Cheatsheet: The Colonial Era in India | Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT PDF Download
Introduction
British colonial rule in India lasted nearly two centuries, bringing major changes to the economy, politics, and society.
Key impacts included:
- Exploitation of resources and wealth
- Disruption of traditional ways of life and local governance
- Establishment of British administrative and legal systems
The Age of Colonialism
Colonialism began when powerful nations took control of weaker regions to gain wealth, power, and influence, often harming native people and traditions.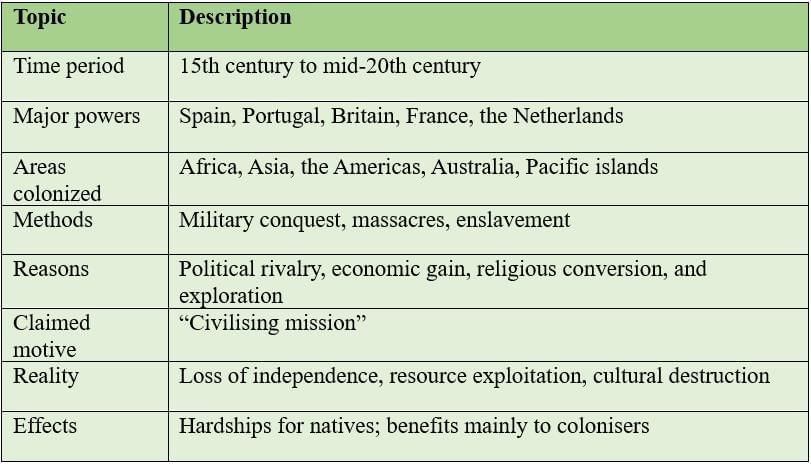
Europeans in India
European nations like the Portuguese, Dutch, and French came to India drawn by its wealth and trade. They established trading posts, which later became bases for colonial control.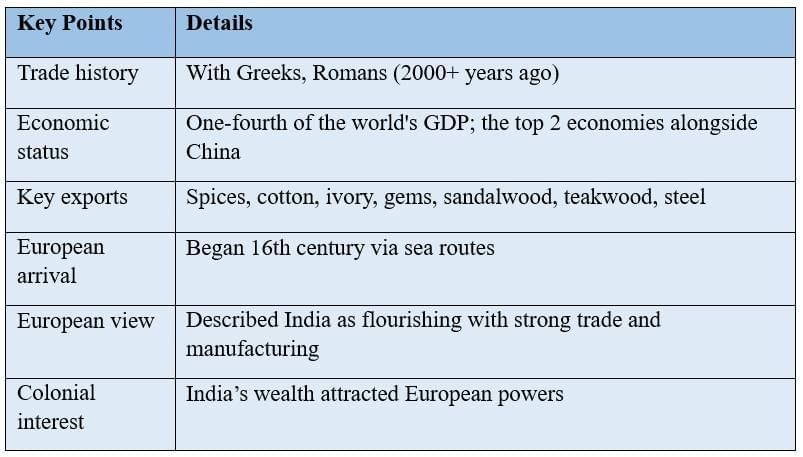
The Portuguese: Commerce and Atrocities
The Portuguese arrived first, establishing control over key ports, but they were known for aggressive actions and religious persecution.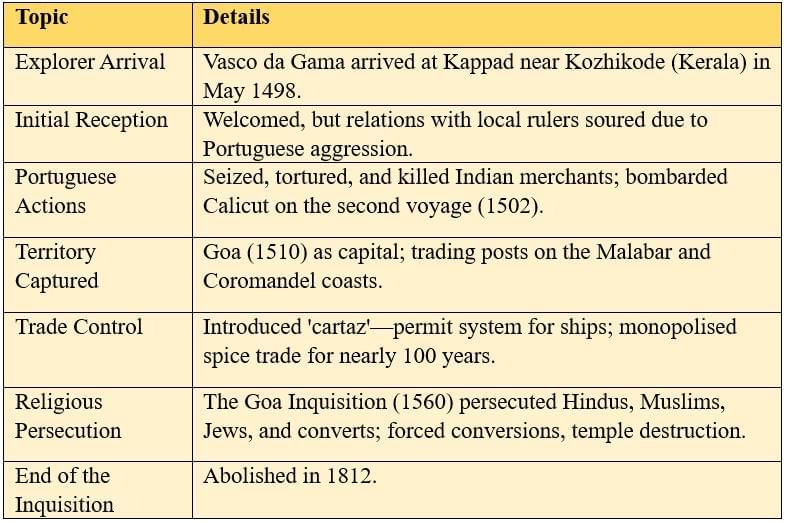
