Energy - How Things Work NCERT Solutions | Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 115 |

|
| Page No. 116 |

|
| Page No. 117 |

|
| Page No. 119 |

|
| Page No. 120 |

|
| Page No.121 |

|
| Page No. 122 |

|
| Page No. 123 |

|
| Page No. 123-124 |

|
| Page No. 125 |

|
| Page No. 127-128 |

|
| Page No. 130 |

|
Page No. 115
Discuss
Q. What makes these things move, shine, make a sound or get warm and cold?
Ans: Things move, shine, make sounds, or get warm and cold because of energy. Energy is what powers all these actions and changes. It can come from different sources like food for living beings, fuel for machines, electricity for lights and sounds, or heat for warming and cooling. Energy makes everything around us work and change.
Page No. 116
Activity 1
 Explanation: When you blow up a balloon and release it, the air rushes out, pushing the balloon forward. This shows that moving air can create energy and cause things to move.
Explanation: When you blow up a balloon and release it, the air rushes out, pushing the balloon forward. This shows that moving air can create energy and cause things to move.
The extension activity called the "Balloon Air Rocket" gives ideas to see this effect in another way:
- Attach the filled balloon to a small light object to see it move.
- Or, attach the balloon to a straw taped to it, thread the straw onto a string, and release the balloon. It will zip along the string, acting like a rocket.
This activity helps you see that air movement can make things move—showing how energy works to push or pull objects.
Think
Q. What would you change in the balloon activity to make the toy move faster or slower? Ans: Blow the balloon bigger and release it with more force for faster movement; use less air or a heavier object for slower.
Ans: Blow the balloon bigger and release it with more force for faster movement; use less air or a heavier object for slower.
Page No. 117
Activity 2
 Explanation: This activity shows how to make a rubber band guitar to demonstrate sound energy:
Explanation: This activity shows how to make a rubber band guitar to demonstrate sound energy:
- When you pluck the stretched rubber bands, they start to vibrate.
- These vibrations travel through the air as sound waves, reaching your ears as sound.
- The different thickness and tightness of the bands change the way they vibrate, which changes the sound you hear (high or low notes).
- Placing a ruler or pencil under the bands helps them vibrate more freely.
- This simple activity helps you see that vibrating objects create sound and that the energy of your plucking is turned into sound energy.
In short, the experiment shows that when rubber bands vibrate, they create sound energy we can hear.
Think
Q. What happens if you use thinner or thicker rubber bands? Do they sound different?
Ans: Yes, using thinner or thicker rubber bands will make them sound different when you pluck them. Thinner rubber bands usually make higher-pitched sounds, while thicker rubber bands produce lower-pitched sounds. This is because thinner bands vibrate faster and thicker bands vibrate more slowly, which changes the pitch of the sound you hear. So, by using rubber bands of different thicknesses, you can hear a variety of notes.
Activity 3

