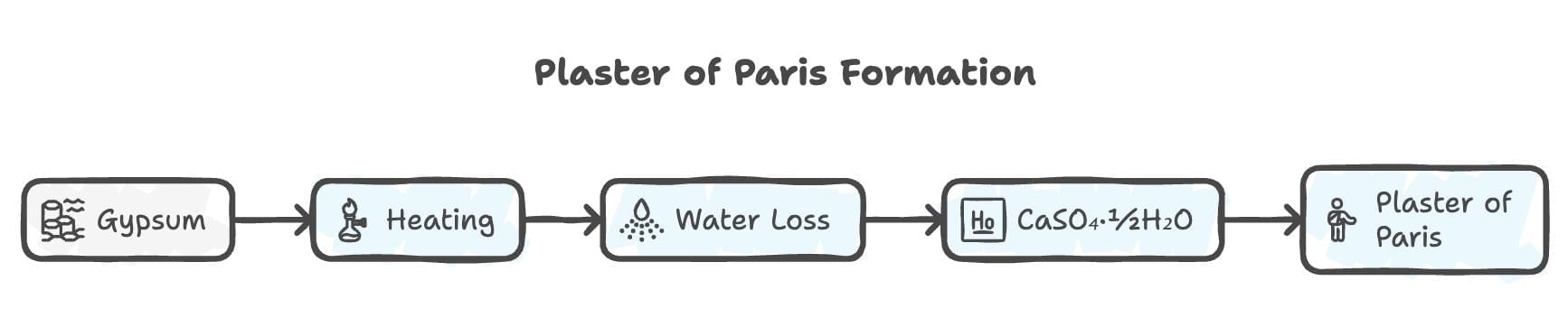
15. Plaster of Paris
Mnemonic: Gypsum Halves Water, Forms Plaster
Gypsum: CaSO₄· 2H₂O.
Halves Water: Heated to 100°C, looses water to forms CaSO₄·½H₂O.
Forms Plaster: Used in casts, sculpting.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Acids, Bases and Salts - Science Class 10
| 1. What are the main types of acids, and how do they differ from each other? |  |
| 2. What is the significance of indicators in acid-base chemistry, and how can they be remembered? |  |
| 3. What is a neutralization reaction, and what are its products? |  |
| 4. What types of salts can be formed from neutralization reactions? |  |
| 5. How do acids react with metals and carbonates, and what are the products of these reactions? |  |

















