Cheatsheet: Reshaping India’s Political Map | Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Rise and Fall of the Delhi Sultanate |

|
| The Vijayanagara Empire |

|
| The Mughals |

|
| Resistance to the Mughals |

|
| Administering India |

|
| People’s Lives |

|
| Key Figures |

|
| Important Battles |

|
Introduction
The medieval period (roughly 11th–17th centuries) witnessed foreign invasions, the rise and fall of dynasties, shifting boundaries, and the evolution of society and economy.
Examples of change during this period:
- Delhi Sultanate → Introduced new governance, culture, and religion.
- Vijayanagara Empire → Strengthened southern India’s culture and power.
- Mughal Empire → Expanded and influenced art, administration, and society.
Rise and Fall of the Delhi Sultanate
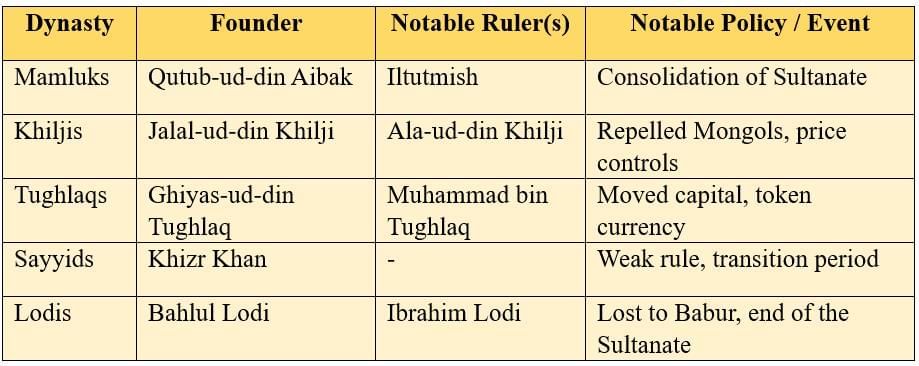
The Delhi Sultanate (1206–1526) was founded after the defeat of Prithviraj Chauhan. It saw five main Turkic-Afghan dynasties: the Mamluks (also known as the Slave Dynasty), the Khiljis, the Tughlaqs, the Sayyids, and the Lodis.
Resistance to the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate faced significant resistance from various regional kingdoms, internal rebellions, and external invasions throughout its rule, weakening it over time.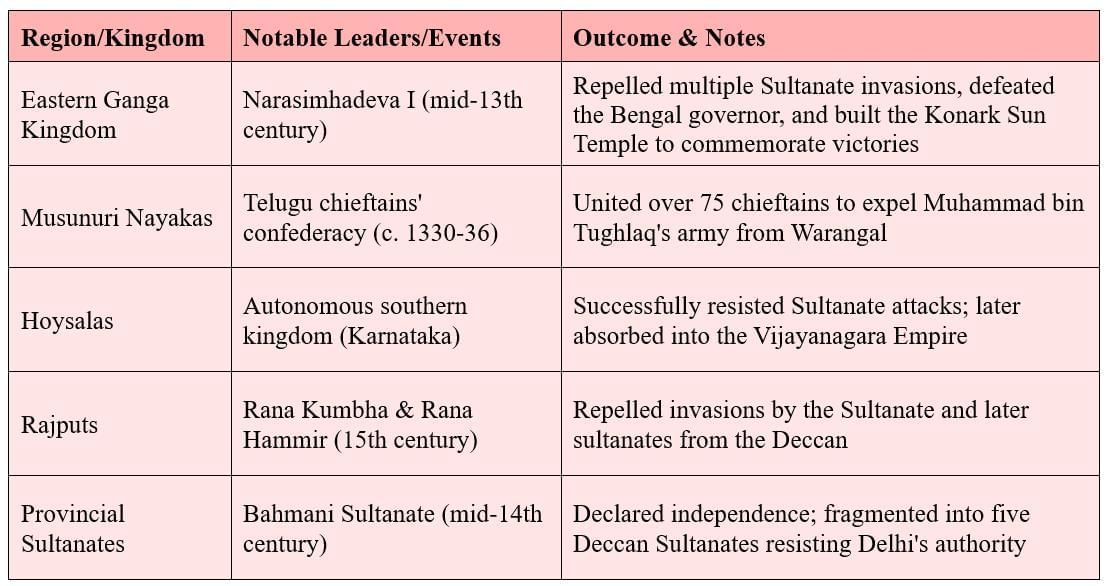
The Vijayanagara Empire
The Vijayanagara Empire emerged as a powerful Hindu kingdom in South India, established in 1336 by the brothers Harihara and Bukka.
