Human activities affect natural resources and ecosystems in many harmful ways. These actions disturb environmental balance, reduce biodiversity, and threaten future sustainability.
Cheatsheet: Natural Resources and Their Use | Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Introduction to Natural Resources
Everything we use (water, food, materials) comes from nature. These materials provided by nature become a resource only when humans know how to use it.
Examples:
Trees → Furniture
Water → Drinking, irrigation
When Does Nature Become a Resource?
Nature includes all living and non-living things found naturally. When humans extract or use these elements, they become resources.
Conditions for a Resource
For a natural thing to be classified as a resource, it must be accessible, affordable, and culturally accepted.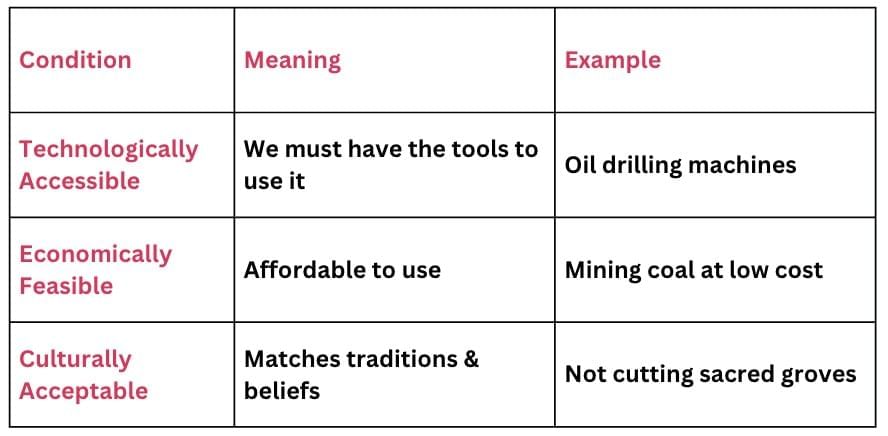
Some Important Natural Resources
Some resources are obvious and widely used; others are hidden and formed over millions of years.
Obvious Resources: Air, water, and soil — needed for breathing, drinking, and farming.
Less Obvious Resources: Coal, petroleum, precious stones, metal ores, and timber — used in energy, industry, and trade.
Exploitation: Using natural resources; can be fair (sustainable use) or unfair (overuse/wastage).
Categories of Natural Resources
Based on Use
- Natural resources are classified by how humans utilise them.
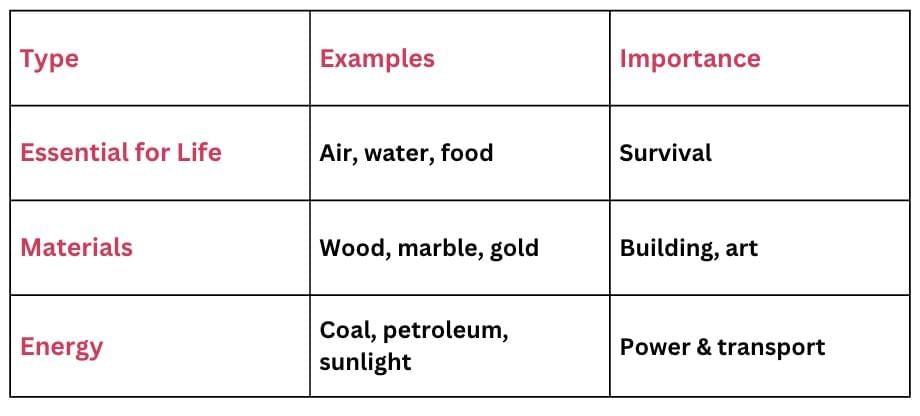
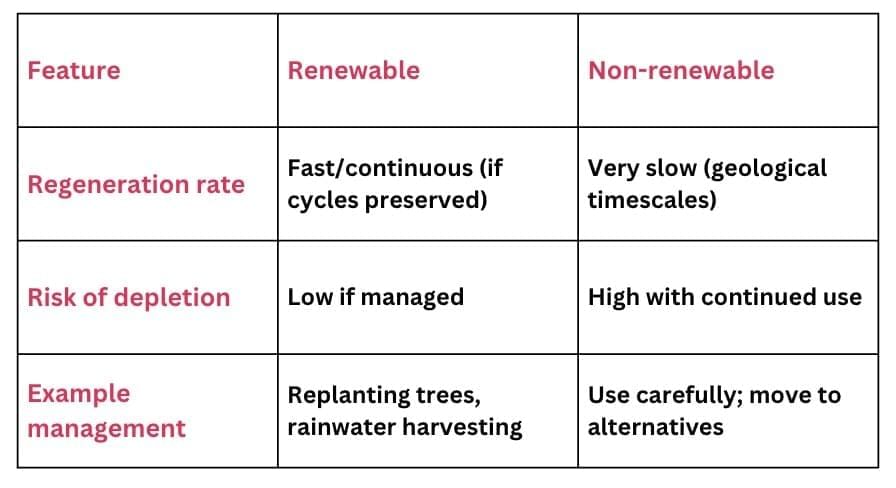
Based on Renewability
Natural resources are classified by whether they can be naturally replenished or not.
