Grade 3 Exam > Grade 3 Notes > Science for Grade 3 > Chapter Notes: Motion
Motion Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 3 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| What is Motion? |

|
| Forces and Motion |

|
| Observing and Predicting Motion |

|
Introduction
Motion is all about how things move around us! When you run, jump, or play with a toy car, you are seeing motion. In this chapter, we will learn what motion is, the different ways things can move, and what makes them move, stop, or change direction. We will also explore how we can watch and guess what will happen when things move. Let’s dive into the fun world of motion!
What is Motion?

Motion means when something changes its place over time.
- Examples of motion:
- A ball rolling on the ground.
- A car driving on the road.
- Types of motion:
- Straight motion: When something moves in a straight line, like a toy car going forward.
- Zigzag motion: When something moves in a curvy or twisty path, like a toy moving around blocks.
- Back and forth motion: When something moves forward and then backward, like a swing at the park.
- Round and round motion: When something spins or turns, like a spinning top or a wheel on a bike.
- Words to describe motion:
- Fast: Moving quickly, like a running dog.
- Slow: Moving not so fast, like a turtle walking.
- Forward: Moving ahead, like a car going straight.
- Backward: Moving back, like pulling a wagon toward you.
- Up: Moving higher, like a balloon going into the sky.
- Down: Moving lower, like a ball falling to the ground.
- Spinning: Turning around and around, like a top.
Forces and Motion
A force is a push or pull that makes things move, stop, or change direction.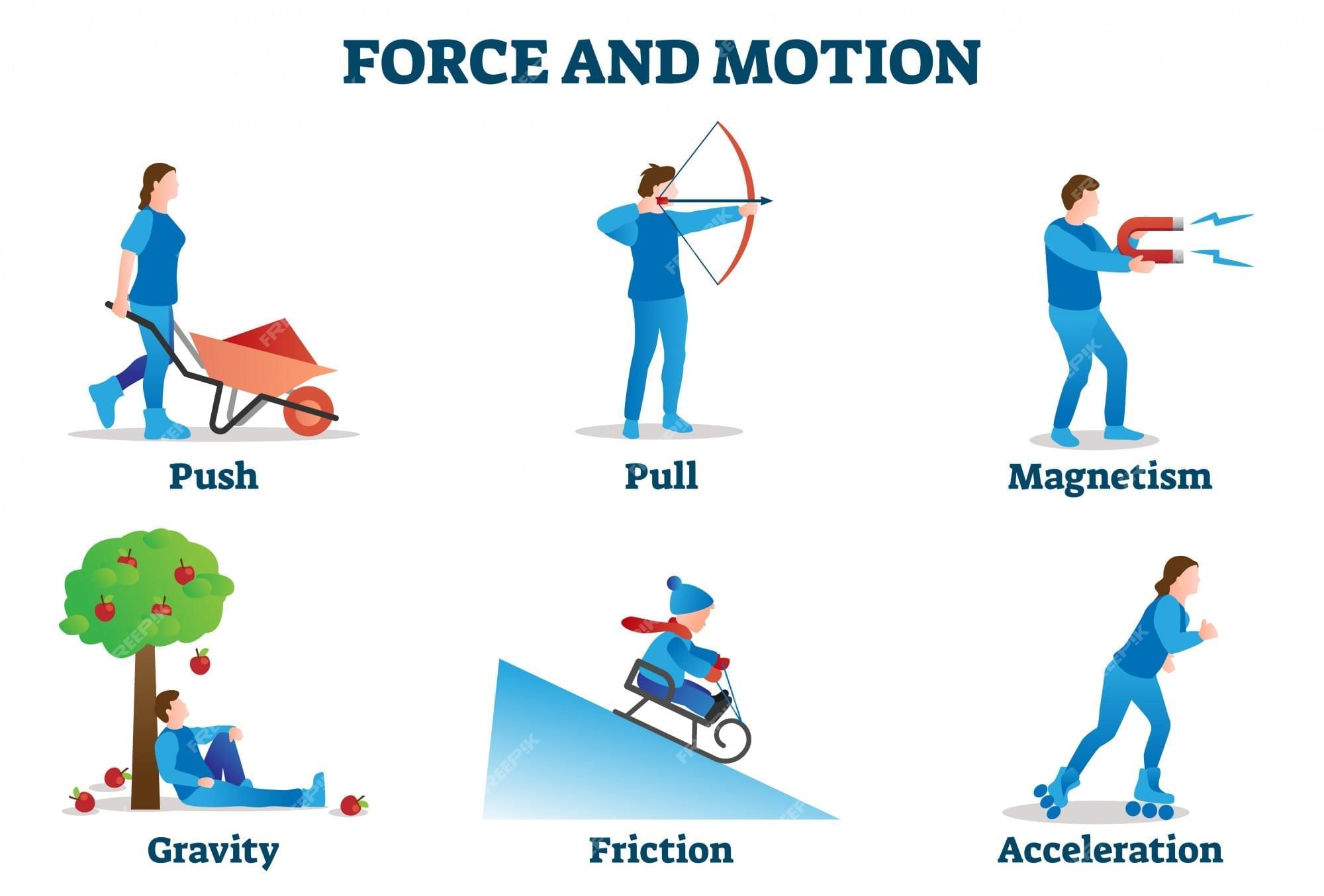
- Examples of forces:
- Pushing a toy car to make it roll forward.
- Pulling a wagon to bring it closer to you.
- Kicking a ball to make it move (a push).
- Tugging a rope in a game of tug-of-war (a pull).
- Gravity pulling a ball down a slide to make it move.
- How forces affect motion:
- A stronger push or pull makes things move faster or go farther.
- A weaker push or pull makes things move slower or go a shorter distance.
Observing and Predicting Motion
- Patterns of motion:
- Some motions happen the same way every time.
- Example: A ball rolled down a ramp goes in a straight line unless something stops it or changes its path.