The Dutch: Commerce and Competition
The Dutch East India Company focused on the spice trade, setting up trading posts, but it declined after a key defeat.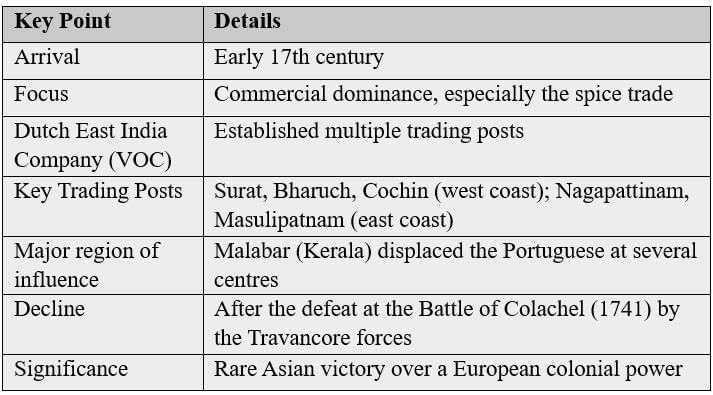
The French: Colonial Ambitions
The French established trading bases and sought an empire through military and political means, but with lesser social interference.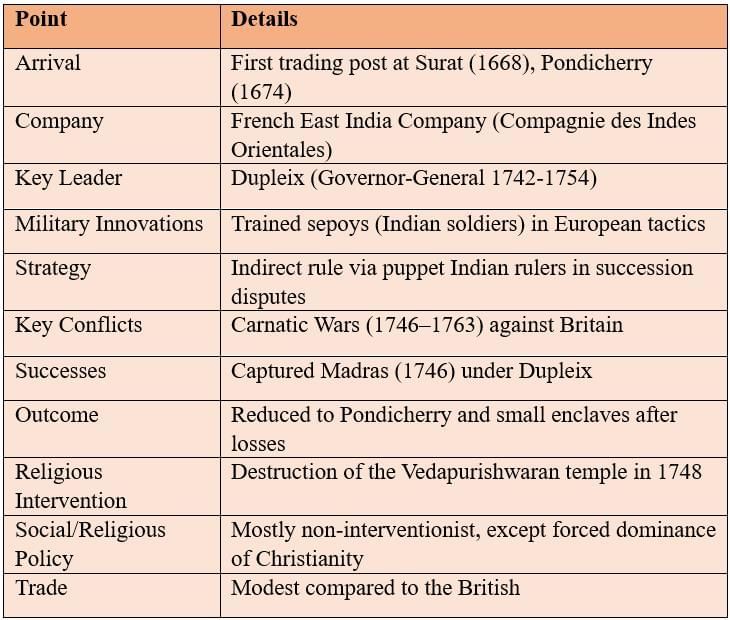
Enter the British
The British East India Company transitioned from trade to political dominance in India through strategic alliances and military power.
From Traders to Rulers
The East India Company, established with a royal charter, gradually built trading posts and private armies, gaining political control under the guise of trade.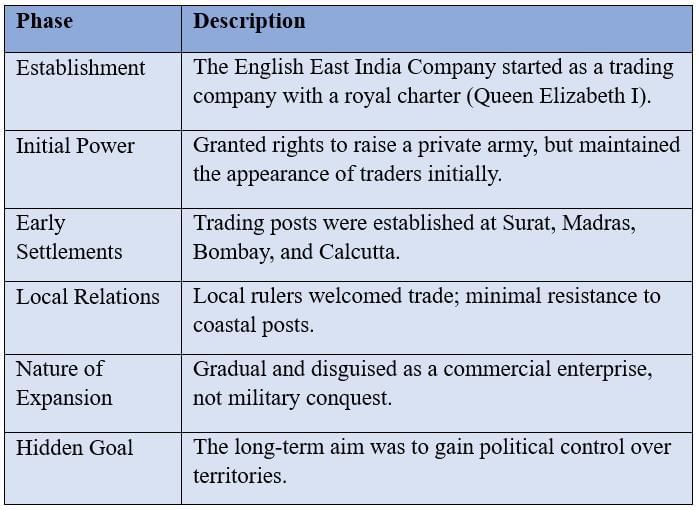
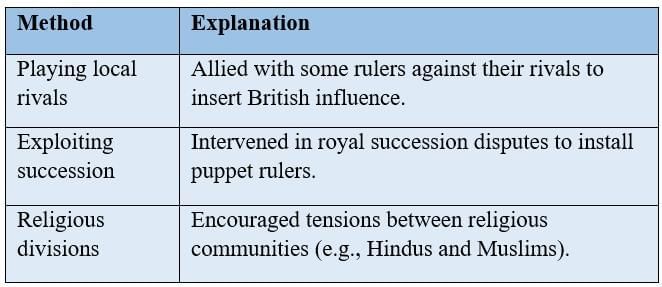
The Strategy of ‘Divide and Rule’
The British exploited divisions among Indian rulers and communities to maintain control, preventing unified resistance.