Renewable Resources → Can be replaced or regenerated naturally.
Examples: Air, water, soil, forests, sunlight, wildlife.Non-renewable Resources → Limited in supply; take millions of years to form.
Examples: Coal, petroleum, natural gas, metals, precious stones.
Let's explore the difference between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Nature’s Cycles
Restoration = healing (e.g., forests regrow after fire).
Regeneration = creating new life (fallen tree decomposes → enriches soil).
Balance disturbed by: deforestation, overfishing, overuse of fossil fuels.
Human Impact on Natural Resources and Environment

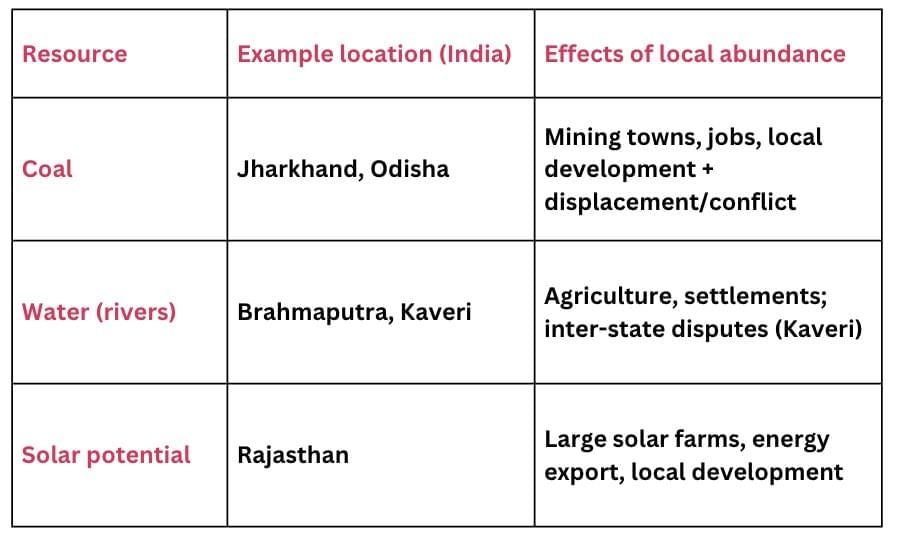
Distribution of resources — implications
Distribution of resources in India is uneven. Some states like Jharkhand and Odisha are rich in coal and minerals, while Punjab and Haryana