Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th September 2025) | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
Emerging Science Innovation Conclave Replaces Indian Science Congress
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Department of Science and Technology (DST) is set to organize the inaugural Emerging Science, Technology and Innovation Conclave (ESTIC) in November 2025, marking a significant transformation in India's scientific gatherings.
Key Takeaways
- The ESTIC aims to replace the Indian Science Congress (ISC), which has lost relevance in recent years.
- This conclave will gather prominent scientists and innovators from India and globally to discuss advanced research.
- Traditionally, the ISC was held annually in January and was a major event attended by the Prime Minister and Nobel Laureates.
Additional Details
- Indian Science Congress: Established before India's independence, it was the oldest scientific congregation in the country. However, it faced challenges, including cancellations in 2021 and 2022 due to the pandemic and disagreements leading to its cancellation in 2024 and 2025.
- India International Science Festival (IISF): Since 2015, supported by the government, this festival promotes science among students and youth but lacks the high-profile participation seen in the ISC.
- ESTIC Venue and Schedule: The conclave will be held at Bharat Mandapam from November 3 to 4, 2025, featuring thematic sessions and exhibitions from deep-tech start-ups.
- Notable Participants: Esteemed figures such as Nobel Laureate Andre Geim and former French Space Agency head Jean-Yves Le Gall are expected to attend.
The introduction of ESTIC is envisioned as a modern replacement for the ISC, aimed at showcasing India's leadership in science and innovation. According to Science Minister Jitendra Singh, the conclave seeks to ignite a new era of scientific leadership, aligned with the goal of achieving Viksit Bharat by 2047.
India Launches Hydrogen-Powered Train
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Indian Railways has successfully conducted tests on a hydrogen-powered train, developed at the Integral Coach Factory in Chennai. This innovative train is set to operate between Jind and Sonipat in Haryana as part of the National Green Hydrogen Mission, which aims to produce five million metric tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030, contributing to India's goal of achieving net zero emissions by 2070.
Key Takeaways
- The hydrogen-powered train will enhance sustainable transport in India.
- It is equipped with hydrogen fuel cells that generate electricity with zero carbon emissions.
- India aims to become the fifth country to deploy hydrogen-powered trains.
Additional Details
- Hydrogen Train Technology: The train operates on hydrogen fuel cells that convert hydrogen into electricity. The hydrogen is produced using a 1-MW polymer electrolyte membrane electrolyser, which splits water into hydrogen and oxygen using renewable electricity.
- Electrolyser and Fuel Cell Mechanism: Electrolysers split water into hydrogen and oxygen. In fuel cells, hydrogen is converted back into water, generating electricity to power the train. This process emits no carbon dioxide.
- Green Hydrogen Production: The production of green hydrogen utilizes renewable energy sources, ensuring zero carbon emissions. India plans to enhance its renewable energy capacity to meet its green hydrogen targets.
- Cost and Material Challenges: Current catalysts for electrolysers and fuel cells are expensive (like platinum). Research is focused on finding cheaper alternatives such as nickel and iron, with promising results from Indian scientists on nickel-based electrodes.
- Significance and Future Prospects: The new hydrogen-powered train can carry 2,638 passengers and reach speeds of 110 km/h, powered by a 1,200 HP engine. The government has allocated Rs 2,800 crore to develop 35 hydrogen trains by 2024-25, marking a significant step towards sustainable transportation and India’s zero-carbon emissions target.
This initiative not only represents a technological advancement in the Indian railways but also aligns with global efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources.
Arunachal Pradesh Hosts Inaugural Sunrise Festival
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The northeastern state of Arunachal Pradesh is preparing to launch its first-ever Sunrise Festival in Dong village, Anjaw district. Scheduled from 29 December 2025 to 2 January 2026, the festival aims to celebrate the unique geographical significance of Dong, which is recognized as the easternmost village in India, capturing the first rays of sunlight each day. The event is designed to bolster tourism, promote adventure, and preserve the cultural heritage of this remote border area.
Key Takeaways
- The Sunrise Festival will be held from 29 December 2025 to 2 January 2026.
- Dong village, located at 1,240 meters above sea level, is known for its stunning sunrise views.
- The festival aims to attract tourists and promote the region's cultural and adventure tourism.
Additional Details
- Location: Dong is situated near the tri-junction of India, China, and Myanmar, making it the first place in India to see sunrise.