Explanation: Sun-powered Water Warmer
This activity shows how sunlight gives us heat energy:
- Fill two cups with water.
- Place one cup in the sunlight and the other in the shade.
- Wait for 15–20 minutes, then touch the water in both cups.
What do you notice?
The water kept in the sunlight is warmer because the Sun heats it up. This proves that sunlight gives us heat energy.
Page No. 119
Think
Q. What do cars and scooters need to keep running?
Ans: They need fuels such as petrol or diesel.
Write
Q. How is food cooked in your house?
Ans: (Can differ according to the students)
Food is cooked using LPG gas, electricity, wood, or coal depending on the household.
Page No. 120
Discuss
Q1. What kind of fuel do you use at home?
Ans: LPG or electric cooking.
Q2. What problems arise from using wood or coal?
Ans: Problems with wood/coal include smoke, pollution, health issues, and deforestation.
Activity 4
 Observation:
Observation: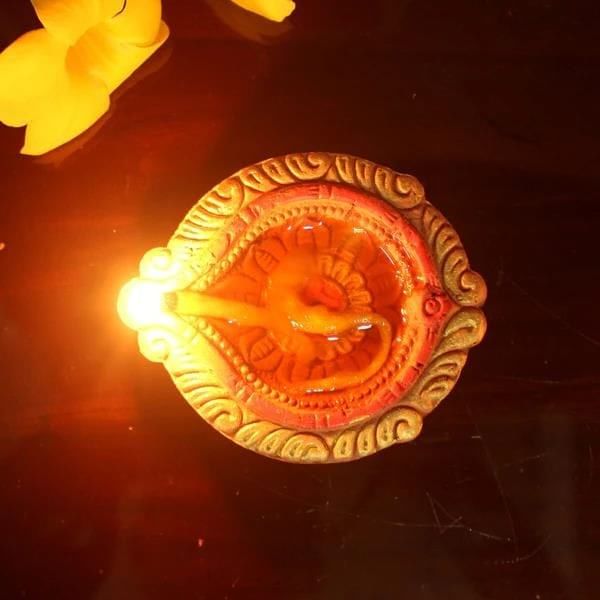
(a) Which diya burns longer? Why?
The diya with the cotton wick and oil (Diya 2) burns longer. This is because the oil acts as a fuel, supplying energy to keep the flame burning. In Diya 1, without oil, the cotton wick burns out quickly as there is no extra fuel to keep it burning.
(b) What is acting as a fuel here?
The oil in Diya 2 is acting as the fuel. The cotton wick simply helps in transporting the oil to the flame, but it is the oil that actually burns and keeps the diya alight for a longer time.
Page No.121
Activity 5
Q. Walk around your home or classroom. Identify five things that run on electricity. Fill in the following table.
Students are advised to do this themselves. A sample answer/ findings can be:
Page No. 122
Think
Q. What would your day be like without electricity?
Ans: A day without electricity would be very different and challenging.
- Without electricity at home or school, everything would be dark once the sun goes down.
- Fans and air conditioners would not work, making hot weather feel very uncomfortable.
- Devices like televisions, computers, and phones couldn't be charged or used, which would limit entertainment, communication, and work.
- You wouldn't be able to cook with electric stoves or microwaves, so you might need to use other methods like gas or firewood.
- Refrigerators would stop working, leading to the risk of food spoilage.
- Daily activities would become slower, and many conveniences we depend on would be gone, highlighting how essential electricity is in our lives.
Page No. 123
Think
Q. Place one damp cloth in the Sun and another in the shade; which dries first and why?
Ans: The damp cloth placed in the Sun will dry first because the Sun's heat causes the water in the cloth to evaporate more quickly. In the shade, there is less heat, so the water evaporates slower, making the cloth take longer to dry. Sunlight also helps warm the air around the cloth, speeding up evaporation compared to the cooler, shaded area.
Page No. 123-124
Activity 6

