HOTS: Natural Resources and Their Use | Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Q1. If groundwater continues to be overused in Punjab, which of the following will be the MOST immediate effect?
(a) Decrease in coal reserves
(b) Falling water table levels
(c) Increase in rainfall
(d) Rise in forest cover
Ans: (b) Falling water table levels
The Punjab caselet states that overusing groundwater for crops lowers the water table (e.g., to ~30 meters deep in 80% of Punjab), making it the most immediate effect.
Q2. Which of the following BEST explains why coal is considered a non-renewable resource?
(a) It is very expensive
(b) It pollutes the air
(c) It takes millions of years to form
(d) It is found only in India
Ans: (c) It takes millions of years to form
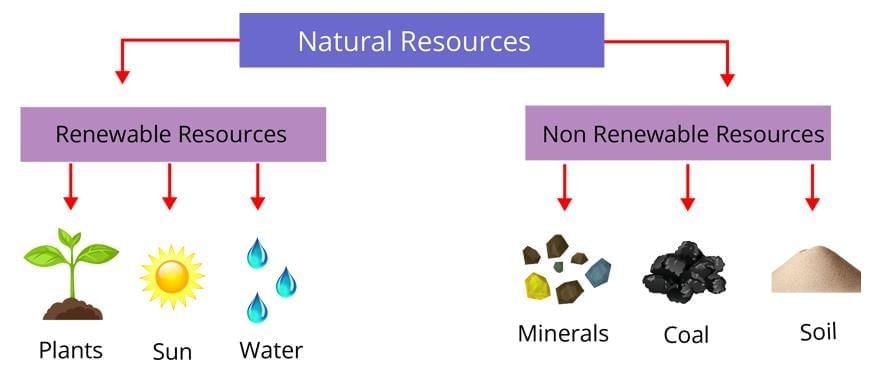
Non-renewable resources like coal form over millions of years and cannot be replenished quickly, unlike renewable resources.
Q3. When communities stopped fishing during spawning seasons, their main aim was:
(a) To punish fishermen
(b) To increase the fish trade
(c) To allow fish populations to grow back
(d) To avoid water pollution
Ans: (c) To allow fish populations to grow back
The communities historically stopped fishing during spawning seasons to help fish populations (e.g., tuna) regenerate, preventing depletion.
Q4. Which of the following situations BEST shows fair access to resources?
(a) A city giving 24-hour water to luxury apartments but limited supply to slums
(b) Villagers and towns sharing the same river water through agreed-upon timings
(c) A factory using all groundwater for industry
(d) Farmers cutting down sacred groves for cultivation
Ans: (b) Villagers and towns sharing the same river water through agreed-upon timings
The fair access to resources like water through stewardship, as equitable sharing reflects responsible management, unlike unequal or exploitative practices.
Q5. Which of the following is the MOST sustainable practice?
(a) Mining coal rapidly for export profits
(b) Using solar energy in place of diesel generators
(c) Building factories in forests
(d) Throwing untreated waste in rivers
Ans: (b) Using solar energy in place of diesel generators
Solar energy (e.g., Bhadla Solar Park) is a renewable, sustainable alternative to polluting fossil fuels, unlike other environmentally harmful options.
Q6. Why does nature become a “resource” only when humans know how to use it?
Ans: Nature becomes a resource when humans use its elements (e.g., trees, water) for purposes like living or making things, requiring knowledge of how to access and apply them. This involves three conditions: technological accessibility (e.g., machines to cut wood), economic feasibility (affordable extraction), and cultural acceptability (e.g., respecting sacred groves).
The natural elements like trees or rivers are not resources until humans know how to use them (e.g., wood for furniture, water for farming).
Q7. “Sikkim’s organic farming journey is both an environmental and economic success.” Analyse.
Ans:
- Environmental Success: Sikkim’s 100% organic farming (since 2016) restored biodiversity (e.g., more insects and birds) by using natural fertilisers like compost and neem-based pest repellents, avoiding chemical pollution and supporting ecosystem services like soil health.
- Economic Success: Organic farming increased farmers’ incomes by 20% on average and boosted tourism, as visitors were attracted to Sikkim’s sustainable model.
- Analysis: By adopting traditional practices like multi-cropping, Sikkim balanced environmental health with economic growth, making it a global model for sustainability.
The Sikkim caselet highlights how organic farming reversed low yields and debts, benefiting both nature and the economy.

Q8. If you were in charge of reducing cement pollution in India, what two measures would you take? Why?
Ans: 1. Enforce Central Pollution Control Board Guidelines: Strictly implement guidelines to minimise cement factory dust, which harms lungs, plants, and soil. This reduces pollution and protects ecosystems.
2. Promote Sustainable Materials: Encourage using mud, sandstone, or recycled plastic for construction, as seen in Auroville and Jaisalmer Fort, to lower environmental impact.
Why: These measures address health and ecological risks while promoting sustainable alternatives that focus on responsible resource use.
The cement’s pollution suggests traditional materials to reduce environmental harm.
Q9. Compare renewable and non-renewable resources. Which is more threatened today?
