Key Concepts: Natural Resources and Their Use | Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
When Does Nature Become a Resource?
Nature includes all things not made by humans—air, water, trees, minerals, etc..
An element becomes a resource when humans use it for their sustenance or transform it for consumption (e.g., trees for wood, petroleum for fuel).
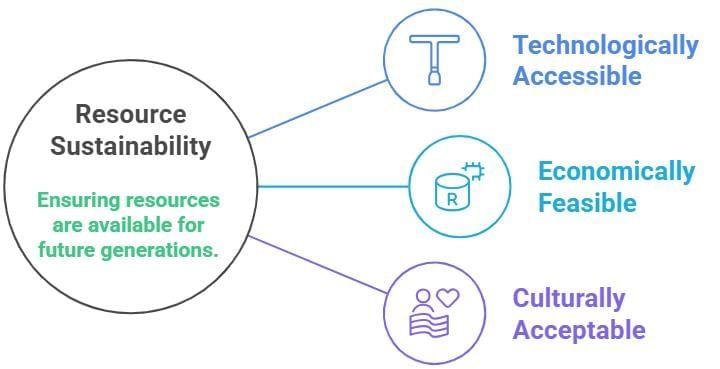
Three conditions must be satisfied:
1. Technological accessibility
2. Economic feasibility
3. Cultural acceptability
Simply put: a resource is any part of nature that is useful, usable, and valued by people.
- Technologically Accessible: A natural resource we can get or use because we have the tools or machines needed.
- Economically Feasible: Using or obtaining a resource is possible without incurring excessive costs or effort.
- Culturally Acceptable: When using a resource fits with people's beliefs and traditions. For example, cutting trees in sacred forests might be unacceptable.
Exploitation: Taking and using natural resources. Here, it means the careful use of resources, not necessarily harming them.
Categories of Natural Resources
Resources are categorised by use and regeneration:
By Use:
- Essential for life: Air, water, soil, and food.
- Materials and beauty: Wood, marble, metal ores, coal, gold.
- Energy sources: Coal, water, petroleum, wind, and solar energy.
By Regeneration:
- Renewable resources: Can naturally replenish if not overused (solar energy, wind, flowing water, timber, fish). Depend on restoration and regeneration cycles.
- Non-renewable resources: Formed over millions of years; exhaustible and not quickly replaced (coal, petroleum, minerals). Require careful, limited use.
Key principle: Even renewable resources can become non-renewable if overexploited.
Distribution of Natural Resources and its Implications
Resources are unevenly distributed across the world and even within countries.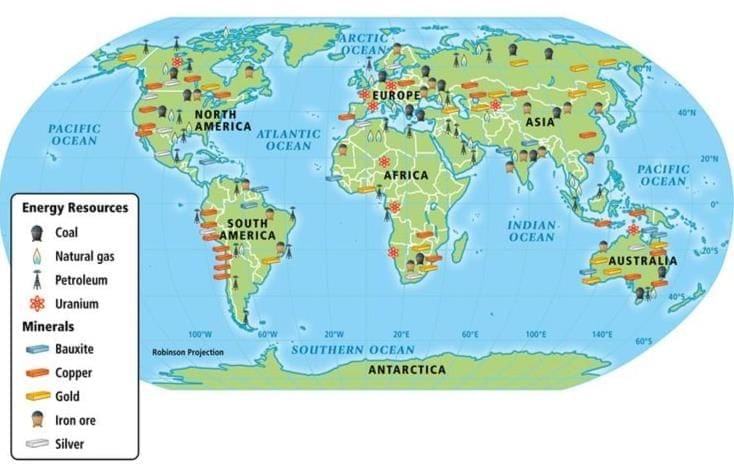 Distribution of Natural Resources in the World
Distribution of Natural Resources in the World
Impact areas:
1. Human Settlements: Towns and cities often grow near natural resources.
2. Economic Opportunities: Local industries, jobs, and infrastructure develop around resource sites.
3. Conflicts: Disputes may arise over access and sharing (e.g., river water among states, mineral-rich regions).
4. Trade and Development: Locations with resources can boost trade, but don’t guarantee prosperity for all.
Example: The distribution of coal, oil, and mineral deposits in India shapes industry, employment, and even national trade policies.
The ‘Natural Resource Curse’
Definition: Regions rich in resources sometimes experience slower economic growth—a paradox called the "resource curse" or "paradox of plenty."
Why does this happen?
- Overdependence on resource extraction may prevent the growth of diversified industries.
- Wealth from resources may benefit only a few, causing social and economic challenges.
India’s case: Investments in technology and skills have helped avoid this to some degree, but balancing extraction with sustainability remains a challenge.
Responsible and Wise Use of Natural Resources: Stewardship
Stewardship means respecting and caring for resources:
- Use only what is needed.