- The festival will feature ethnic cuisine, adventure sports, and eco-tourism activities, showcasing the local tribal culture and traditions.
- Tourism Promotion: Chief Minister Pema Khandu announced the festival to enhance tourism and create new economic opportunities in Arunachal Pradesh.
- Improved air and road connectivity through the UDAN scheme is expected to increase tourist inflow to Dong.
- Strategic Importance: Dong's proximity to international borders enhances its strategic value, supporting tourism and security initiatives.
This inaugural festival not only highlights the natural beauty of Arunachal Pradesh but also positions it as a significant destination for cultural and eco-tourism, fostering local entrepreneurship and community engagement in the region.
MQ-28A Ghost Bat Military Drones
 Why in News?
Why in News?
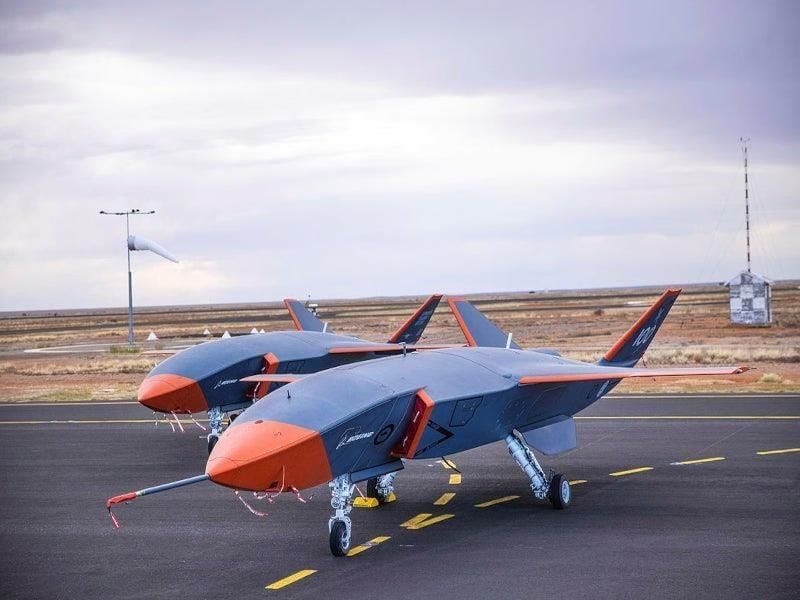
Australia has made significant advancements in military technology with the development of the MQ-28A Ghost Bat, a next-generation drone aimed at enhancing its defense capabilities in response to regional threats.
Key Takeaways
- The MQ-28A Ghost Bat is designed as a collaborative combat aircraft that works alongside manned fighter jets.
- This project marks Australia's first major development of an indigenous combat aircraft in over 50 years.
Additional Details
- Background: Australia has historically depended on the United States for military hardware. Rising tensions in the Indo-Pacific region and the modernization of China's military have pushed Australia towards developing its own defense capabilities.
- Design and Capabilities: The Ghost Bat is 38 feet long and functions as a robotic wingman for manned jets. It can autonomously conduct missions but also allows for remote piloting. With a range of approximately 2,300 miles, it offers significant operational flexibility and is cost-effective compared to traditional fighters like the F-35.
- Production and Industrial Impact: Boeing is leading the production, with 70% of components manufactured in Australia, revitalizing the local defense industry.
- Implications: The introduction of such drones signals a shift in global military dynamics, with Australia enhancing its strategic autonomy while maintaining alliances, particularly under agreements like AUKUS.
- Future Prospects: With an investment of around $650 million, Australia is committed to modernizing its defense forces, though sustaining production and maintaining technological superiority pose challenges.
The development of the MQ-28A Ghost Bat not only strengthens Australia’s military capabilities but also plays a crucial role in its strategic positioning within the increasingly competitive Indo-Pacific landscape.
Supreme Court Allows Aadhaar for Voter Identity Verification
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India has recently mandated the Election Commission of India (EC) to accept Aadhaar as an additional document for identity verification during the Special Intensive Revision (SIR) of electoral rolls in Bihar. This decision aims to promote inclusivity in voter registration ahead of the upcoming Assembly elections.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court ruled that Aadhaar can be used for identity verification, though it is not proof of citizenship.
- The EC must ensure the authenticity of Aadhaar cards, similar to other accepted documents.