Political Manipulation
Example: Battle of Plassey (1757)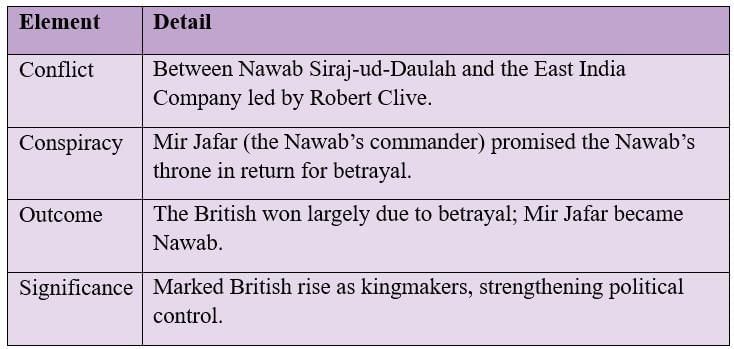
19th Century Policies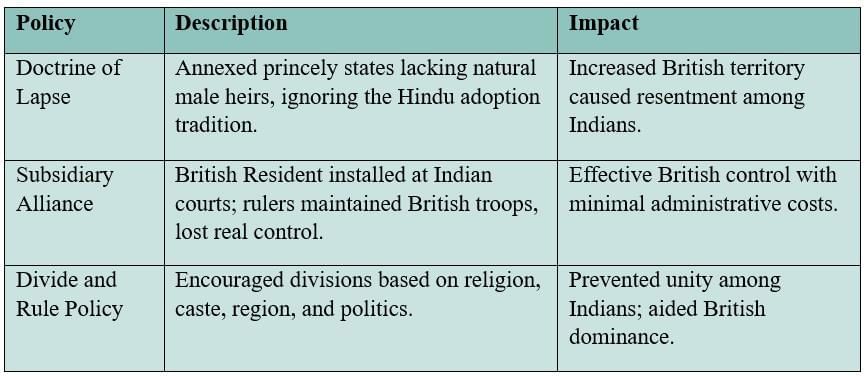
From Paradise to Hell?
British colonial policies led to devastating famines and massive economic drain, turning a prosperous India into a land of widespread poverty and suffering.
Devastating Famines
Excessive taxation, lack of relief, and British policies worsened famines, causing millions of deaths.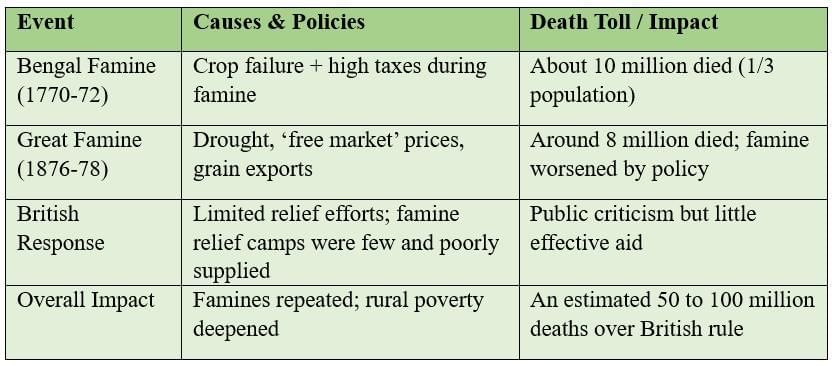
The Drain of India’s Wealth
Economic exploitation enriched Britain at India’s expense, undermining India’s development.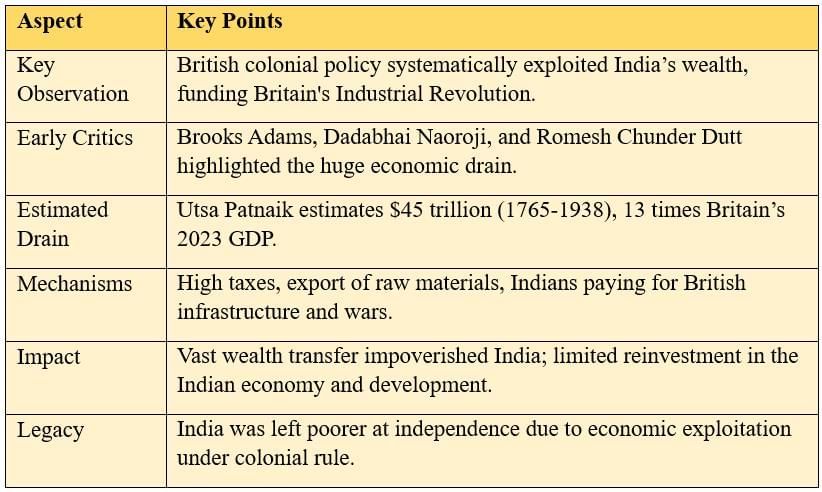
Changing Landscapes
British rule reshaped India’s industries, governance, education, and economy to serve imperial interests, disrupting traditional systems.
