Ancient History- Solved Questions (2025) | UPSC Topic Wise Previous Year Questions PDF Download
Q1: Fa-hien (Faxian), the Chinese pilgrim, travelled to India during the reign of
(a) Samudragupta
(b) Chandragupta II
(c) Kumaragupta I
(d) Skandagupta
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Fa-hien, a Chinese Buddhist pilgrim, traveled to India during the reign of Chandragupta II of the Gupta dynasty in the early 5th century CE. He sought Buddhist scriptures and studied Indian Buddhist practices, documenting valuable insights into Gupta society, governance, and religion. Other rulers listed are not from the time of his visit.
Q2: With reference to ancient India (600–322 BC), consider the following pairs: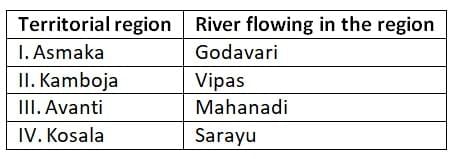
How many of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a)Only one
(b) Only two
(c) Only three
(d) All the four
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
I. Asmaka: Godavari
Correctly matched, as Asmaka, a Mahajanapada in the Deccan, was situated along the Godavari river.
II. Kamboja: Vipas
Incorrect, as Kamboja was located in the northwest (near Afghanistan and Tajikistan), not near the Vipas (Beas) river in Punjab.
III. Avanti: Mahanadi
Incorrect, as Avanti, centered in western Madhya Pradesh with Ujjain as its capital, was associated with the Kshipra river, not the Mahanadi.
IV. Kosala: Sarayu
Correct, as Kosala, in present-day eastern Uttar Pradesh, was traversed by the Sarayu river.
Q3: Ashokan inscriptions suggest that the 'Pradesika', 'Rajuka' and 'Yukta' were important officers at the
(a) village-level administration
(b) district-level administration
(c) provincial administration
(d) level of the central administration
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Ashokan inscriptions refer to 'Pradesika', 'Rajuka', and 'Yukta' as key district-level officials. The Pradesika oversaw district administration, the Rajuka was responsible for revenue collection and judicial duties, and the Yukta served as a subordinate official assisting with administrative tasks and maintaining records.
Q4: Who among the following led a successful military campaign against the kingdom of Srivijaya, the powerful maritime State, which ruled the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, Java and the neighbouring islands?
(a) Amoghavarsha (Rashtrakuta)
(b) Prataparudra (Kakatiya)
(c) Rajendra I (Chola)
(d) Vishnuvardhana (Hoysala)
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
Rajendra I of the Chola dynasty, succeeding his father Rajaraja I, launched a significant naval expedition around 1025 CE against the Srivijaya kingdom, a dominant maritime power in the Malay Peninsula, Sumatra, and Java. This campaign strengthened Chola control over vital sea trade routes. The other rulers—Amoghavarsha (Rashtrakuta), Prataparudra (Kakatiya), and Vishnuvardhana (Hoysala)—did not undertake campaigns against Srivijaya, focusing instead on regional affairs in the Deccan and South India.
Q5: Who among the following rulers in ancient India had assumed the titles 'Mattavilasa', 'Vichitrachitta' and 'Gunabharata'?
(a) Mahendravarman I
(b) Simhavishnu
(c) Narasimhavarman I
(d) Simhavarman
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
The correct answer is A. Mahendravarman I.
Mahendravarman I, a 7th-century Pallava king, was known for his literary talent and artistic patronage. He adopted the titles ‘Mattavilasa’ (lover of playful sport), ‘Vichitrachitta’ (curious-minded or inventive), and ‘Gunabharata’ (full of virtues). He also authored the Sanskrit play Mattavilasa Prahasana, reflecting his cultural contributions.
The other rulers listed did not assume these titles.
Q6: The irrigation device called 'Araghatta' was
(a) a water bag made of leather pulled over a pulley
(b) a large wheel with earthen pots tied to the outer ends of its spokes
(c) a larger earthen pot driven by bullocks
(d) a large water bucket pulled up by rope directly by hand
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
The Araghatta was an ancient Indian irrigation device consisting of a large wheel with earthen pots fixed around its rim. As the wheel rotated—usually powered by animals or humans—the pots dipped into a water source and lifted water for irrigation. This mechanism is distinct from leather bags or simple buckets pulled by hand and represents early mechanical water-lifting technology.
Q7: The famous female figurine known as 'Dancing Girl', found at Mohenjo-daro, is made of
(a) Carnelian
(b) Clay
(c) Bronze
(d) Gold
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The 'Dancing Girl' from Mohenjo-daro is a renowned artifact of the Indus Valley Civilization, showcasing exceptional bronze metalwork crafted through the lost-wax casting technique.
Q8: The first Gandharva Mahavidyalaya, a music training school, was set up in 1901 by Vishnu Digambar Paluskar in
(a) Delhi
(b) Gwalior
(c) Ujjain
(d) Lahore
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
In 1901, Vishnu Digambar Paluskar founded the first Gandharva Mahavidyalaya in Lahore, a pivotal move to formalize music education in India and promote the revival of classical music traditions.
|
72 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Ancient History- Solved Questions (2025) - UPSC Topic Wise Previous Year Questions
| 1. What are the key features of ancient civilizations that are often highlighted in historical studies? |  |
| 2. How did trade influence the development of ancient societies? |  |
| 3. What role did religion play in ancient civilizations? |  |
| 4. What were some notable technological advancements in ancient history? |  |
| 5. How did ancient societies manage to sustain their populations? |  |
















