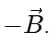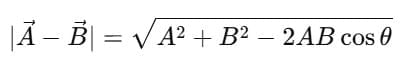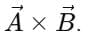Mnemonics: Vectors | Physics for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
MNEMONICS are powerful tools to simplify complex concepts in Vectors and make learning easier.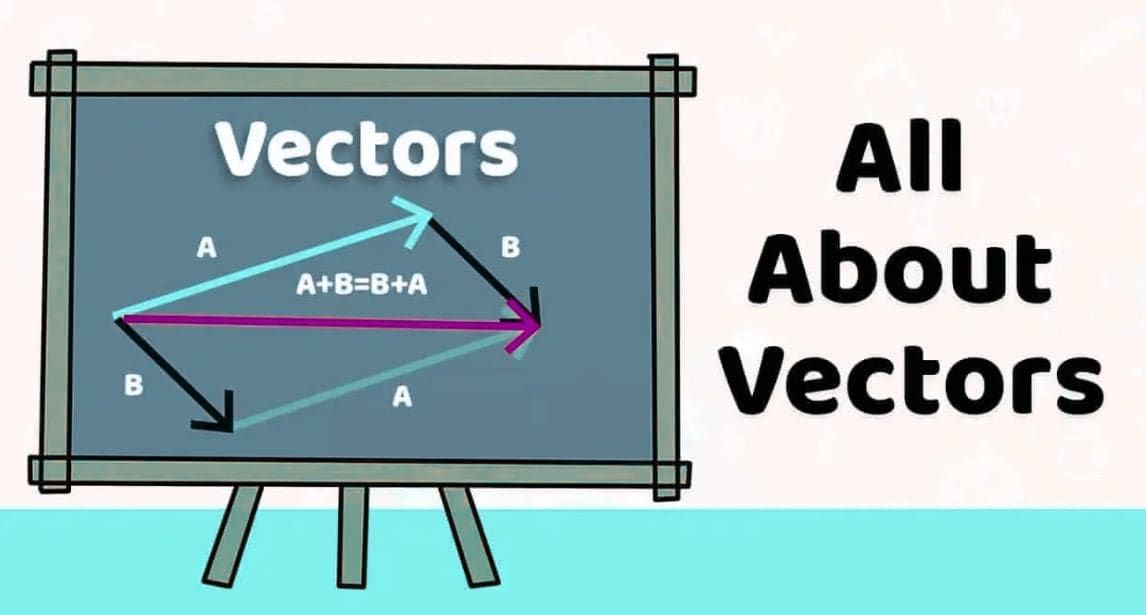
This EduRev document provides creative and concise mnemonics that help students quickly grasp, recall, and apply the core ideas of vectors. From the basics of scalars and vectors to advanced topics like dot product, cross product, and triple products, these memory aids make revision faster and problem-solving more efficient.
1. Scalars and Vectors
Mnemonic: "Some Values Need Direction!"
Explanation:
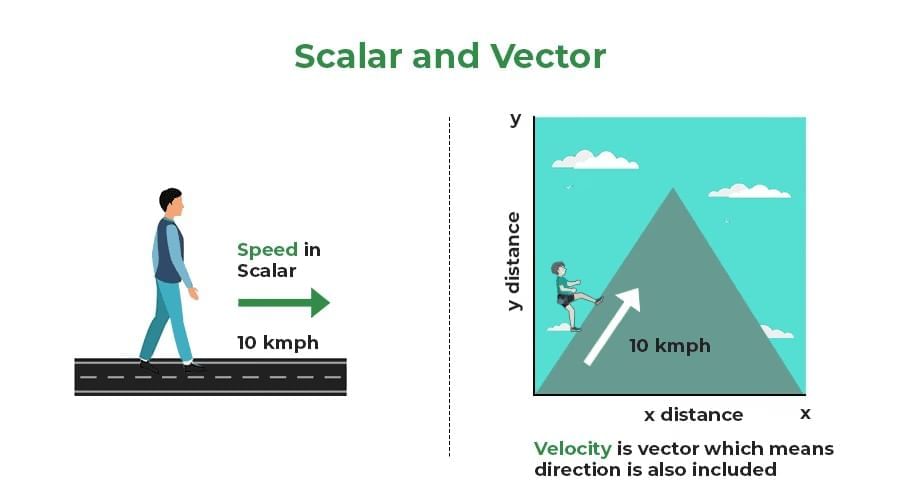
Scalars: Represent "Some Values"
- Scalars are quantities that only have magnitude (size) but no direction.