- This inclusion addresses concerns over disenfranchisement due to strict document requirements.
Additional Details
- Context: The court's decision was influenced by concerns regarding voter disenfranchisement caused by the limited number of documents previously accepted (11). The inclusion of Aadhaar is intended to prevent genuine voters from being excluded.
- Legal Status of Aadhaar: While Aadhaar is recognized under the Aadhaar Act, 2016, it does not serve as proof of citizenship. The Representation of the People Act, 1950, permits Aadhaar as a document for identity verification but not for citizenship confirmation.
- Role of the Election Commission: The EC is tasked with finalizing electoral rolls and can verify the authenticity of Aadhaar cards. It must update its guidelines to include Aadhaar as a valid form of identity during the Bihar SIR.
- Implications for Voter Inclusion: The addition of Aadhaar is expected to decrease voter exclusion, particularly for individuals lacking traditional documents. Although a significant majority of Bihar's voters have submitted the required documents, Aadhaar provides an alternative option.
- Documents Accepted for Electoral Roll Revision: The EC's list includes various documents such as birth certificates, passports, government-issued identity cards, and now Aadhaar for identity verification.
- Ongoing Challenges: Despite the Supreme Court's directive, some Booth Level Officers (BLOs) continue to reject Aadhaar, resulting in legal disputes and notices. The court plans further hearings to ensure compliance and address petitions for nationwide Special Intensive Revisions.
This ruling represents a significant step towards enhancing voter inclusivity in Bihar, while also highlighting the ongoing challenges related to document verification and potential fraud prevention.
Giant African Snail Invasion
Why in News?
The recent detection of the Giant African Snail (Lissachatina fulica) in Chennai and its surrounding areas has raised significant concerns regarding public health and ecological stability. This species is recognized as one of the most invasive in the world, posing risks due to its ability to carry parasites that can lead to severe illnesses in humans. The situation is exacerbated by the flooding during the monsoon season, which facilitates the spread of these snails throughout the city.
Key Takeaways
- The Giant African Snail has been confirmed in various locations in Chennai.
- It poses serious health risks due to its role as a vector for harmful parasites.
- Its impact on agriculture and local ecosystems can be severe.
- The species has a long history of spreading globally, initially introduced in India in 1847.
Additional Details
- Health Risks: The Giant African Snail is known to carry parasites such as Angiostrongylus cantonensis and Angiostrongylus costaricensis, which can cause serious conditions like eosinophilic meningoencephalitis and abdominal angiostrongyliasis. These infections generally occur through the consumption of contaminated snails or their residues.
- Ecological Impact: This snail feeds on over 500 different plant species, leading to significant agricultural damage and competition with native species. Its adaptability to various environments makes controlling its population particularly challenging.
- Global Distribution: Originally from East Africa, this species has proliferated in several Indian states and across many countries in Asia, Africa, and the Americas. It is classified among the world's 100 worst invasive species due to its detrimental effects on biodiversity and economies.
- Management Challenges: The rapid reproduction rate and survival in diverse habitats complicate efforts to eradicate this species. Increased flooding during monsoon seasons aids its spread, highlighting the need for public education and strict regulations in areas where the snail is present.
The invasion of the Giant African Snail underscores the urgent need for integrated pest management strategies in urban settings. It serves as a reminder of the challenges invasive species pose to human health, biodiversity, and agriculture. The situation in Chennai highlights the importance of early detection and coordinated responses to biological invasions.
India’s Mission Sudarshan Chakra Air Defence System
 Why in News?
Why in News?