 What happens to the pinwheel?
What happens to the pinwheel?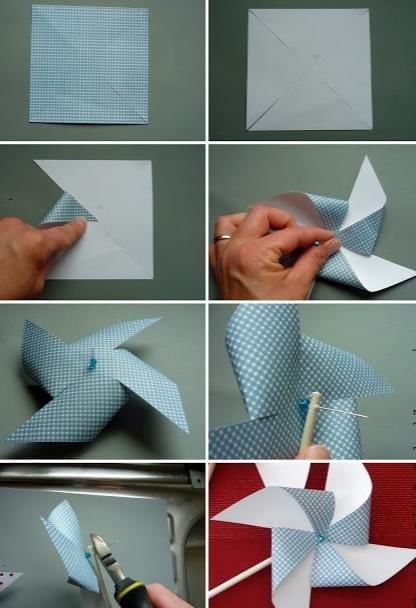
When you hold your pinwheel in the wind, or run while holding it, the pinwheel spins quickly.
The moving air pushes against the folded parts of the pinwheel, causing it to turn around its pin. This is because wind (or your movement through the air) creates a force that makes the pinwheel spin.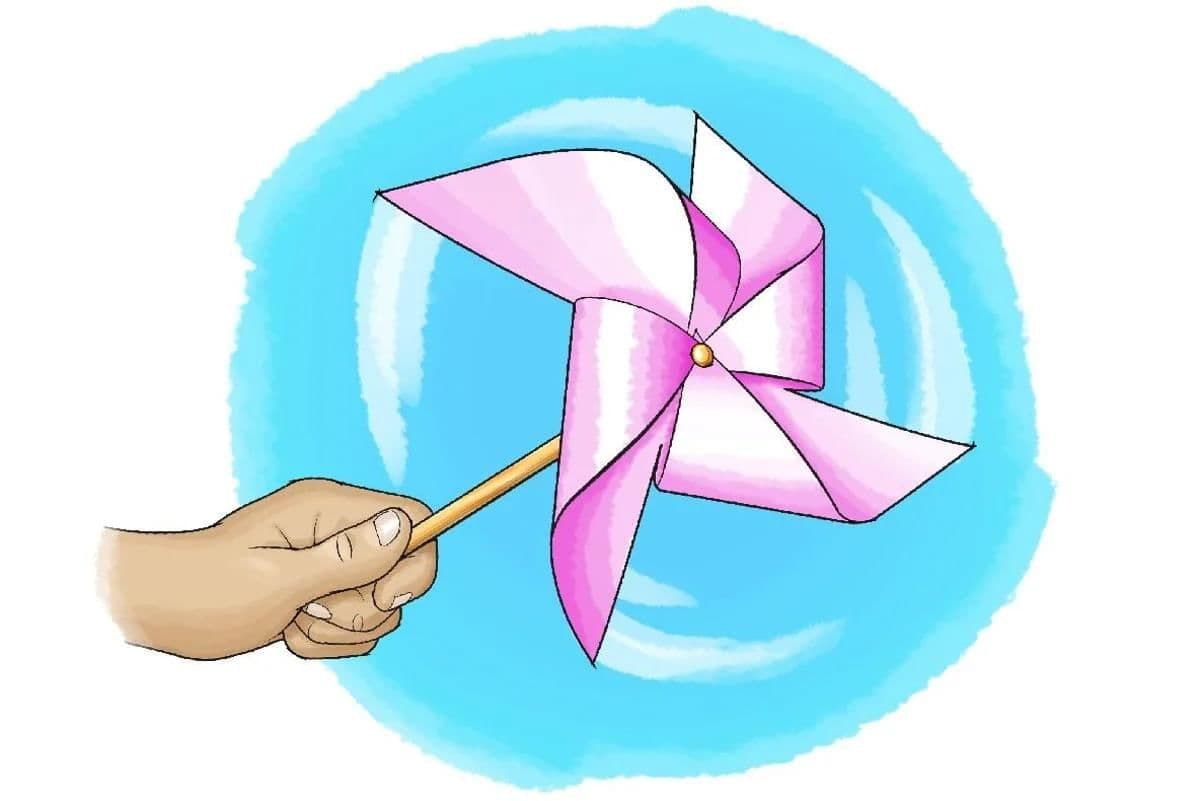
This shows that moving air (wind) has energy and can make objects move. The energy from the wind is used to spin the pinwheel!
Activity 7