- Rejected Delhi's authority, united many southern territories.
- Capital at Hampi (chosen for resilience and symbolism)
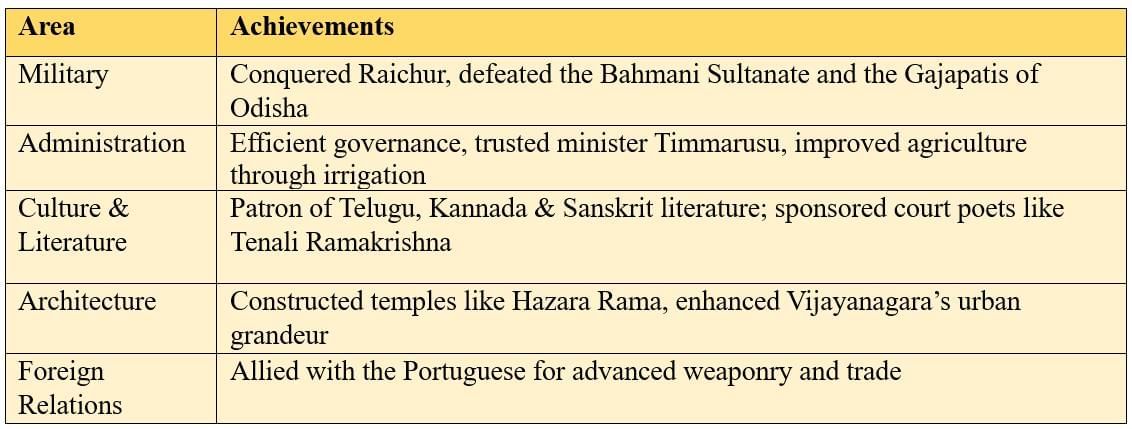
Krishnadevaraya
The Vijayanagra Empire was at its peak under Krishnadevaraya (reign: 1509–1529).
The Mughals
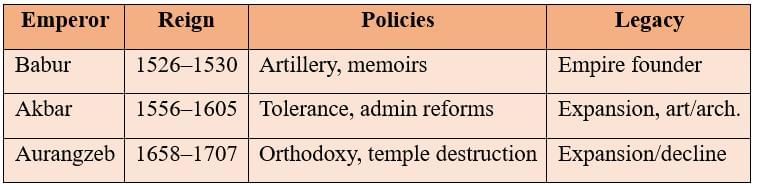
- The Mughal Empire was established in 1526 by Babur, who introduced gunpowder weaponry and artillery, defeating Ibrahim Lodi at the First Battle of Panipat.
- His son Humayun lost and regained the throne amid turmoil before his untimely death.
Akbar
Ruled from 1556–1605. Began at age 13; blended strategy, tolerance, and force.
Akbar’s Major Policies
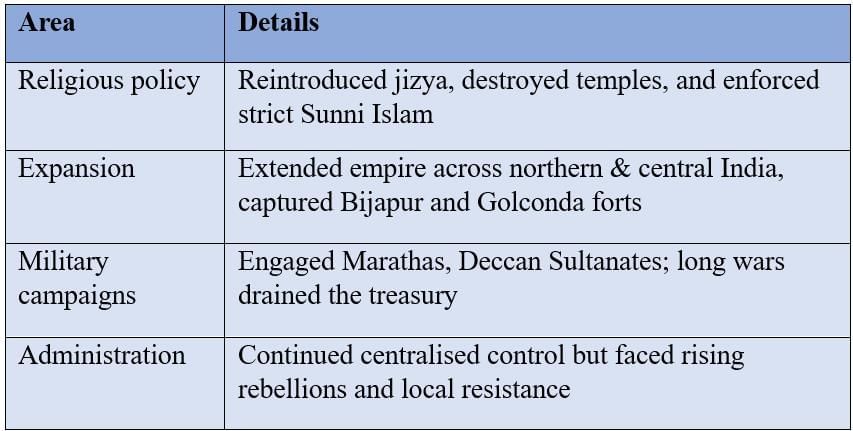
Aurangzeb
Ruled 1658–1707: Last strong emperor, expanded the empire to the greatest extent.