Decline of India’s Indigenous Industries
India’s skilled textile and other manufacturing sectors collapsed due to British economic policies favouring imports.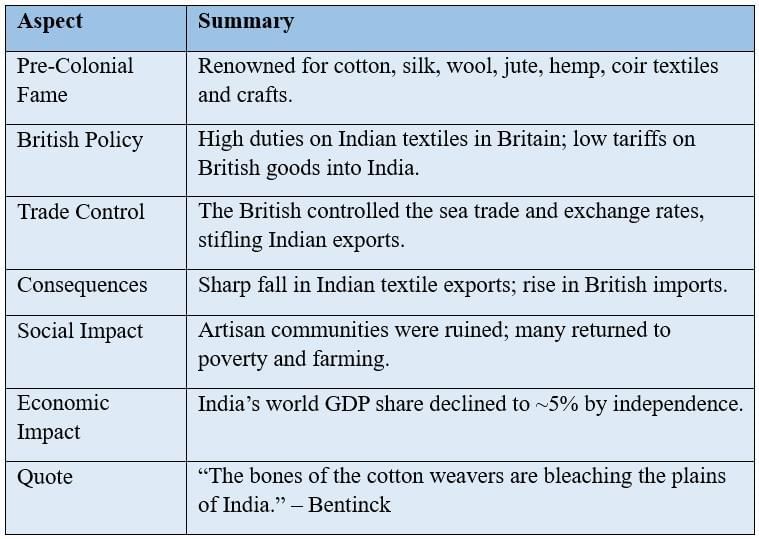
Dismantling Traditional Governance Structures
The British replaced vibrant local governance systems with centralised bureaucracy focused on revenue and control.

Transforming Indian Education – Creating ‘Brown Englishmen’
British education aimed to create a class loyal to colonial rule, promoting English and European values over Indian traditions.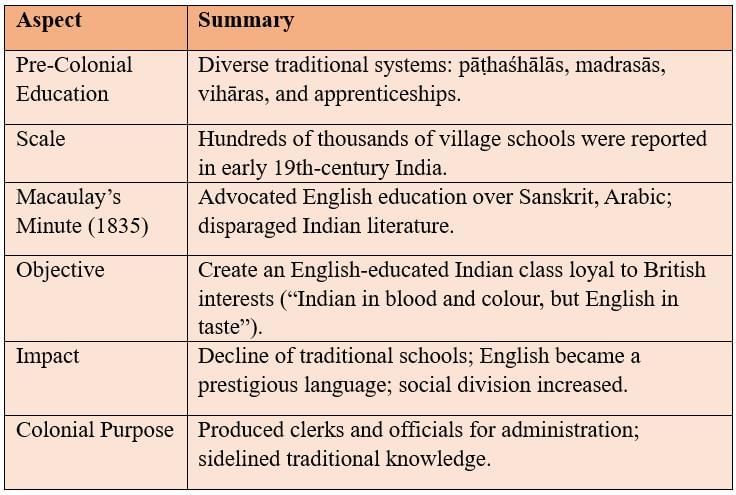
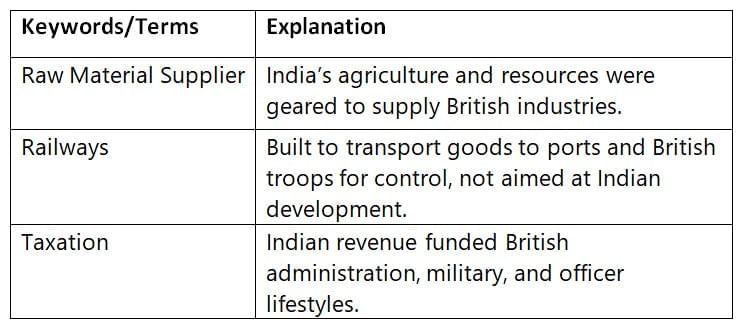
Reshaping Economic Structures to Serve Imperial Needs
India’s economy was restructured to provide raw materials and serve as a market for British goods.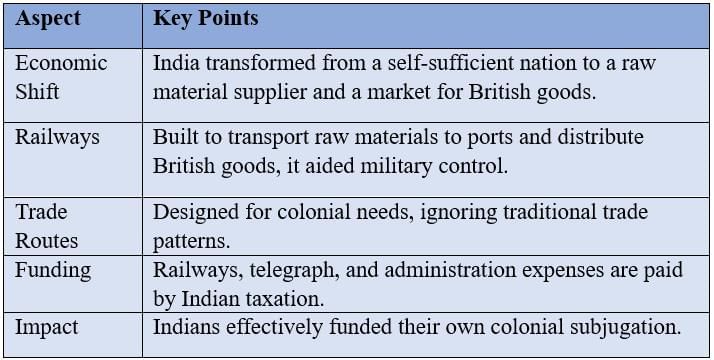
Early Resistance Movements: Challenging Colonial Authority