- Examples: Speed, Distance, Mass, Energy, Time, etc.
- They add algebraically.
Vectors: Represent "Need Direction"
- Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.
- Examples: Velocity, Displacement, Force, Acceleration, etc.
- They require vector rules (head-to-tail, components).
NOTE: If direction matters or negative answers can mean “opposite direction,” you’re likely dealing with a vector. Units don’t decide vector/scalar; directionality does.
2. Representation of a Vector
Mnemonic: “Arrow Marks Way.”
Explanation:
- Arrow → Drawn as a directed line segment
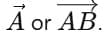
- Marks → Magnitude: The longer the arrow, the greater the magnitude.
- Way → Direction: The arrow-head shows the direction in which the vector acts.
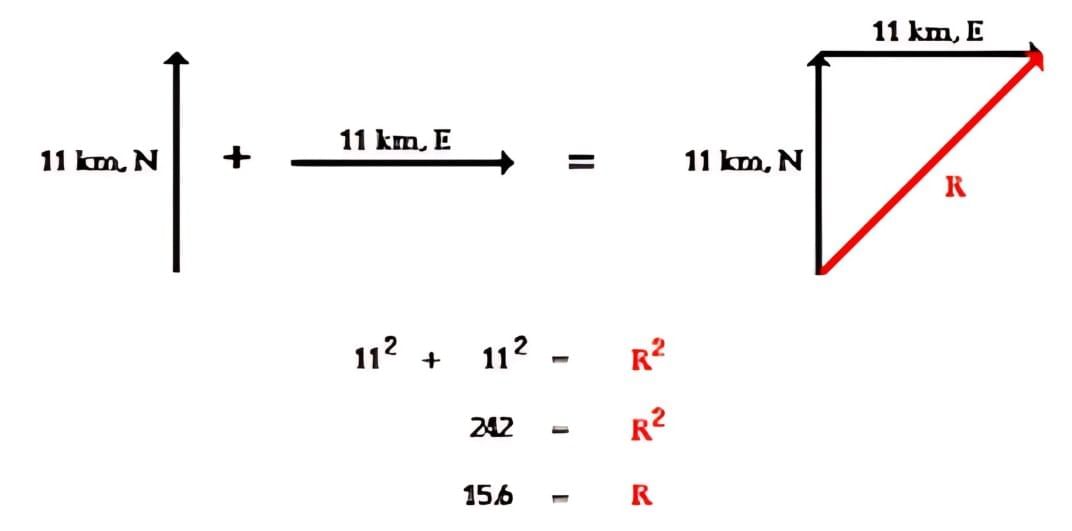
3. Addition of Vectors
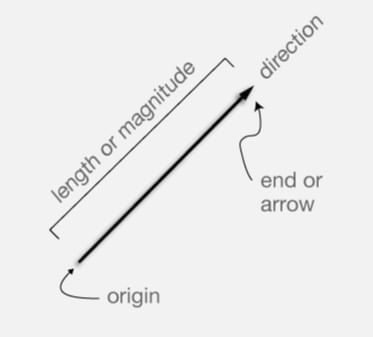
Mnemonic: "Tail-Head Adds Right!"
Explanation:
This mnemonic simplifies the process of vector addition using the head-to-tail rule:
"Tail-Head"
- When adding vectors, place the tail of the second vector at the head of the first vector.
- This method ensures that vectors are connected in a sequence.
"Adds Right"
- The resultant vector is drawn from the tail of the first vector to the head of the last vector.
- This resultant represents the combined effect of the vectors being added.
Without knowing vector addition, one cannot solve the numericals that frequently appear in exams.
For Example -
4. Vector Subtraction
Mnemonic: “Add the Negative”
Explanation:
- To subtract one vector from another, you don’t really “subtract” in the normal sense.
- Instead, you reverse the direction of the vector you want to subtract (make it negative) and then perform normal vector addition.