Aurangzeb’s Major Policies
Resistance to the Mughals
Mughal rule faced persistent challenges and local resistance.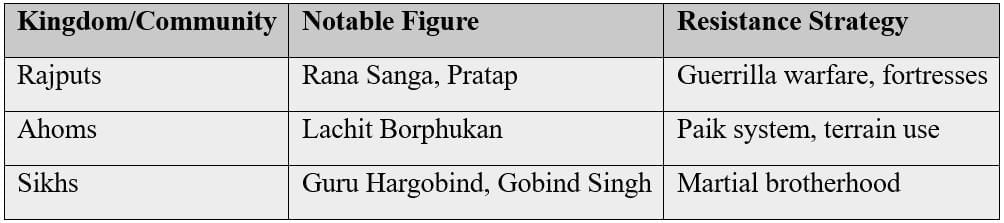
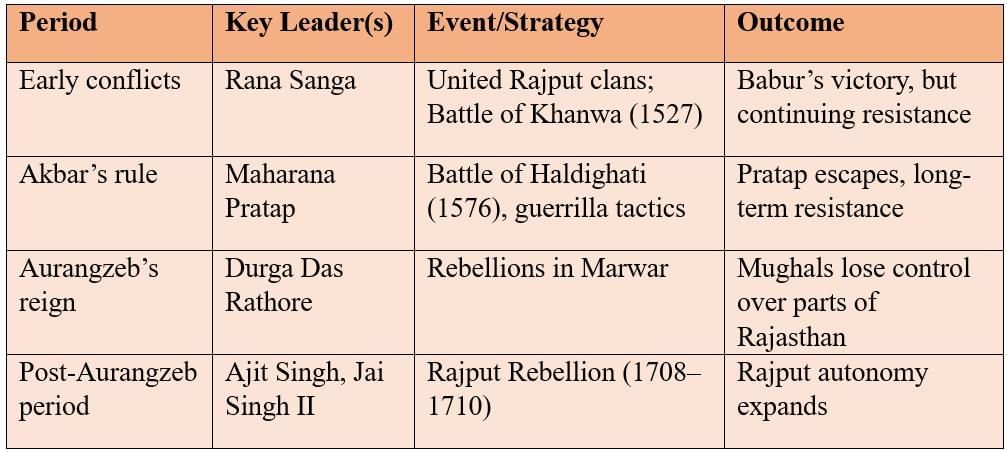
Surge of the Rajputs
- Mewar/Marwar leaders (Rana Sanga, Maharana Pratap): Consistent resistance; famous for guerrilla warfare after defeat at Haldighati (1576).
- Durga Das Rathore (Marwar): Rebelled against Aurangzeb, limited Mughal authority in Rajasthan.
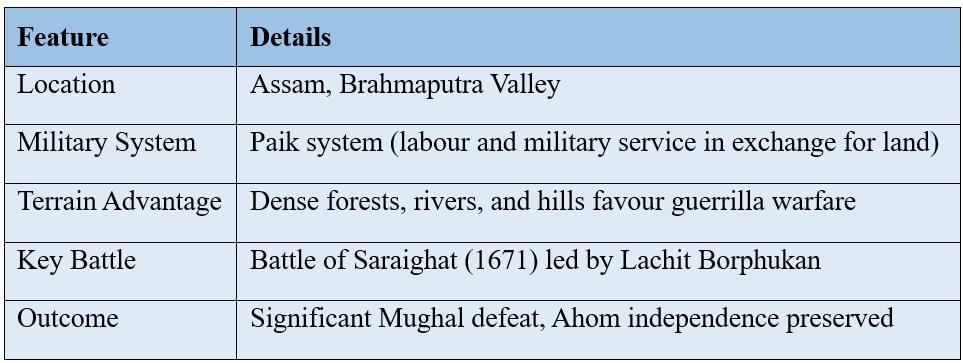
The Ahoms
Migrated from Myanmar (13th century), formed the Ahom Kingdom in Assam.