From the onset of British rule, Indians resisted colonial control through religious rebellions, tribal uprisings, and peasant revolts.
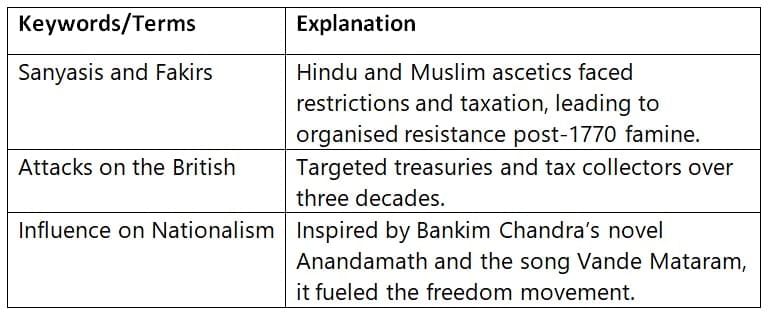
The Sanyasi-Fakir Rebellion
Religious ascetics in Bengal resisted British tax policies and restrictions on pilgrimage during tough economic times.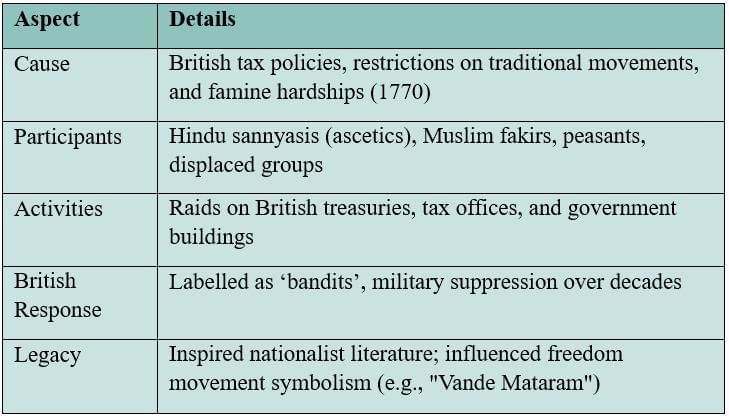
Tribal Uprisings
Indigenous tribes revolted against British land seizures, forest restrictions, taxes, and cultural suppression.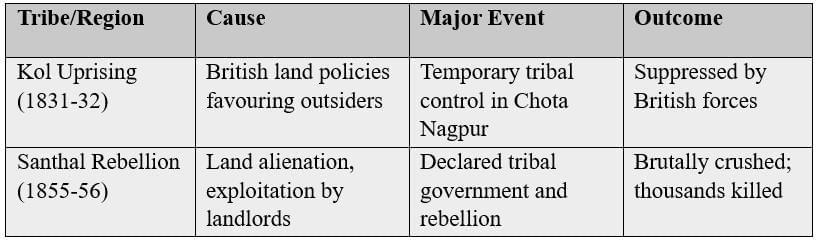

Peasant Uprisings Against Economic Exploitation
Peasants protested unfair taxation, forced cultivation, and exploitation by landlords and European planters.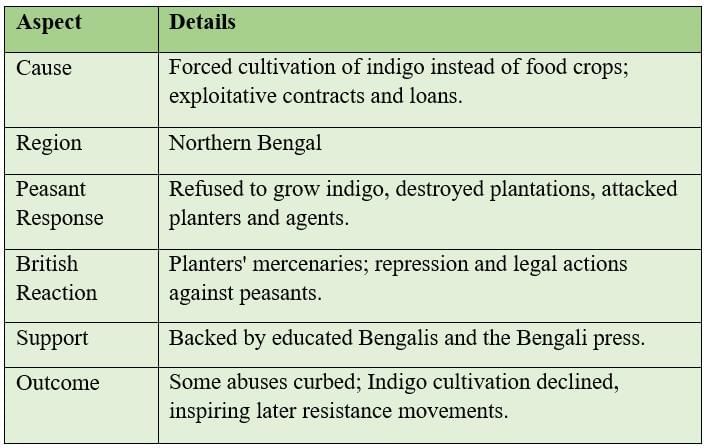
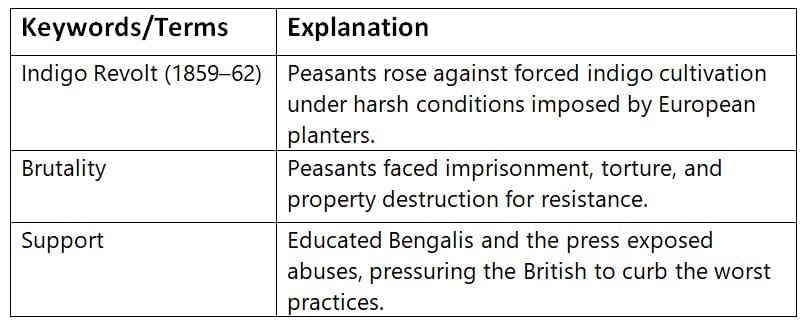
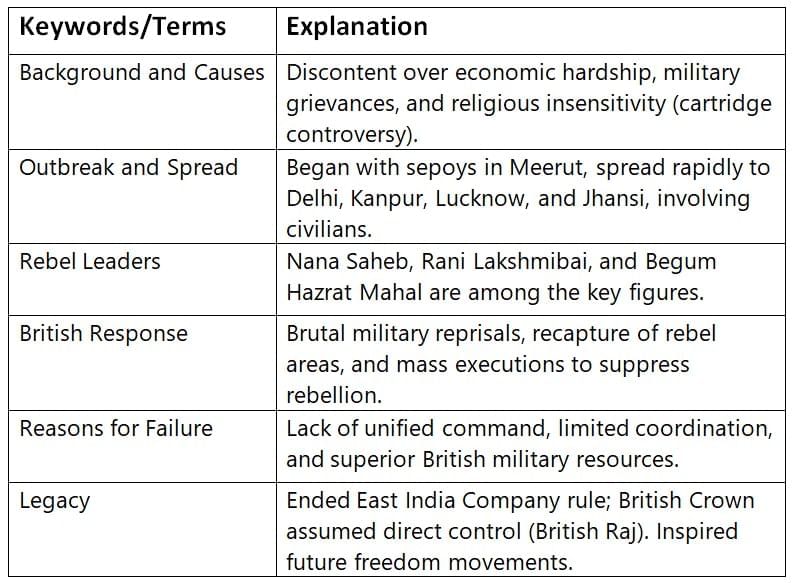
The Great Rebellion of 1857
A massive uprising of soldiers and civilians that challenged British rule and marked a turning point in Indian history.
Causes of the Rebellion

Key Events & Leaders
British Response
Outcomes & Impact
The Legacy of European Colonialism in India
European colonialism, predominantly British, systematically exploited India’s resources and people, but also facilitated cultural exchanges and historical documentation.
Colonial Exploitation and Repression
Cultural Documentation and Loss
Cultural Exchange and Influence
|
31 videos|128 docs|7 tests
|
FAQs on Cheatsheet: The Colonial Era in India - Social Science Class 8 - New NCERT
| 1. What were the major reasons for British colonization in India? |  |
| 2. How did the British impact Indian society and culture? |  |
| 3. What were the key events leading up to the Great Rebellion of 1857? |  |
| 4. What were the consequences of the Great Rebellion of 1857 for India and British rule? |  |
| 5. How did early resistance movements challenge colonial authority in India? |  |





