- Replenish what is taken to maintain restoration and regeneration cycles.
- Combine traditional knowledge (like water harvesting, crop rotation, organic inputs) with modern methods for sustainability.
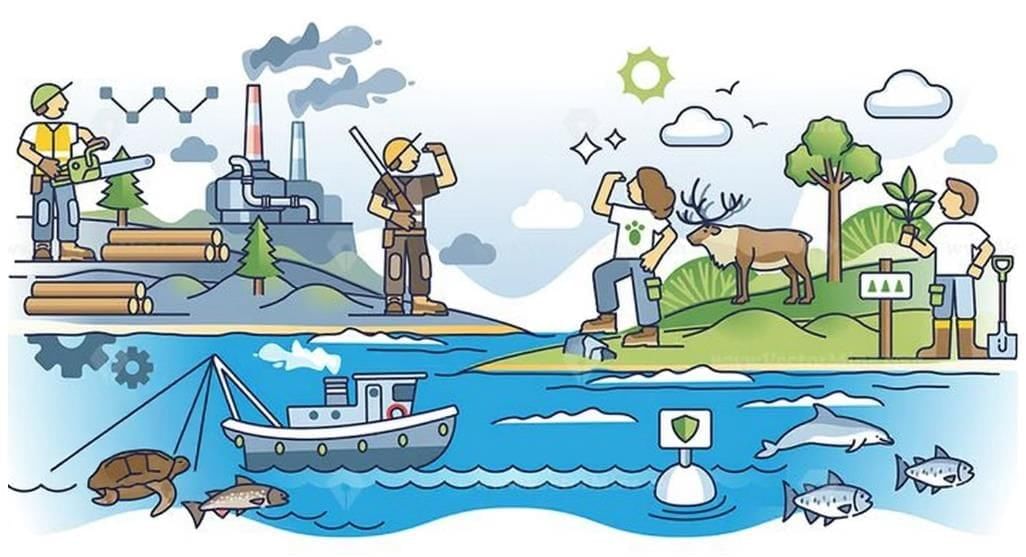 Exploiting Natural Resources
Exploiting Natural Resources
Examples:
- Groundwater Crisis: Overuse for irrigation causes depletion (e.g., Punjab), requiring restoration efforts like recharging wells and rainwater harvesting.
- Soil Degradation: Excess chemical fertiliser use harms soil; organic methods offer alternatives.
- Cement Pollution: Modern building materials pollute; the use of local mud and stone can reduce harm.
- Success story: Sikkim transformed farming to fully organic, improving ecology and farmer incomes.
Responsible and Judicious Use of Resources
Judicious use means:
- Stretching non-renewable resources to last until sustainable alternatives are found.
- Monitoring the rate of renewable resource use to prevent depletion.
- Ensuring fair access to basic resources like water and air for all sections of society.
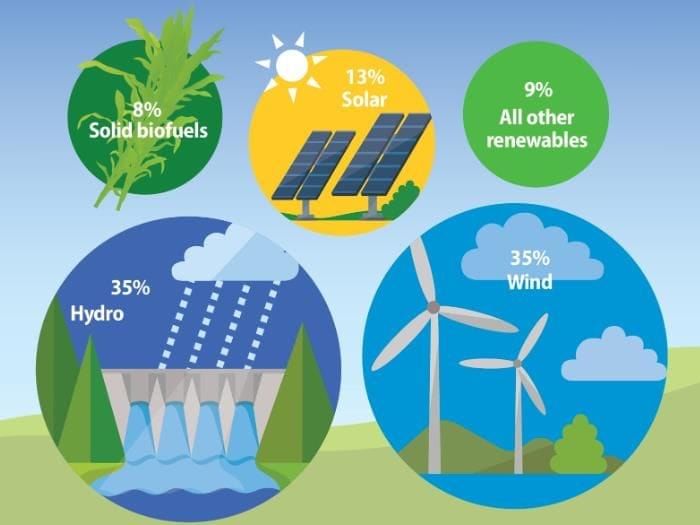 Example of Renewable Resources
Example of Renewable Resources
Moral guidance: Ancient texts and traditions emphasise acting for the well-being of all—lokasangraha (common good) is key.
In practice:
- Switch to sustainable energy (solar, wind).
- Recycle, minimise waste, and support responsible consumption.
|
31 videos|128 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts: Natural Resources and Their Use - Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. When does nature become a resource? |  |
| 2. What are the categories of natural resources? |  |
| 3. How does the distribution of natural resources impact societies? |  |
| 4. What is the ‘Natural Resource Curse’? |  |
| 5. What does responsible stewardship of natural resources entail? |  |
















