Summary of Union Interim Budget 2024 | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Overview of Union Budget 2025-26
 Balanced Growth
Balanced Growth
Union Budget 2025-26 was presented by the Union Finance Minister in Parliament, highlighting four key drivers of development. agriculture, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), investment, and exports.
Balanced Growth
- The theme of the Union Budget 2025-26 is 'Sabka Vikas', aiming to promote balanced growth across all regions.
- The Finance Minister also outlined the broad principles of Viksit Bharat, which envisions a developed India.
Focus on Development
- The Budget emphasizes development measures targeting the poor (Garib), youth, farmers (Annadata), and women (Nari).
Four Engines of Development in the Union Budget 2025-26
 Four Engines of Development
Four Engines of Development
The Union Budget 2025-26 focuses on four key areas to drive development: Agriculture, MSMEs, Investment, and Social Infrastructure.
1. Agriculture
- Prime Minister Dhan-Dhan Krishi Yojana: Targeting 100 districts with low agricultural productivity, this initiative aims to assist 1.7 crore farmers by enhancing irrigation and post-harvest storage facilities.
- Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme:. new programme in collaboration with states to address underemployment in agriculture through training, investment, and technology.
- Atma Nirbharta in Pulses:. six-year project focused on Tur, Urad, and Masoor pulses, ensuring climate-resilient seeds and fair pricing for farmers. Central agencies like NAFED and NCCF will procure these pulses over the next four years.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Limit: The KCC limit will be increased from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh to enhance credit flow for 7.7 crore farmers.
- National Mission on High Yielding Seeds: This mission aims to boost research and ensure the availability of over 100 high-yield, pest-resistant seed varieties.
- Mission for Cotton Productivity:. five-year plan to promote sustainable cotton farming practices and improve the production and quality of extra-long staple cotton.
- Makhana Board in Bihar:. new board will be established in Bihar to enhance the production, processing, and value addition of Makhana (fox nuts).
- Comprehensive Programme for Fruits and Vegetables: This programme aims to improve supply chains and secure better market prices for farmers producing fruits and vegetables.
- Fisheries Development:. new approach for sustainable fishing within the Indian Exclusive Economic Zone and High Seas, with a focus on Andaman & Nicobar and Lakshadweep.
- Urea Plant in Assam:. new urea plant with a capacity of 12.7 lakh metric tons will be established in Assam by Brahmaputra Valley Fertilizer Corporation Ltd (BVFCL) to boost agricultural productivity.
2. Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs)
- Revised MSME Classification: The investment and turnover limits for MSMEs have been increased to 2.5 times, expanding credit access for small businesses.
- Micro Enterprise Credit Cards:. new credit facility of ₹5 lakh for 10 lakh micro enterprises to promote financial inclusion.
- Credit Cover for MSMEs: The guarantee cover for MSME loans has been raised from ₹5 crore to ₹10 crore, allowing for greater loan access.
- Focus Product Scheme for Leather and Footwear: This scheme is expected to create 22 lakh jobs, generate ₹4 lakh crore in turnover, and exports exceeding ₹1.1 lakh crore.
- Toy Sector Development: Initiatives to support the development of toy manufacturing clusters and innovation-driven production to enhance the 'Made in India' brand globally.
- National Institute of Food Technology:. new institute will be established in Bihar to promote food processing, skills development, and entrepreneurship in the food sector.
- Fund of Funds for Startups:. broader scope for the Fund of Funds for Startups with an additional ₹10,000 crore contribution to support startup growth.
3. Investment
- Urban Challenge Fund:. fund of ₹1 lakh crore to support 'Cities as Growth Hubs,' 'Creative Redevelopment of Cities,' and 'Water and Sanitation,' with ₹10,000 crore allocated for 2025-26.
- Jal Jeevan Mission: The total budget for this mission has been increased to ₹67,000 crore, extended until 2028, to ensure universal piped water coverage, with additional funding for rural water projects.
