Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Mensuration-Volume, Surface Area & Solid Figures | CSAT Preparation - UPSC PDF Download
Note: No questions being asked from this topic in the year 2025
Q1. What is the least possible number of cuts required to cut a cube into 64 identical pieces? (2024)
(a) 8
(b) 9
(c) 12
(d) 16
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (b)
Let n be the number of cubes on each edge of the cube. n3 = 64
or n = 4
So, there are 4 cubes on each edge of the cube.
For this to happen we need to cut each edge 3 times.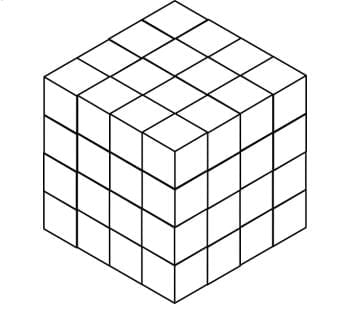 This can be achieved by cutting the cube 3 times along each of the three axes – x, y and z.
This can be achieved by cutting the cube 3 times along each of the three axes – x, y and z.
So, the total number of minimum possible cuts required = 3 + 3 + 3 = 9
Q2. 125 identical cubes are arranged in the form of cubical block. How many cubes are surrounded by other cubes from each side? (2023)
(a) 27
(b) 25
(c) 21
(d) 18
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
We have to find the number of internal cubes, i.e. the number of cubes that are not exposed
There are 125 cubes. Now, 53 = 125. So, n = 5
Number of internal cubes = (n - 2)3 = (5 - 2)3 = 33 = 27
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q3. What is the unit digit in the expansion of (57242)9 × 7 × 5 × 3 × 1? (2023)
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (a)
(57242)9 × 7 × 5 × 3 × 1 = (57242)945
The unit digit of the resultant number only depends on the unit digit of the given number 57242, i.e. 2.
Now, we know that:
21 = 2
22 = 4
23 = 8
24 = 16 (unit digit 6)
25 = 32 (unit digit 2)
.
.
.
And so on.
So, 2 has a cyclicity of 4. Exponent of any number ending in 2 will produce a number that will end in 2, 4, 8, or 6.
Now, 945 = 944 + 1
944 is divisible by 4. So, the last digit of (57242)945 will be the same as that of (57242)1, which is 2.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Q4. Consider the following statements in respect of a rectangular sheet of length 20 cm and breadth 8 cm: (2022)
1. It is possible to cut the sheet exactly into 4 square sheets.
2. It is possible to cut the sheet into 10 triangular sheets of equal area.
Which of the above statements is are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (c)
The rectangle is of dimensions 20 cm × 8 cm.
Statement I: You may think that as the area of rectangle is not a perfect square, it is not possible to cut it into exactly 4 square sheets.
But there’s a catch. The statement never says that the 4 squares have to be equal in area.
We can do so as follows: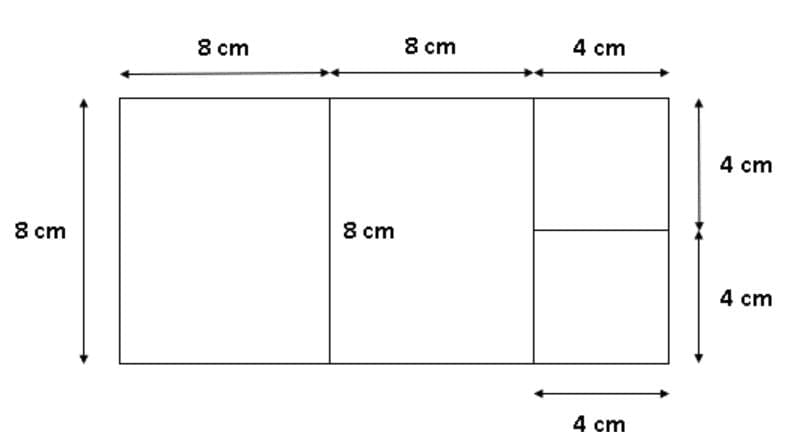 Statement II: You may think that we can cut the rectangle into 8 triangles of equal area (as shown below), but not in 10.
Statement II: You may think that we can cut the rectangle into 8 triangles of equal area (as shown below), but not in 10.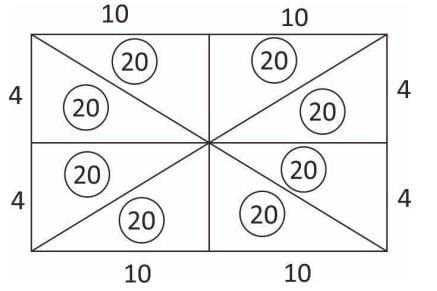
But again, this can be done. It has been shown below: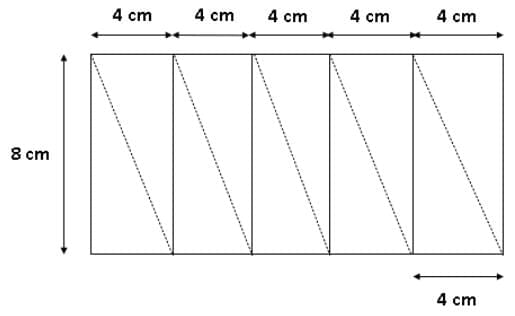
Hence, both statements 1 and 2 are correct.
Q5. A cubical vessel of side 1 m is filled completely with water. How many millilitres of water is contained in it (neglect thickness of the vessel)? (2021)
(a) 1000
(b) 10000
(c) 100000
(d) 1000000
 View Answer
View Answer 
Ans: (d)
Volume of the cube = Side × Side × Side = 1 × 1 × 1 = 1 cubic meter
Now, 1 cubic meter = 1000000 mililiters
|
205 videos|265 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Previous Year Topic Wise Questions With Solutions: Mensuration-Volume, Surface Area & Solid Figures - CSAT Preparation - UPSC
| 1. What is the formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder? |  |
| 2. How do you find the surface area of a sphere? |  |
| 3. What is the difference between the volume and surface area of a cube? |  |
| 4. How can the volume of a cone be determined? |  |
| 5. What is the formula for the surface area of a rectangular prism? |  |