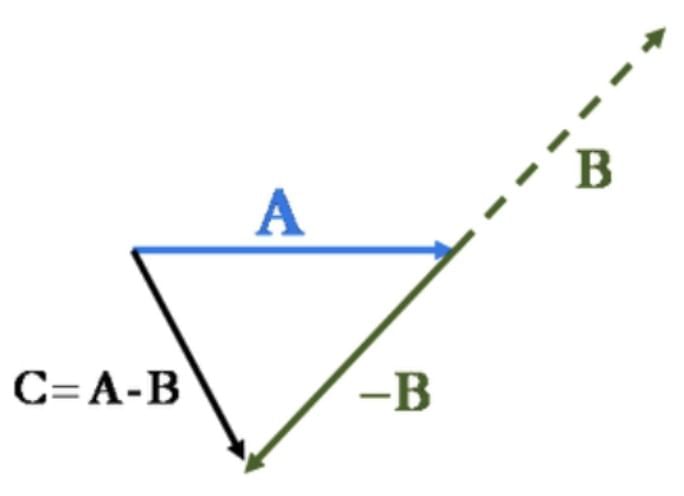
Step 1: Reverse the second vector.
- If you want
, replace
with
has the same magnitude as
but points in the opposite direction.
Step 2: Add the two vectors.
Now do
using the head-to-tail rule.
Magnitude Formula:
5. Dot Product (Scalar Product)
Mnemonic: “Dot loves COS"
Explanation:
Dot → Dot Product
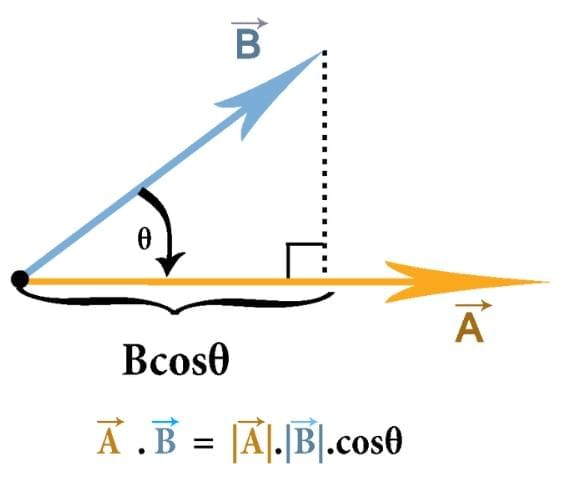
- Dot product of two vectors is:
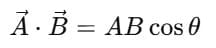 , where A and B are magnitudes, and θ is the angle between them.
, where A and B are magnitudes, and θ is the angle between them.
Loves COS → Projection Meaning
- The dot product measures the projection of one vector onto another.
- Example:
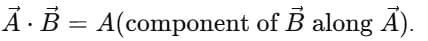
- That’s why “cos” appears — it picks the part of one vector along the other.
Scalar Result → No Direction
- The result of a dot product is a scalar (just a number).
- It has no direction, only magnitude (positive, negative, or zero).
6. Cross Product (Vector Product)
Mnemonic: “Cross Loves sin”
Explanation:
Cross → Cross Product
- The cross product of two vectors is defined as:
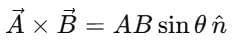 , where A and B are magnitudes, θ is the angle between them, and
, where A and B are magnitudes, θ is the angle between them, and 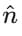 is a unit vector perpendicular to the plane of
is a unit vector perpendicular to the plane of 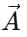 and
and 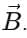
Loves Sin → Sinθ (Perpendicular Meaning)
- The value depends on sinθ, which measures the part of one vector perpendicular to the other.
- That’s why cross product is linked with “rotation” and “area.”
- Maximum when θ=90∘ (completely perpendicular).
- Zero when vectors are parallel or anti-parallel (sin0∘= 0).
Vector Result → Direction
- The result of a cross product is a vector, not a number.
- Its direction is given by the Right-Hand Rule: curl your fingers from
thumb points along
7. Vector Triple Product
Mnemonic: “BAC–CAB Rule.”
Explanation:
Formula: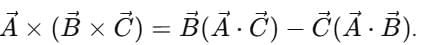 Why BAC–CAB?
Why BAC–CAB?
- The letters inside the brackets
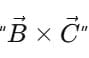 are rearranged in the result as BAC – CAB.
are rearranged in the result as BAC – CAB. - That’s why the name is easy to remember: BAC–CAB Rule.
Properties:
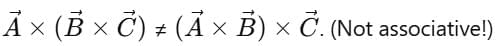
Result is always a vector lying in the plane of

The unit normal
 cancels out during expansion.
cancels out during expansion.
|
320 videos|1028 docs|210 tests
|
FAQs on Mnemonics: Vectors - Physics for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What are the basic differences between scalars and vectors? |  |
| 2. How can a vector be represented graphically? |  |
| 3. What is the method to add two vectors? |  |
| 4. How is vector subtraction performed? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of the dot product in vector analysis? |  |