- Maritime Development Fund:. ₹25,000 crore fund (49% government contribution) to support long-term financing for shipbuilding, ports, and logistics infrastructure.
- Expansion of IITs: Additional facilities to accommodate 6,500 more students in Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) to enhance technical education capacity.
- PM Research Fellowship: 10,000 fellowships for advanced research at IITs and the Indian Institute of Science (IISc).
- Day Care Cancer Centres: Establishment of cancer treatment centres in all district hospitals over the next three years, with 200 centres planned for 2025-26 to ensure affordable access to cancer treatment.
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme: Digital Indian language books to improve access in schools and higher education institutions.
- Nuclear Energy Mission for Viksit Bharat:. budget of ₹20,000 crore for Small Modular Reactors (SMRs) with the goal of having five indigenously developed SMRs operational by 2033. Amendments to the Atomic Energy Act and the Civil Liability for Nuclear Damage Act will facilitate private sector partnerships.
- UDAN - Regional Connectivity Scheme: The revised scheme aims to enhance regional connectivity to 120 new destinations, targeting the transport of 4 crore passengers over the next 10 years, supporting helipads and smaller airports in hilly, aspirational, and North Eastern regions.
- Greenfield Airport in Bihar: Development of new airports in Bihar, expansion of Patna airport, and a brownfield airport project at Bihta (Patna).
- Western Koshi Canal ERM Project: Financial support for irrigation infrastructure development in Mithilanchal, Bihar.
- Tourism for Employment-led Growth: Development of the top 50 tourist destinations across the country in collaboration with states through a competitive challenge mode.
Export Promotion Mission
 Economic Reforms
Economic Reforms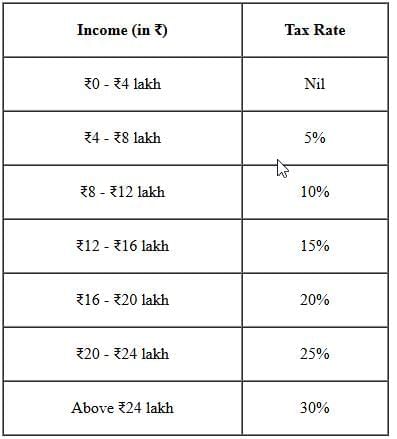
The Export Promotion Mission will be established with clear objectives targeting specific sectors and ministries. It will be spearheaded by the Ministries of Commerce, Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSME), and Finance.
BharatTradeNet (BTN)
BharatTradeNet (BTN) is an integrated digital platform designed to streamline international trade documentation and financing options.
National Framework for Global Capability Centres (GCC)
The National Framework for GCC aims to provide policy incentives to promote the establishment of Global Capability Centres in emerging Tier-2 cities.
Warehousing Facility for Air Cargo
The government plans to develop warehousing facilities for high-value perishable exports to enhance storage capabilities for air cargo.
Major Highlights of the Union Budget 2025-26
Taxation and Financial Reforms
- Direct Taxes: Individuals with annual incomes up to ₹12 lakh will not pay income tax. This threshold is increased to ₹12.75 lakh for salaried taxpayers eligible for deductions.
- Tax Deducted at Source (TDS): The TDS limit on rent has been raised from ₹2.4 lakh to ₹6 lakh, reducing the tax compliance burden for taxpayers.
- Tax Returns: The time limit for filing updated tax returns has been extended from 2 years to 4 years, facilitating voluntary tax compliance.
- Basic Customs Duty (BCD) Exemptions: BCD has been fully exempted for 36 life-saving drugs used in the treatment of cancer, chronic, and rare diseases.
- Lithium-ion Battery Manufacturing: Exemptions on capital goods for electric vehicles (EVs) and mobile devices have been introduced to promote domestic production.
- Textile and Electronics Sector: Exemptions on components for the textile and electronics sectors have been implemented to support local manufacturing and reduce reliance on imports.
