UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19th September 2025 | Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly PDF Download
GS3/Economy
Onion Sector in India - Price Distress and Policy Challenges
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Maharashtra’s onion farmers are currently protesting due to a significant drop in onion prices, which have fallen below their production costs. The farmers are demanding compensation, stable export policies, and procurement support to alleviate their financial distress.
Key Takeaways
- India is the second-largest producer of onions globally, with Maharashtra being the leading state in production.
- Recent protests by farmers highlight the challenges of price volatility and inadequate storage infrastructure.
- Farmers are seeking government intervention, including compensation and stable export policies.
Additional Details
- Onion Production in India: India produces between 25 to 30 million tonnes of onions annually, primarily in states like Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, and Karnataka. The Rabi crop, which accounts for nearly 60% of total production, is favored for its storage potential.
- Challenges Faced:
- Price Volatility: Onions experience extreme price fluctuations due to factors such as overproduction and poor storage.
- Storage Losses: Many Rabi onions spoil due to inadequate storage facilities, leading to wastage.
- Export Policy Issues: Frequent changes in export policy damage India’s reputation in international markets, causing a loss of competitiveness to countries like China and Pakistan.
- High Production Costs: The cost of production ranges from Rs. 2,200 to Rs. 2,500 per quintal, while farmers receive only Rs. 800 to Rs. 1,000, resulting in significant financial losses.
- Farmers’ Protests: Beginning on September 12, 2025, farmers are demanding a compensation of Rs. 1,500 per quintal and an immediate halt to the sale of buffer stocks by the government to stabilize prices.
In conclusion, the ongoing crisis in the onion sector highlights critical weaknesses in India's agricultural pricing and export policies. While initiatives like the release of buffer stocks aim to stabilize consumer prices, they often adversely affect farmers. The current protests illustrate the pressing need for structural reforms, including reliable export strategies, improved procurement models, and enhanced infrastructure, to support India’s onion farmers effectively.
GS3/Science and Technology
How the DeepSeek-R1 AI Model Was Taught to Teach Itself to Reason
Why in News?
The introduction of the DeepSeek-R1 AI model has garnered attention due to its groundbreaking ability to reason independently, without relying on human-generated examples. This innovative approach has led to significant advancements in problem-solving accuracy, particularly demonstrated through its performance on mathematical assessments.
Key Takeaways
- DeepSeek-R1 achieved a remarkable improvement in solving the American Invitational Mathematics Examination (AIME) problems, increasing its accuracy from 15.6% to 86.7%.
- The model's development of reflective reasoning capabilities marks a significant shift in AI learning methodologies.
Additional Details
- Reinforcement Learning: This is a trial-and-error approach where an AI system learns by receiving rewards for correct answers and penalties for incorrect ones. DeepSeek-R1 was rewarded solely for correct final answers, which fostered the development of reflective reasoning.
- Self-Reasoning Development: R1 began with solving math and coding problems, evolving through trial and error. The emergence of reflective phrases like "wait" or "let’s try again" indicated its capacity for self-correction.
- Major Successes: R1 demonstrated significant improvements in various benchmarks, including a jump in AIME performance from 15.6% to 86.7% accuracy and enhancements in general knowledge evaluation metrics.
- Limitations and Risks: High energy costs associated with reinforcement learning and the continued necessity for human input in open-ended tasks reveal the model's current constraints. Additionally, ethical concerns arise from the model's ability to reflect on its reasoning, posing potential risks in generating unsafe content.
The developments surrounding DeepSeek-R1 illustrate a pivotal moment in AI evolution, highlighting the potential for machines to learn and reason autonomously. This advancement not only reduces dependence on human labor but also raises important questions regarding creativity, autonomy, and the ethical implications of AI capabilities.
GS2/Governance
Technology as the Grammar of Governance
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Over the last two decades, technology has become a crucial equalizer in India's governance landscape, with initiatives ranging from localized experiments in Gujarat to nationwide digital public infrastructure aimed at reaching the most marginalized sections of society.
Key Takeaways
- Gujarat's innovative governance models have served as templates for broader national initiatives.
- The integration of technology has significantly improved transparency, efficiency, and accessibility in government services.
- India's digital identity initiatives have brought millions into the formal economy and improved service delivery.