Ans: The careless use of renewables (e.g., water drying up) risks depletion, while non-renewables are inherently limited.
- Renewable Resources: Can be replenished naturally in a short time (e.g., solar energy, forests) if nature’s cycles are maintained. Overuse, like deforestation, can deplete them.
- Non-Renewable Resources: Formed over millions of years (e.g., coal, petroleum) and cannot be replenished quickly, with coal reserves potentially lasting only 50 years.
- Comparison: Renewables are sustainable with proper management; non-renewables are finite and deplete with use.
- More Threatened: Renewable resources are more threatened today because human actions (e.g., overusing groundwater in Punjab, deforestation) disrupt their regeneration cycles, making them behave like non-renewables.
Q10. How can the uneven distribution of natural resources lead to cooperation and conflict?
Ans: The uneven distribution shapes trade and conflicts, emphasising the need for fair resource management.
- Cooperation: Uneven resource distribution encourages trade and collaboration. For example, resource-rich areas (e.g., Jharkhand’s coal) trade with resource-scarce areas, fostering economic growth and job creation, as seen with India’s Wootz steel trade historically.
- Conflict: Resources like water crossing borders (e.g., Kaveri River disputes among Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and Puducherry) cause tensions when access is unequal. Sacred sites or land lost to mining can also spark protests.
- Solution: Fair management and negotiations can promote peace and equitable sharing.
Q11. “Overuse of renewable resources can make them behave like non-renewable resources.” Explain.
Ans: Renewable resources (e.g., water, forests) can regenerate naturally if used sustainably, but overuse disrupts their cycles, making them behave like non-renewable resources, which deplete permanently. For example, overharvesting timber faster than forests regrow leads to forest loss. Similarly, overusing groundwater in Punjab lowers water tables, reducing availability, as seen in the caselet. Sustainable practices like rainwater harvesting are needed to maintain renewability.
Q12. How is the idea of lokasangraha useful in resource use?
Ans: Lokasangraha, from the Bhagavad Gita, means working for the good of all, not just oneself. In resource use, it encourages responsible stewardship by promoting fair access to resources (e.g., clean water, air) and sustainable practices. For example, sharing river water equitably (like the Brahmaputra example) or adopting organic farming in Sikkim ensures resources benefit everyone and last for future generations. It discourages selfish exploitation and calls for collective responsibility.
Q13. Punjab groundwater case: What were the short-term benefits and long-term harms?
Ans: The Punjab caselet highlights how groundwater overuse provided immediate food security but caused long-term environmental and health damage.
- Short-Term Benefits: In the 1960s, Punjab’s farmers used groundwater for high-yielding crops, supported by free electricity, ensuring food security and increased agricultural output.
- Long-Term Harms: Over-pumping lowered water tables to ~30 meters deep in 80% of Punjab, marked as “overexploited.” Chemical fertilisers polluted groundwater, posing health risks and reducing sustainability, as water became scarce for future use.
Q14. Design a school awareness campaign on sustainable resource use.
Ans: Campaign Name: “Green Today, Thriving Tomorrow”
Activities:
- Workshops: Educate students on sustainable practices like rainwater harvesting and organic farming (e.g., Sikkim’s model), using posters and videos.
- Tree-Planting Drive: Plant trees to promote ecosystem services like oxygen production, inspired by the chapter’s example of trees producing 275 litres of oxygen daily.
- Recycle Club: Encourage reducing, reusing, and recycling to mimic nature’s no-waste cycles, as described in the chapter.
- Goal: Raise awareness about responsible resource use, emphasising stewardship and sustainability.
Q15. What if India had not invested in renewable energy like solar parks?
Ans: If India had not invested in renewable energy like solar parks (e.g., Bhadla Solar Park), several consequences would arise:
- Increased Non-Renewable Depletion: India would rely more on coal and petroleum, depleting reserves faster (e.g., coal may last only 50 years) and increasing import costs for oil.
- Environmental Damage: Greater fossil fuel use would worsen pollution and climate change, accelerating Himalayan glacier melting, threatening water security for rivers like the Brahmaputra.
- Economic Challenges: Without solar energy’s job creation and cheaper electricity (e.g., Bhadla meets ~15% of Rajasthan’s needs), India would face higher energy costs and slower economic growth.
- Missed Global Leadership: India’s role in the International Solar Alliance (ISA) would weaken, reducing its influence in promoting clean energy globally.
- Sustainability Risks: Overuse of non-renewables would harm ecosystems, reducing services like oxygen production and soil health, making sustainable development harder.
Conclusion: Investing in renewables has reduced environmental harm, supported economic growth, and ensured long-term resource availability emphasis on stewardship.
|
31 videos|128 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on HOTS: Natural Resources and Their Use - Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are natural resources and why are they important for human life? |  |
| 2. How are renewable and non-renewable resources different? |  |
| 3. What are the major uses of water as a natural resource? |  |
| 4. What role do forests play in the ecosystem and the economy? |  |
| 5. How can individuals contribute to the sustainable use of natural resources? |  |
