have fertile soil, and southern states depend more on water and forests. This affects settlement, development, and sometimes causes disputes.
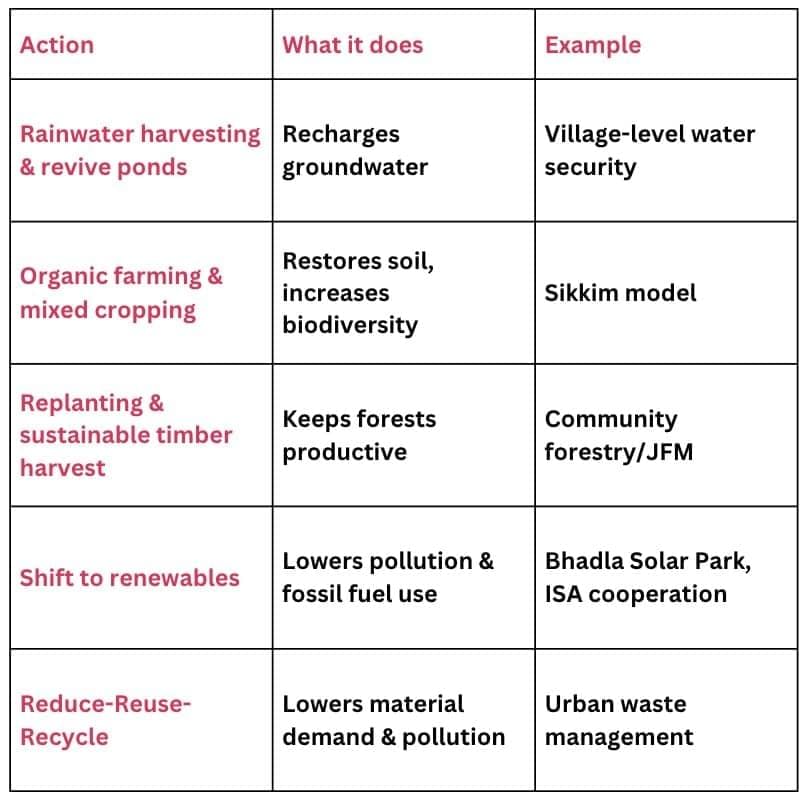
Stewardship: Actions → Benefits
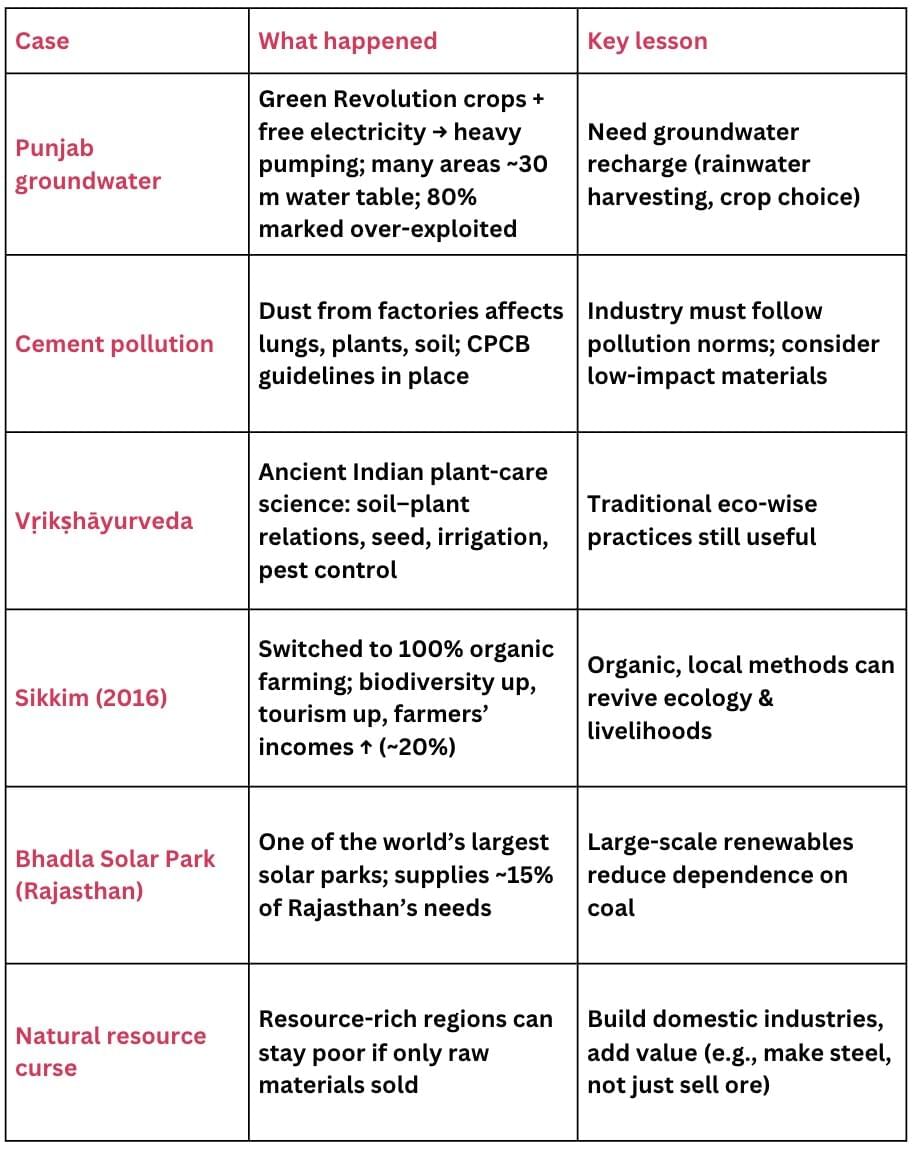
Case studies
|
31 videos|128 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Natural Resources and Their Use - Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What are natural resources and how do they differ from other types of resources? |  |
| 2. How does nature become a resource for human use? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of renewable and non-renewable resources? |  |
| 4. Why is the sustainable management of natural resources important? |  |
| 5. How do human activities impact natural resources and their availability? |  |





