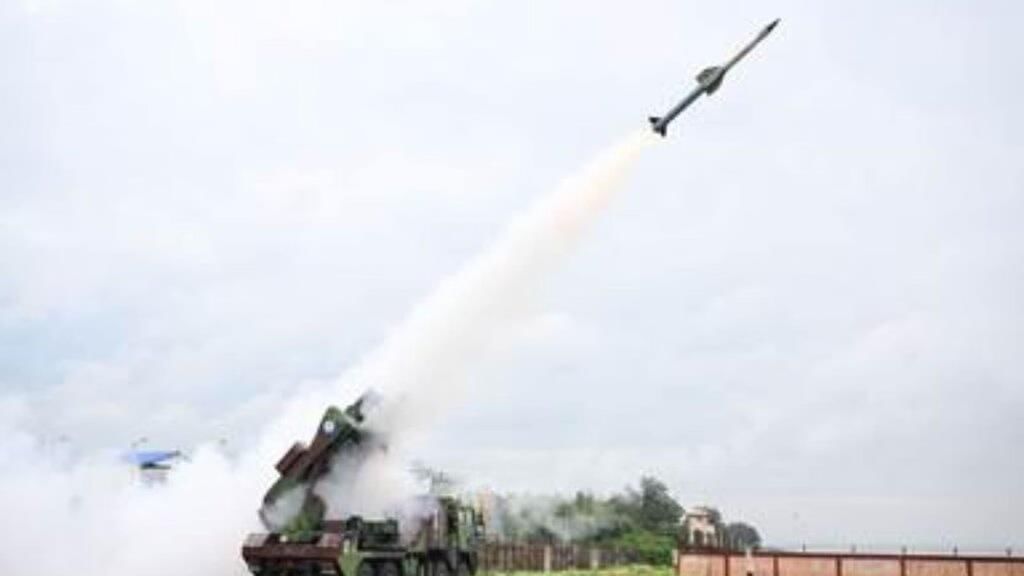
India's Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has made significant progress by successfully testing an integrated air defence system as part of Mission Sudarshan Chakra, which was announced by Prime Minister Narendra Modi. This system is expected to be fully operational by 2035 and has demonstrated capabilities to intercept targets at various altitudes and ranges.
Key Takeaways
- The system showcases a multi-layered air defence shield combining both legacy and modern weaponry.
- Recent tests involved engaging three targets simultaneously at different heights and distances.
- Mission Sudarshan Chakra aims to establish a comprehensive air defence umbrella by 2035.
- It integrates long-range, medium-range, and short-range weapon systems to counter diverse aerial threats.
Additional Details
- Multi-Tiered Defence: The system reflects India’s strategic focus on future warfare, integrating capabilities from the Indian Air Force and Army to adapt to modern aerial threats.
- Integration of Systems: India’s air defence combines older systems like Pechora and OSA-AK with modern platforms such as the S-400 and SPYDER, ensuring operational readiness and cost-effectiveness.
- Future warfare is expected to involve unmanned systems and long-range strikes, necessitating a shift towards low-cost drones, which this mission addresses through layered defences.
- Challenges include the need for affordable solutions to counter low-tech aerial threats while maintaining effective operational capabilities.
In summary, India's Mission Sudarshan Chakra represents a strategic initiative to enhance national defence capabilities by integrating various air defence systems and preparing for future warfare challenges. The focus on both legacy and modern technologies ensures a versatile and effective defence posture in the evolving landscape of aerial threats.
India Launches UPI-UPU Project For Cross-Border Payments
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Union Minister for Communications, Jyotiraditya M. Scindia, officially launched the UPI-UPU Integration Project during the 28th Universal Postal Congress held in Dubai on September 11, 2025. This initiative is a significant advancement in the realm of international remittances, combining India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) with the Universal Postal Union’s (UPU) Interconnection Platform. The primary goal is to facilitate fast, affordable, and secure cross-border payments, thereby enhancing global financial inclusion.
Key Takeaways
- The UPI-UPU Integration Project is a collaboration between India's Department of Posts, NPCI International Payments Ltd (NIPL), and UPU.
- This project aims to reduce costs and processing times associated with remittances, benefiting millions of families relying on cross-border transfers.
Additional Details
- What is the UPI-UPU Integration? This project merges two influential systems: UPI, which is widely used for domestic transactions in India, and the UPU's Interconnection Platform that links postal services across 192 member countries. This integration will provide a swift, secure, and economical channel for international payments.
- Significance of the Project: It addresses major challenges in international remittances such as high fees, slow processing times, and limited access, thereby enhancing financial inclusion and providing alternatives to traditional banking systems.
- Investment and Global Role: India is set to invest $10 million to improve global postal services, focusing on digital payments and capacity building. It aims to host regional workshops to ensure inclusive participation worldwide.
- Impact on Cross-Border Remittances: In the fiscal year 2024-25, UPI processed over 185 billion transactions worth $2.83 trillion, which comprised nearly half of the world’s digital payments. The UPI-UPU link will make international remittances as straightforward as sending a text message, benefiting the Indian diaspora and other communities.