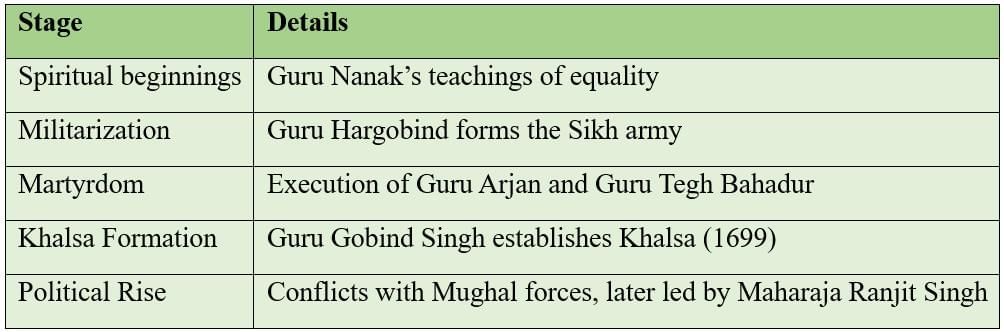
The Rise of the Sikhs
Administering India
Administration under the Delhi Sultanate
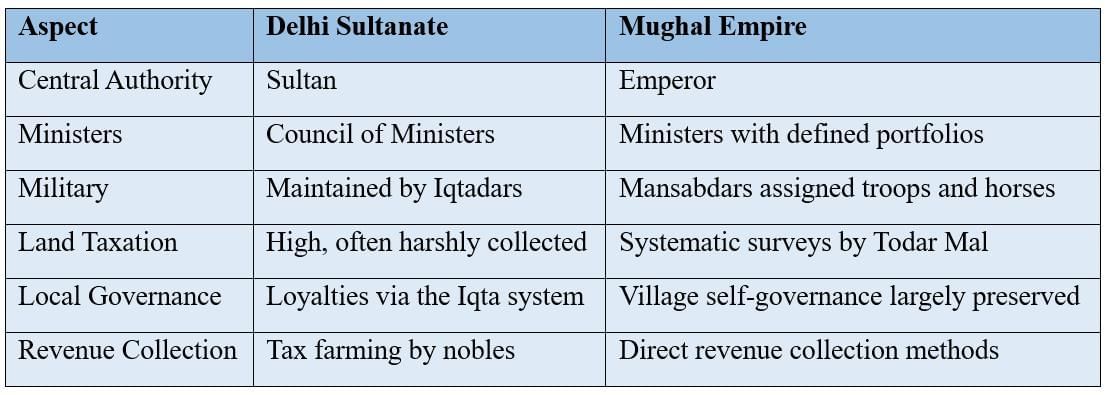
The Delhi Sultanate featured centralised authority with the Iqta system for military and revenue management.