What happens to your paper when you focus sunlight on it with a magnifying glass?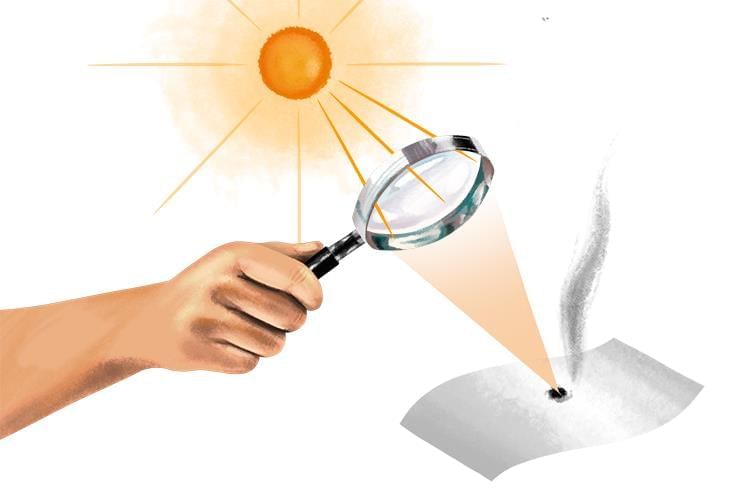
When you use the magnifying glass to focus sunlight onto a small spot on the paper, that spot becomes very hot. After some time, the paper at that spot may turn brown, blacken, or even catch fire and start burning.
Why does this happen?
The magnifying glass concentrates the sunlight into a tiny area, increasing the amount of heat energy at that point. This extra heat is enough to heat the paper to its burning point.
The focused sunlight can make the paper burn or char because the energy from the Sun is concentrated in one small spot!
(Remember to always do this experiment safely and with adult supervision.)
Activity 8
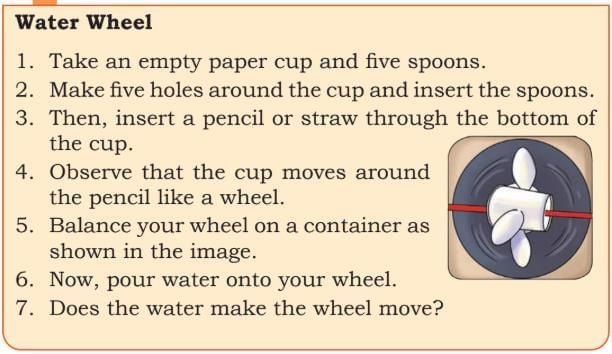
Explanation: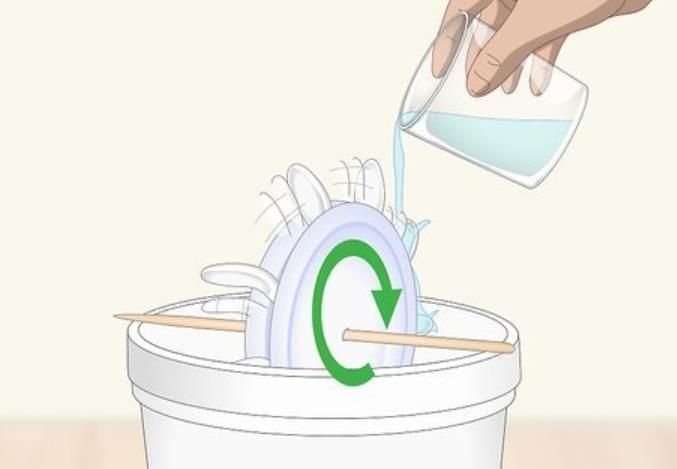 When you pour water onto your homemade wheel (paper cup with spoons attached and balanced on a pencil), the water pushes against the spoons. This force causes the wheel to spin around the pencil, just like a water wheel in a mill or a turbine.
When you pour water onto your homemade wheel (paper cup with spoons attached and balanced on a pencil), the water pushes against the spoons. This force causes the wheel to spin around the pencil, just like a water wheel in a mill or a turbine.
What does this show?
- The moving water has energy.
- The energy in water can make things move by pushing and turning the wheel.
Does the water make the wheel move?
Yes, pouring water on the wheel makes it spin because water's energy is transferred to the wheel, causing movement.
Page No. 125
Think
Q. Have you seen papads or clothes drying in the sunlight?
Ans: Yes, these use the Sun’s energy to dry.
Write
Q. Can you think of more examples where the Sun, wind, or flowing water are used?
Ans: Solar water heaters, sails on boats, water mills for grinding grain.
Page No. 127-128
Write
 List actions that you see in the picture above and fill in the following table.
List actions that you see in the picture above and fill in the following table.
(Answers may differ as per students' perspective)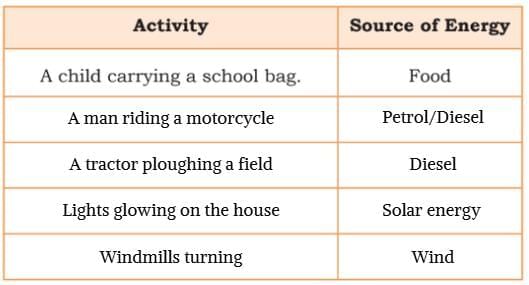
Activity 9