- Global Collaboration: This project showcases international cooperation in digital finance, with India’s leadership focused on developing interoperable solutions to enhance global commerce.
In conclusion, the UPI-UPU Integration Project is a landmark initiative that promises to transform the landscape of international remittances, making them more accessible and cost-effective for millions around the world.
India Achieves Major Milestone In Literacy 2025
 Why in News?
Why in News?
India has celebrated a significant achievement in literacy as of 2025. The Ministry of Education observed International Literacy Day with the theme "Promoting Literacy in the Digital Era." Notably, Himachal Pradesh has become the fifth State/UT to reach full functional literacy, joining Tripura, Mizoram, Goa, and Ladakh. This event highlights not only the rising literacy rate in India but also the evolving definition of literacy in today's context.
Key Takeaways
- India's literacy rate increased from 74% in 2011 to 80.9% in 2023-24.
- The ULLAS Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram was instrumental in this progress.
- Himachal Pradesh achieved a literacy rate of 99.3%, surpassing the national average of 95%.
- Modern literacy encompasses digital, financial, and civic awareness.
Additional Details
- ULLAS Nav Bharat Saaksharta Karyakram: This initiative led to over three crore learners enrolling and 42 lakh volunteers mobilizing, focusing on foundational literacy and numeracy.
- The definition of literacy has expanded to include skills, livelihoods, and social awareness, emphasizing the role of volunteerism in sustaining literacy progress.
- States achieving full literacy include Mizoram (98.2%), Goa (100%), Tripura (over 95%), and Ladakh (97%).
- Collective efforts and youth participation have been encouraged to further literacy initiatives.
The literacy journey in India is remarkable, moving from a mere 12% post-Independence to the current statistics, with aspirations for universal literacy by the next census. The sustained efforts by the government, combined with community participation and innovative programs, reflect the commitment to building a developed and literate nation.
Discrepancies in India’s Household Consumption Data
 Why in News?
Why in News?
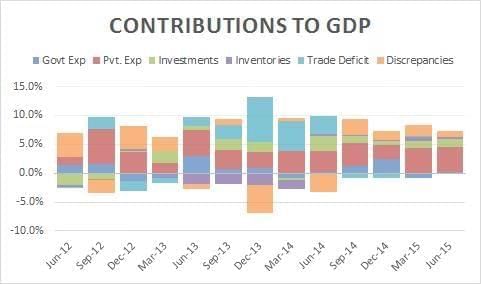
Recent analyses have highlighted a significant disparity between two critical measures of household consumption in India. The estimates from the Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE) and the Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES) show a staggering difference of nearly 45 percent for the fiscal year 2022-23. Understanding these discrepancies is vital for accurate assessments of consumption, poverty, and welfare policies.
Key Takeaways
- The gap between PFCE and HCES poses challenges for economic policy-making.
- PFCE captures the total consumption value, while HCES focuses on actual household spending.
- The divergence has increased from 5 percent in 1972-73 to approximately 45 percent today.
Additional Details
- Private Final Consumption Expenditure (PFCE): A macroeconomic metric that estimates the total value of goods and services consumed by households and non-profit institutions. It includes all consumption, even those goods and services provided for free or at subsidized rates, such as government healthcare.
- Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (HCES): A micro-level survey that records self-reported household spending, concentrating solely on out-of-pocket expenditures. It is essential for evaluating poverty and food security but often omits free or subsidized consumption.
- Reasons for Consumption Gap:
- Methodological differences: PFCE includes all consumption while HCES does not account for free services.
- Price discrepancies: PFCE uses market prices while HCES relies on household reports.
- Timing issues: HCES aligns with the agricultural year, whereas PFCE corresponds to the financial year.
- Changing Consumption Patterns: Data from HCES indicate a shift in spending habits, with food expenses decreasing and non-food expenditures rising, driven by transport, healthcare, and education.
- Policy Implications: Misestimating consumption can lead to inappropriate welfare programs and ineffective resource allocation for initiatives like the Public Distribution System and Direct Benefit Transfers.
- Measures to Bridge the Gap:
- Enhancing HCES sampling to include affluent households.
- Utilizing income tax data and digital payment records to cross-reference and correct under-reporting.
- Updating HCES questionnaires to reflect modern consumption trends.
- Revising PFCE methodologies to improve accuracy.
- Establishing a reconciliation mechanism to combine the strengths of both PFCE and HCES for better consumption estimates.