Mughal Administrative Framework
The Mughals under Akbar introduced efficient reforms, including the Mansabdari system and provincial divisions.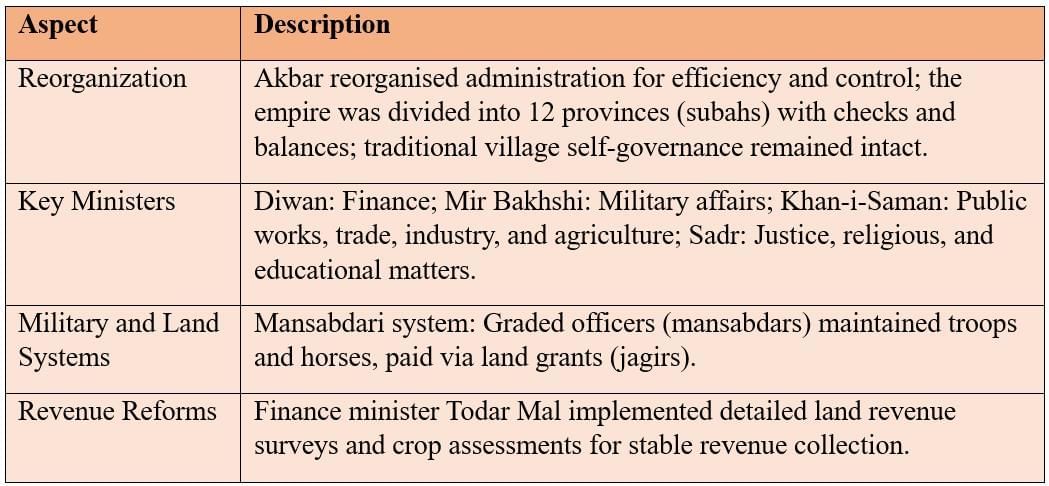
Let's explore how the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughal Empire were different:
People’s Lives
Economic activity was vibrant despite political instability.
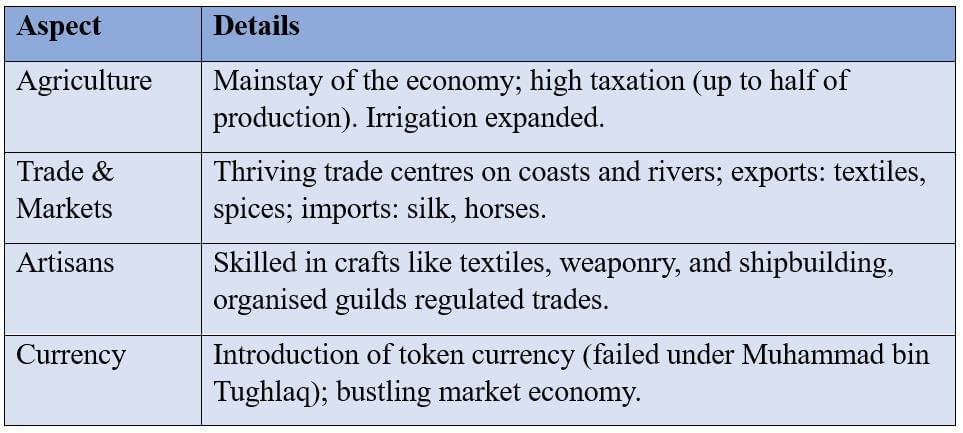
Social Hierarchy and Communities
Cultural Life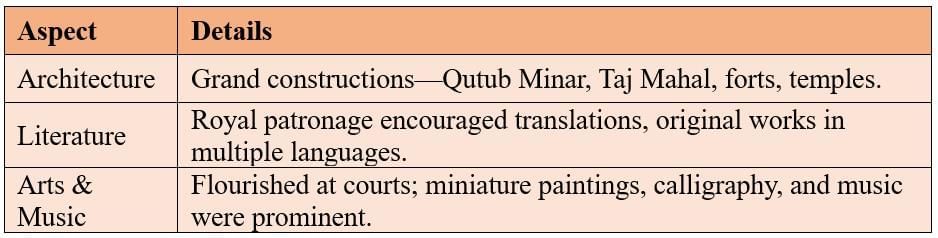
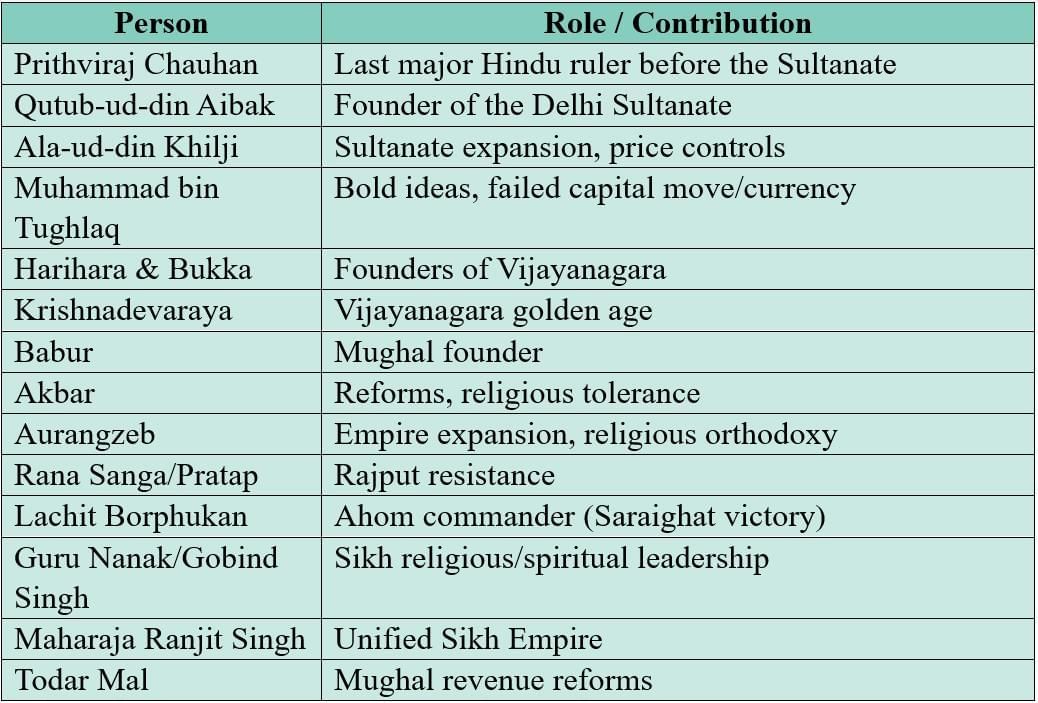
Key Figures
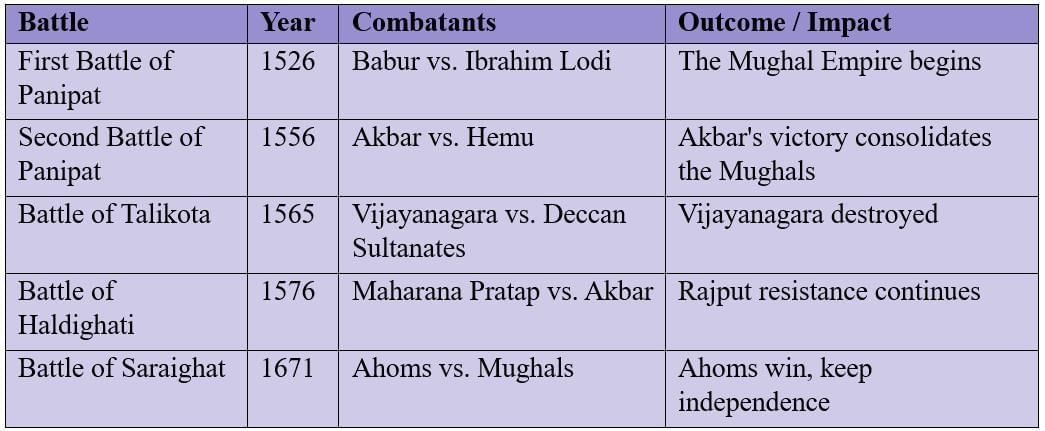
Important Battles
|
31 videos|128 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: Reshaping India’s Political Map - Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What were the key factors that led to the rise of the Delhi Sultanate? |  |
| 2. How did the Vijayanagara Empire contribute to the cultural landscape of India? |  |
| 3. What were the main strategies of resistance against Mughal rule in India? |  |
| 4. How did the Mughal Empire impact trade and economy in India? |  |
| 5. What were the consequences of the decline of the Delhi Sultanate? |  |