Additional Details
- Gujarat - The Laboratory of Innovation:
- Jyotigram Scheme (2003): Introduced feeder separation technology, providing 24/7 power to rural areas, which contributed to reduced groundwater depletion and revived rural industries, with an investment of ₹1,115 crore recovered in just 2.5 years.
- Solar Panels on Narmada Canal (2012): Generated 16 million units annually, powering 16,000 homes and reducing water evaporation.
- Governance Technology:
- e-Dhara: Digitized land records.
- SWAGAT: Facilitated direct CM-citizen video interactions.
- Online Tenders: Implemented to reduce corruption.
- National Canvas - From Gujarat to Delhi:
- India Stack and JAM Trinity:
- Jan Dhan Accounts: Included over 53 crore people in the banking system.
- Aadhaar: Provided digital identities to 142 crore citizens, facilitating easier access to government services.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT): Eliminated middlemen, saving over ₹4.3 lakh crore.
- India Stack and JAM Trinity:
India's technological advancements in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and infrastructure have showcased the potential of digital solutions to enhance governance and service delivery. The digital identity initiatives not only democratize access to services but also instill trust among citizens, thereby redefining the relationship between the government and the governed.
GS2/Polity
SC Precedents vs Gag Order in Adani Case
 Why in News?
Why in News?
Recently, a lower court issued a sweeping ex-parte gag order restraining several journalists, including Paranjoy Guha Thakurta, from publishing content deemed defamatory against Adani Enterprises Limited (AEL). This order also mandated the removal of numerous articles and social media posts. Following this, the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting issued takedown notices, resulting in the removal of 138 YouTube videos and 83 Instagram posts, some of which were satirical or indirect references to Adani.
Key Takeaways
- The Supreme Court's guidelines on defamation injunctions emphasize the need for careful consideration before imposing restrictions on speech.
- The Delhi Court quashed the gag order, highlighting the violation of principles of natural justice.
- Ex parte orders in free speech cases are only justified in exceptional circumstances.
Additional Details
- Bonnard Standard: The Supreme Court follows the Bonnard principle established in 1891 (Bonnard vs Perryman), which states that an injunction can only be granted if the court is satisfied that the defendant may not justify the alleged defamation, rather than based on mere suspicion.
- The recent ruling by the SC on Bloomberg (2024) reinforced that pre-trial injunctions should be rare, only granted when withholding them would cause greater injustice.
- The Delhi Court's blanket gag order was criticized for lacking judicial examination of the allegedly defamatory content, allowing AEL to control public information about itself.
- Prior restraint on speech is problematic as it requires a heavy burden of proof and often undermines the public's right to know.
The ruling by the Delhi Court emphasized the necessity of allowing journalists the opportunity to present their defense before imposing sweeping takedown orders, warning against the irreversible harm that could arise from premature content removal.
GS3/Economy
Equalising Primary Food Consumption in India
Why in News?
The recent release of the National Sample Survey's Household Consumption Expenditure Survey (2024) has shed light on poverty measurement in India after more than a decade. According to the Poverty and Equity Brief: INDIA (2025), extreme poverty has significantly decreased from 16.2% in 2011-12 to 2.3% in 2022-23. However, this data raises concerns about whether it fully represents the extent of deprivation, particularly regarding food consumption.
Key Takeaways
- Extreme poverty in India has reportedly fallen drastically.
- Concerns exist regarding the accuracy of poverty measurements based solely on income.
- The 'thali' approach offers a more holistic view of food security.
- Significant disparities in food consumption, especially in pulses, highlight nutritional deficits.
- Restructuring the Public Distribution System (PDS) is necessary for equitable food access.
Additional Details
- Traditional Poverty Measurement: Historically, poverty in India has been assessed through a calorie-based standard linked to minimum calorific intake. This method, while useful, may overlook essential aspects of food security such as nutrition and cultural significance.
- Thali Meal Approach: The thali, which includes rice, dal, vegetables, roti, curd, and salad, provides a more comprehensive metric for assessing food adequacy. Research indicates that many households struggle to afford the cost of two thalis per day.
- Public Distribution System (PDS): Although the PDS is crucial for food security, it exhibits inefficiencies. For example, wealthier households receive subsidies almost equal to those in the lowest income brackets, indicating a misallocation of resources.