- Cause and effect in motion:
- Forces make things move differently.
- Example: Pushing a toy car harder makes it go faster.
- Example: Pushing a toy car in a new direction makes it turn.
The document Motion Chapter Notes | Science for Grade 3 is a part of the Grade 3 Course Science for Grade 3.
All you need of Grade 3 at this link: Grade 3
|
38 videos|91 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Motion Chapter Notes - Science for Grade 3
| 1. What is motion and why is it important to understand? |  |
Ans. Motion is the change in position of an object over time. Understanding motion is important because it helps us explain how objects move, how forces affect their movement, and how we can predict future positions of objects. This knowledge is fundamental in various fields, including physics, engineering, and everyday activities.
| 2. What are the different types of motion? |  |
Ans. There are several types of motion, including linear motion (straight-line movement), rotational motion (movement around an axis), and periodic motion (repetitive movement, such as a pendulum). Each type of motion has unique characteristics and can be influenced by different forces.
| 3. How do forces affect motion? |  |
Ans. Forces are pushes or pulls that can cause an object to start moving, stop moving, or change direction. According to Newton's laws of motion, the greater the force applied to an object, the greater the change in its motion. For example, pushing a toy car harder will make it go faster than a gentle push.
| 4. What tools can be used to observe and measure motion? |  |
Ans. Tools such as rulers, stopwatches, and motion sensors can be used to observe and measure motion. A ruler helps measure distance, while a stopwatch measures the time taken for an object to move from one point to another. These measurements can help us calculate speed and understand how fast something is moving.
| 5. How can we predict the motion of objects? |  |
Ans. We can predict the motion of objects by observing their current motion and knowing the forces acting on them. Using formulas like speed = distance/time, we can calculate future positions based on their current speed and direction. Understanding patterns in motion also helps us make accurate predictions.
Related Searches