Energy Flow Game: Sample Solutions
How the Game Works
Students are assigned cards:
- Energy source (Sun, wind, battery, food, fuel, electricity)
- Type of energy (Heat, movement, light, electricity)
- Use of energy (Drying clothes, turning a turbine, powering a torch, running, cooking, lighting a bulb)
- Each student finds two others to complete an energy chain (source → type → use).
- The group presents a short explanation of their energy chain.
Sample Energy Chains
1. Sun → Heat → Helps dry clothes
“We are the heat of the Sun and we help to dry clothes.”
2. Wind → Movement → Turns turbine to make electricity
“We are the movement from wind and we help turn turbines to make electricity.”
3. Battery → Electricity → Powers a torch
“We are electricity from the battery and we help light up torches.”
4. Food → Movement → Helps a child run
“We are movement from the energy in food and we help children run and play.”
5. Fuel → Heat → Used for cooking
“We are heat from fuel and we help to cook food.”
6. Electricity → Light → Lights up a bulb
“We are light from electricity and we help brighten the room.”
What does this activity show?
It helps you understand how energy from different sources changes form and is used in everyday life—for drying, moving things, making sound, and more. This makes learning about energy fun and easy to understand!
Page No. 130
Q1. What will happen if there is no electricity in your house for a day?
Ans: If there is no electricity in your house for a day, many things would be affected. You would have no lights when it gets dark, fans and air conditioners wouldn’t work, and electrical devices like televisions, computers, and phones could not be used or charged. Cooking with electric stoves or microwaves would not be possible, and refrigerators would stop cooling, risking food spoilage. Overall, daily activities would slow down and be less convenient.
Q2. Why is it better to use solar or wind energy instead of coal?
Ans: It is better to use solar or wind energy instead of coal because solar and wind energy are clean, renewable sources that do not produce harmful pollution or greenhouse gases. Coal, on the other hand, is a fossil fuel that releases carbon dioxide and other pollutants when burned, which harms the environment and contributes to climate change.
Q3. Give two examples where you have seen energy being stored.
Ans: Two examples where energy is stored are:
- In batteries that store electrical energy to power devices like remote controls and flashlights.
- In food, where chemical energy is stored and used by our bodies to do work and stay active.
Q4. What is the one thing you can do at home to save energy?
Ans: One thing you can do at home to save energy is to switch off lights, fans, and electrical appliances when they are not in use. This simple habit reduces electricity consumption and helps save energy.
Q5. Find out how many kilometres a vehicle travels per litre of petrol or diesel. Ask about different vehicles. How will you compare them?
Ans: The number of kilometres a vehicle travels per litre of petrol or diesel (fuel efficiency) varies by vehicle type. For example, small cars may travel around 15 to 20 km per litre, while larger cars or SUVs may travel about 8 to 12 km per litre. To compare them, you look at the fuel efficiency numbers—the higher the kilometres per litre, the more fuel-efficient the vehicle is, meaning it uses less fuel for the same distance.
Q6. Look around your home or classroom. List any three objects that use energy and mention their source of energy.
Ans: Three objects in your home or classroom that use energy and their sources are:
- Fan → Electricity
- Television → Electricity
- Refrigerator → Electricity
Q7. Create and share:
(a) Draw or make a simple plan of a ‘clean energy home’ that uses solar, wind or any such source of energy.
Ans:
(b) Make ‘my energy diary’ for one day, record the number of times you have used the electricity, fuel and so on.
Ans:
|
16 videos|144 docs|10 tests
|
FAQs on Energy - How Things Work NCERT Solutions - Our Wondrous World Class 5 - New NCERT
| 1. What is energy and why is it important in our daily lives? |  |
| 2. What are the different forms of energy? |  |
| 3. How does energy transfer occur? |  |
| 4. What are renewable and non-renewable sources of energy? |  |
| 5. How can we conserve energy in our daily lives? |  |















