Worksheet: Exploring Forces | Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Short Answer Questions |

|
| Long Answer Questions |

|
| Match the Following |

|
| Application/Reasoning (Short Problems) |

|
 Force
Force
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Instruction: Select the correct option for each question.
Q1. In science, a force is defined as:
a) Only a push
b) Only a pull
c) A push or a pull
d) Energy of motion
Q2. Which of these is NOT an effect of force?
a) Change of shape
b) Change of direction
c) Production of light
d) Start/stop motion
Q3. Forces always involve:
a) Only one object
b) Interaction between two objects
c) Only moving objects
d) Only heavy objects
Q4. The SI unit of force is:
a) Joule (J)
b) Watt (W)
c) Newton (N)
d) Pascal (Pa)
Q5. Friction is a force that:
a) Aids motion
b) Always increases speed
c) Opposes motion between surfaces in contact
d) Acts only in liquids
Q6. Which is a non-contact force?
a) Muscular force
b) Friction
c) Magnetic force
d) Push with a stick
Q7. Gravity is:
a) Sometimes attractive, sometimes repulsive
b) Always repulsive
c) Always attractive
d) Only acts on Earth
Q8. Weight is measured in:
a) Kilogram (kg)
b) Newton (N)
c) Meter (m)
d) Joule (J)
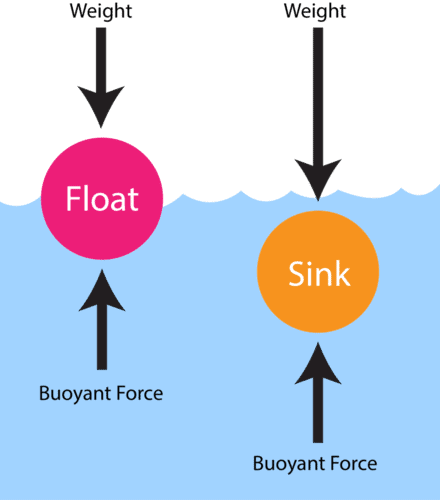
Q9. An object floats in a liquid when:
a) Weight > buoyant force
b) Weight = buoyant force
c) Weight < buoyant force
d) There is no gravity
Fill in the Blanks
Instruction: Fill in the blanks with the correct word based on the chapter.
Q1. A force is a __________ or a __________.
Q2. If an object’s speed or direction changes, a __________ has acted.
Q3. The SI unit of force is the __________ (symbol: N).
Q4. Friction always acts in a direction __________ to motion.
Q5. Forces that act without contact are called __________ forces.
Q6. The force with which Earth pulls objects is called __________.
Q7. Weight is a __________ and is measured in newtons.
Q8. The device used to measure weight (force) in newtons is a __________ balance.
Q9. The upward force exerted by a liquid on an immersed object is called __________ force.
Q10. An object sinks when its __________ is greater than the buoyant force.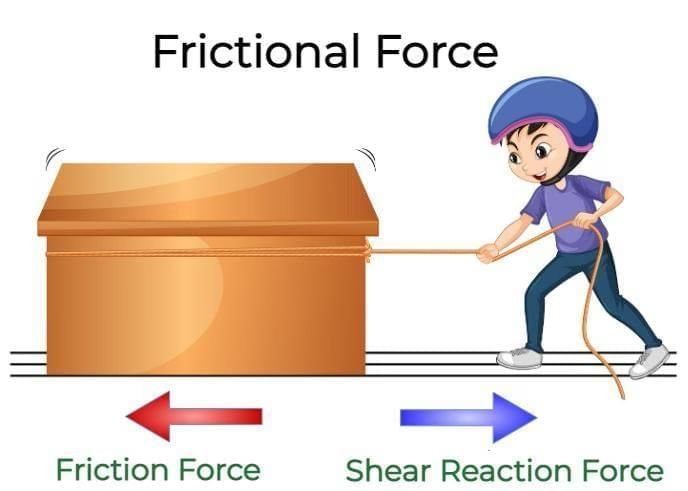
Short Answer Questions
Instruction: Answer the following questions in 2–3 lines.Q1. How does friction depend on the nature of surfaces?
Q2. Explain why cycling uphill feels harder than cycling downhill.
Q3. What does “forces work in pairs” mean?
Q4. How do we find the least count of a spring balance?
Q5. Why do streamlined shapes help in air or water?

Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Give one practical application of magnetic force.
Q.2. Which force can be used to gather iron pins scattered on the floor?
Q.3. Write one example where force changes the speed of a moving object.
Q.4. What is meant by a non-contact force? Give an example.
Q.5. What is muscular force? Give one example.
Q.6. What is meant by gravitational force (or force of gravity)? Give one example.
Q.7. Explain why the frictional force is said to be a contact force.
Q.8. What do you understand by the state of Motion?
Q.9. Why does a plastic comb rub with dry hair attract tiny pieces of paper?
Match the Following
Instruction: Match Column A with the correct option in Column B.

Application/Reasoning (Short Problems)
Instruction: Answer the following briefly in 2–3 lines.
Q1. A wooden block is pushed on a rough table and stops after some distance. Why?
Q2. A 1 kg object has a weight of about 10 N on Earth. What will be its weight on the Moon (g ≈ 1.6 m/s²)?
Q3. A spring balance has marks 0 to 5 N with 10 equal divisions between each newton. What is its least count?
Q4. Two balloons rubbed with wool repel each other. Which force is acting and why?
Q5. A stone sinks in water but a sealed empty plastic bottle floats. Why?
Check the solutions of worksheet here.
FAQs on Worksheet: Exploring Forces - Worksheets with Solutions for Class 8
| 1. What are the different types of forces that are studied in Class 8 science? |  |
| 2. How does friction affect motion? |  |
| 3. Can you explain Newton's laws of motion and their significance? |  |
| 4. What is the role of gravitational force in our daily lives? |  |
| 5. How can we apply the concept of forces in real-life scenarios? |  |















