UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Indian Economy for UPSC CSE > Cheat Sheet: Price and Inflation
Cheat Sheet: Price and Inflation | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE PDF Download
Basic Concepts
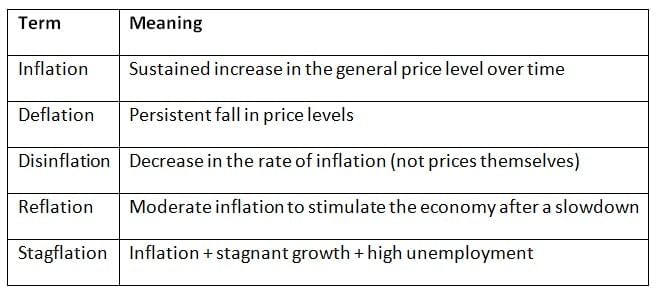
Types of Inflation
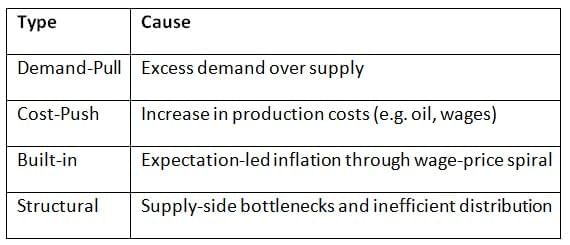
Measurement of Inflation in India
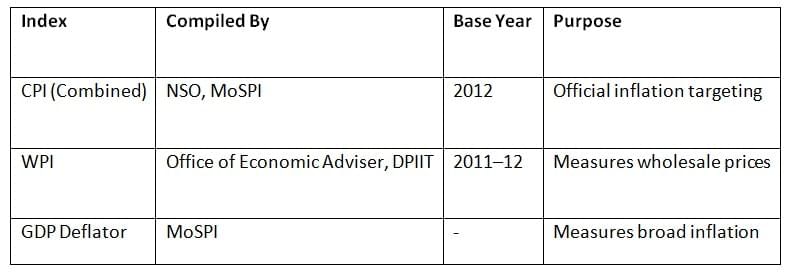
CPI (Consumer Price Index) Categories
- Food & Beverages
- Housing (Urban only)
- Fuel & Light
- Clothing & Footwear
- Miscellaneous (health, education, transport, etc.)
Note: Food items have the highest weight in CPI (~46%).
Recent Developments
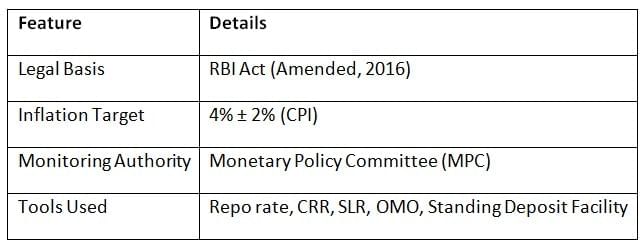
- RBI has used repo rate hikes since 2022 to curb high CPI inflation.
- Food inflation remains high due to erratic monsoons and global supply chain disruptions.
- Retail inflation (CPI) in 2024-25 has shown moderation but remains volatile in food categories.
Inflation Targeting Framework
Government Measures to Tame Inflation
- Use of buffer stock (e.g., rice, wheat, pulses)
- Export restrictions on essential commodities
- Import duty reduction on oilseeds, pulses
- Price caps and MSP adjustments
- Release of LPG, petrol and fertilizer subsidies
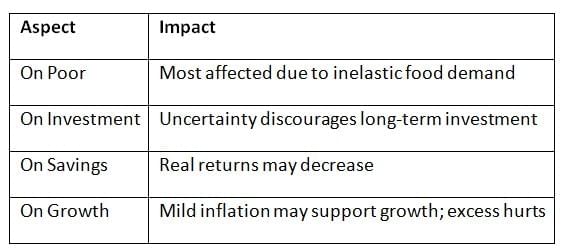
Effects of Inflation
The document Cheat Sheet: Price and Inflation | Indian Economy for UPSC CSE is a part of the UPSC Course Indian Economy for UPSC CSE.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
121 videos|490 docs|159 tests
|
FAQs on Cheat Sheet: Price and Inflation - Indian Economy for UPSC CSE
| 1. What are the different types of inflation, and how do they impact the economy? |  |
Ans. The main types of inflation include demand-pull inflation, cost-push inflation, and built-in inflation. Demand-pull inflation occurs when the demand for goods and services exceeds their supply, leading to increased prices. Cost-push inflation results from rising costs of production, such as wages and raw materials, which pushes prices higher. Built-in inflation is related to adaptive expectations, where businesses and workers expect future inflation and adjust their wages and prices accordingly. Each type affects the economy differently, influencing purchasing power, interest rates, and economic growth.
| 2. How is inflation measured in India, and what are the key indicators? |  |
Ans. In India, inflation is primarily measured using two indices: the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and the Wholesale Price Index (WPI). The CPI reflects the changes in prices of a basket of goods and services consumed by households, while the WPI measures the price changes at the wholesale level. The Reserve Bank of India uses these indices to monitor inflation trends and make policy decisions, focusing particularly on the CPI for its inflation targeting framework.
| 3. What are the categories included in the Consumer Price Index (CPI) in India? |  |
Ans. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) in India is categorized into several groups, including Food and Beverages, Clothing and Footwear, Housing, Fuel and Light, and Miscellaneous items. Each category captures the price changes of specific goods and services that households typically consume, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of inflation's impact on different segments of the population.
| 4. What recent developments have influenced inflation trends in India? |  |
Ans. Recent developments influencing inflation trends in India include fluctuations in global oil prices, supply chain disruptions due to geopolitical tensions, and changes in agricultural output due to weather conditions. Additionally, government policies, such as taxes on goods and services and subsidies, also play a significant role. These factors can lead to volatility in the inflation rate, impacting both consumers and policymakers.
| 5. What measures has the Indian government implemented to control inflation? |  |
Ans. The Indian government has adopted several measures to control inflation, including monetary policy adjustments by the Reserve Bank of India, such as changing interest rates to manage money supply. Fiscal measures include subsidies for essential commodities, price controls on certain goods, and strategic reserves to stabilize prices. These actions aim to balance demand and supply in the economy, keeping inflation within target levels.
Related Searches
