Social Welfare and Inclusion
- PM SVANidhi Scheme: Street vendors will receive UPI-linked credit cards with a ₹30,000 limit to enhance financial inclusion.
- Identity Cards for Gig Workers: Gig workers will be registered on the e-Shram portal to ensure social security and health benefits through the PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- Atal Tinkering Labs: 50,000 Atal Tinkering Labs will be established in government schools over the next five years to foster innovation among students.
- Expansion of Medical Education: The government plans to increase medical seats by 10,000, with a total increase of 75,000 seats over five years.
Financial Sector Reforms
- Grameen Credit Score:. new system to assist Self-Help Group (SHG) members and rural borrowers in accessing formal credit facilities more easily.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0: This bill aims to decriminalise over 100 legal provisions, simplifying business operations and reducing regulatory compliance burdens.
- SWAMIH Fund 2.0:. ₹15,000 crore fund to complete an additional 1 lakh dwelling units, supported by the government, banks, and private investors.
- FDI in Insurance Sector: The Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) cap in the insurance sector will increase from 74% to 100% for companies that invest all premiums in India.
- Investment Friendliness Index of States:. new ranking system to encourage competitive cooperative federalism among states.
- Credit Enhancement Facility: The National Bank for Financing Infrastructure and Development (NaBFID) will create a ‘Partial Credit Enhancement Facility’ to support corporate bonds for infrastructure projects.
- Pension Sector:. forum will be established for regulatory coordination and the development of new pension products.
- High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms:. committee will be formed to review non-financial sector regulations, certifications, licenses, and permissions.
Major Sources of Revenue and Expenditure from the Budget
- Major Central Government Expenditure (Budget Estimates): Total transfers to States and Union Territories are expected to rise from ₹20.65 lakh crore in 2023-24 to ₹25.60 lakh crore in 2025-26 (BE).
- Receipts and Expenditure: Revenue receipts are projected to increase from ₹27.3 lakh crore in 2023-24 to ₹31.3 lakh crore in 2024-25 (BE). Effective capital expenditure is estimated to fall from ₹17.1 lakh crore to ₹16.3 lakh crore (RE). Revenue expenditure is expected to rise from ₹34.9 lakh crore to ₹37.0 lakh crore (RE). Capital expenditure is projected to increase from ₹12.5 lakh crore to ₹15.0 lakh crore (BE) but revised to ₹13.2 lakh crore.
- Deficit Trends (as a percentage of GDP): The fiscal deficit is expected to remain at 3.3% in 2024-25 (RE). The revenue deficit is projected to rise from 0.3% in 2023-24 to 0.8% in 2024-25 (RE). The effective revenue deficit is expected to remain at 0.3% in 2023-24 and rise to 0.8% in 2024-25 (RE).
- Total Transfers to States & UTs: Total transfers to States and Union Territories are expected to reach ₹25.60 lakh crore in 2025-26 (BE).
- Net Receipt of the Central Government: Net tax revenue for the Centre is projected at ₹28.4 lakh crore in 2024-25 (RE), with non-tax revenue at ₹5.8 lakh crore. Non-debt capital receipts are estimated at ₹0.8 lakh crore in 2024-25 (RE).
Conclusion
The Union Budget for 2025-26, themed "Sabka Vikas," aims to foster inclusive growth, reduce poverty, enhance quality education, and empower various segments such as youth, women, farmers, and the middle class. The focus is on driving sustainable development, attracting private sector investment, and ensuring social equity.
|
108 videos|425 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on Summary of Union Interim Budget 2024 - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the key components of the Export Promotion Mission outlined in the Union Budget? |  |
| 2. How does BharatTradeNet (BTN) facilitate trade for Indian exporters? |  |
| 3. What is the National Framework for Global Capability Centres (GCC) and its significance? |  |
| 4. What are the benefits of the new Warehousing Facility for Air Cargo introduced in the budget? |  |
| 5. What are the major highlights of the Union Budget for the fiscal period discussed? |  |





