In conclusion, addressing the discrepancies between PFCE and HCES is crucial for formulating effective economic policies and ensuring accurate understanding of consumption patterns in India.
NASA Finds Potential Biosignatures on Mars Surface
 Why in News?
Why in News?
On September 13, 2025, NASA's Mars rover Perseverance made a groundbreaking discovery, indicating the strongest evidence to date that life may have existed on Mars. The rover analyzed a rock named Cheyava Falls in 2024, identifying chemical and structural features that suggest possible ancient microbial activity. This finding has generated significant global interest in the search for extraterrestrial life, although the evidence remains inconclusive and necessitates further research.
Key Takeaways
- The Perseverance rover detected potential biosignatures in a rock sample on Mars.
- Key materials found include clay, silt, organic carbon, sulfur, oxidized iron, and phosphorus.
- The rock's chemical composition suggests the possibility of ancient microbial life.
Additional Details
- Biosignatures: These are indicators of possible biological origins, either created by living organisms or through non-biological processes. The substances found in Cheyava Falls could have been formed without life, complicating the interpretation of the evidence.
- Scientific Caution: NASA has clarified that these findings do not constitute definitive proof of life. The instruments on the rover provide initial clues, but further detailed examinations of the Cheyava Falls sample are required.
- Perseverance has collected over 30 samples intended for future analysis on Earth.
- Future Missions: NASA is planning a mission to return the collected Mars samples to Earth. Perseverance is currently storing these samples in a sealed compartment for retrieval, although budget constraints pose challenges to the sample return mission.
This discovery could significantly enhance our understanding of Mars and the potential for life beyond Earth, pending the successful return and analysis of the samples.
Albania Inducts World’s First AI Minister
 Why in News?
Why in News?
On September 13, 2025, Albania made headlines by becoming the first country to officially appoint an artificial intelligence (AI) entity, named Diella, as a government minister. This groundbreaking decision aims to enhance public procurement processes and combat corruption in government spending.
Key Takeaways
- Albania appoints Diella, the first AI minister, to oversee public procurement.
- Diella is a virtual official designed to streamline government functions and reduce corruption.
- The introduction of an AI minister sets a precedent for the integration of technology in governance.
Additional Details
- Introduction of Diella: Unveiled by Prime Minister Edi Rama on September 11, 2025, Diella is a digital avatar created entirely from code. Unlike a traditional minister, Diella operates without human characteristics and is tasked with evaluating and awarding public tenders.
- Role and Responsibilities: Diella manages procurement tasks through voice commands on the digital services portal, evaluates tenders, selects contractors, and recruits talent globally. This automation aims to minimize human interference and corruption in governmental dealings.
- Objectives and Benefits: With widespread corruption challenges in Albania, Diella's impartial algorithms are expected to enhance transparency and accountability in public spending.
- Human Oversight and Security Concerns: The specifics regarding human supervision over Diella's operations are not clearly defined, raising concerns about potential risks associated with AI decision-making in sensitive areas like procurement.
- Global Significance: Albania's initiative with Diella could inspire other nations to explore innovative digital solutions to improve governance and administrative efficiency.
This historic move underscores the potential of AI in public administration, marking a significant shift in how technology can be utilized to enhance governmental operations and transparency.
Reintroduction of Brown Trout Revives Kashmir Fisheries
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Kashmir fisheries department is initiating the reintroduction of the brown trout into the Valley’s cold-water streams after a century-long absence. This program aims to restore the trout population and enhance angling tourism, with the project set to commence in October following thorough preparation and scientific research to guarantee the fish's survival and ecological harmony.
Key Takeaways
- The brown trout was first introduced in Kashmir by the British in 1900.
- Unregulated fishing and ecological disturbances have led to a decline in the brown trout population.
- Three lakh brown trout eggs have been imported from Denmark for the reintroduction efforts.
- The project is expected to revive angling tourism and support local businesses.
Additional Details
- Historical Introduction: The brown trout was successfully introduced in Kashmir in 1900, facilitated by Frank J Mitchel, an English carpet factory owner. The fish thrived in local streams and became a popular game fish, leading to the establishment of exclusive fishing zones known as 'beats' for regulated angling.
- Decline: Over the years, the brown trout population declined due to unregulated fishing and ecological disturbances, including illegal mining. The fisheries department shifted its focus to trout farming for food, but reviving wild brown trout became a priority for sport and tourism.
- Scientific Challenges: Brown trout require cold, well-oxygenated water and do not adapt well to artificial environments. Unlike rainbow trout, they reject artificial feed. The fisheries team developed a special feeding regimen using crustaceans mixed with cod liver oil and created dark conditions in the hatchery to stimulate feeding, as brown trout primarily feed in low light.
- Current Reintroduction Efforts: The department has imported three lakh pure brown trout eggs from Denmark, which were hatched at the Tchansar Hatchery in Kulgam. The fries have now matured to a size suitable for release into local streams and lakes such as the Veshav river and Kounsarnag lake.
- Ecological Considerations: The planned release is set for October-November, coinciding with the breeding season when brown trout are less aggressive and cannibalistic, thus increasing their survival chances. Officials stress the importance of habitat preservation to ensure the success of this initiative, especially against threats from illegal mining and environmental degradation.
The reintroduction of the brown trout is highly anticipated as it is regarded as a prized game fish due to its fighting spirit, which attracts anglers from around the world. This initiative is expected to significantly boost angling tourism, benefiting local businesses and travel agencies. Ultimately, this project is viewed as a milestone in the conservation of Kashmir’s aquatic biodiversity and the development of sustainable tourism.
AI-Based Monsoon Forecasting
 Why in News?
Why in News?
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare (MoAFW) has introduced the use of artificial intelligence (AI) to deliver early and precise monsoon forecasts to farmers throughout India. Recently, approximately 3.8 crore farmers across 13 states received AI-generated monsoon predictions via SMS through the m-Kisan platform. This advance notice, provided up to four weeks prior to rainfall, aids farmers in making informed decisions regarding crop selection, sowing times, and resource management. This initiative represents a global innovation in targeted AI weather forecasting aimed specifically at enhancing agricultural outcomes.
Key Takeaways
- The MoAFW's initiative utilizes advanced AI to forecast monsoons.
- Nearly 3.8 crore farmers are receiving forecasts via SMS.
- Forecasts are available up to four weeks in advance, allowing better planning.
Additional Details
- AI Revolution in Weather Forecasting: Since 2022, AI has significantly improved the accuracy of weather predictions, tailoring forecasts to meet specific user needs. Advanced models can now predict complex phenomena, such as the Indian monsoon, weeks in advance. Notably, the MoAFW's forecasts integrate Google’s Neural GCM and ECMWF’s Artificial Intelligence Forecasting Systems (AIFS), which have surpassed traditional forecasting methods in predicting local monsoon onset.
- The MoAFW provided weekly updates during the 2025 monsoon season, including alerts about a 20-day mid-season pause in rainfall. This proactive communication allowed farmers to adjust their plans accordingly, reducing risks associated with unexpected weather changes.
- The messages were designed in simple language and tested with farmer groups to ensure clarity and utility, emphasizing the needs of farmers in adapting to fluctuating weather patterns.
The Kharif crop cycle, which is crucial for countless Indian farmers, is heavily reliant on timely monsoon rains. The early AI forecasts provide essential lead time for farmers to make informed decisions about planting and timing, thereby mitigating the risks of crop failure and enhancing income stability. In light of increasing climate variability, these forecasting tools are vital for bolstering agricultural resilience and supporting sustainable farming practices, ultimately strengthening rural livelihoods.
Future plans from the Ministry include expanding and refining the AI forecasting program. Continuous enhancements to the models and communication strategies will improve both accuracy and reach. The successful dissemination of the 2025 monsoon forecasts sets a significant precedent for the integration of AI into agricultural policy, showcasing the potential of technology to empower millions of farmers in effectively addressing climate challenges.
|
201 videos|842 docs|2245 tests
|
FAQs on Weekly Current Affairs (8th to 14th September 2025) - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is the purpose of the Emerging Science Innovation Conclave that has replaced the Indian Science Congress? |  |
| 2. What are the key features of the hydrogen-powered train launched in India? |  |
| 3. What activities were part of the inaugural Sunrise Festival hosted in Arunachal Pradesh? |  |
| 4. What capabilities do the MQ-28A Ghost Bat military drones provide to the armed forces? |  |
| 5. What implications does the Supreme Court's decision to allow Aadhaar for voter identity verification have on privacy and security? |  |
