- Pulses Consumption: There is a stark disparity in pulse consumption, with the poorest households consuming significantly less than wealthier ones. Expanding the PDS to include pulses could enhance nutritional equity.
- Policy Implications: Reforming the PDS to focus on pulses rather than just cereals could lead to better nutritional outcomes and align food security with dignity and well-being.
The ongoing discourse surrounding poverty in India must evolve beyond mere income metrics. By adopting multidimensional indicators like the thali approach, policymakers can address the nuanced realities of deprivation and work towards a more equitable and sustainable food security framework.
GS1/History & Culture
National Maritime Heritage Complex at Lothal
Why in News?
The Prime Minister has recently reviewed the construction progress of the National Maritime Heritage Complex (NMHC) located at Lothal in the Ahmedabad district of Gujarat.
Key Takeaways
- The NMHC aims to highlight India's rich maritime history spanning over 5,000 years.
- Lothal is recognized as the world's earliest dockyard dating back to the Indus Valley Civilization.
Additional Details
- Location: The complex is situated in Lothal, Ahmedabad district, Gujarat, specifically in the Bhal region near the Gulf of Khambhat.
- Developer: It is being developed by the Ministry of Ports, Shipping and Waterways, Government of India.
- Historical Significance of Lothal:
- Established around 2200 BCE as a prominent Harappan trade and craft center specializing in beads, gems, and ornaments.
- The name Lothal translates to "Mound of the Dead," akin to Mohenjo-daro.
- Excavated by S.R. Rao between 1955 and 1960, confirming its status as a major ancient port.
- The dockyard measured 222 x 37 meters and was linked to the old course of the Sabarmati river.
- Evidence of advanced water management systems, including lock gates and sluice systems, has been discovered.
- Trade connections once extended to Mesopotamia and other ancient civilizations.
- Nominated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2014, making Lothal the only known port-town of the Indus Valley Civilization.
- Features of the Complex:
- Will include exhibition halls, a maritime park, an amphitheater, a museum, and educational research facilities.
- Focus on ancient trade routes, shipbuilding traditions, and navigation techniques.
- Expected to serve as a significant center for cultural tourism and heritage education.
The National Maritime Heritage Complex is anticipated to become a pivotal site for understanding and appreciating India's maritime history, fostering tourism, and promoting educational initiatives related to India's ancient maritime prowess.
GS2/International Relations
US Revokes Sanctions Waiver on Chabahar Port
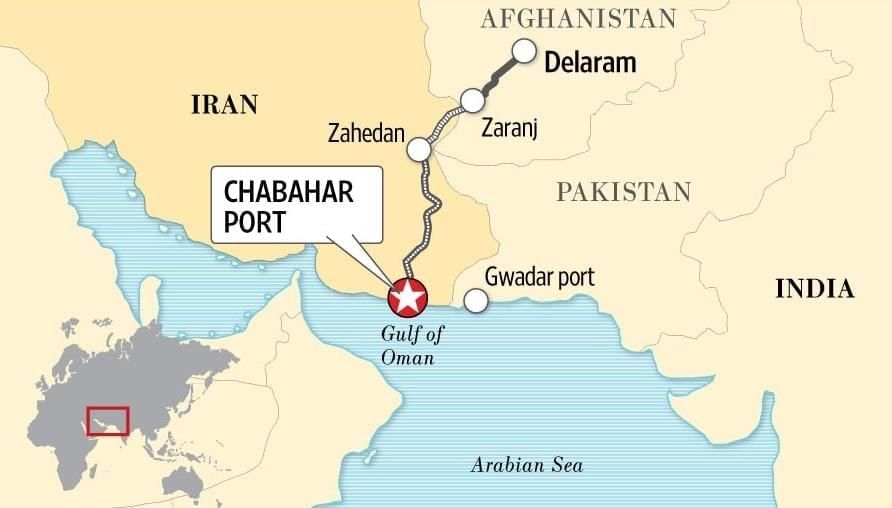 Why in News?
Why in News?
The U.S. has ended the 2018 waiver that allowed India to utilize Iran’s Chabahar Port for the reconstruction efforts in Afghanistan. This decision has been enacted with a revocation notice issued within 10 days.
Key Takeaways
- The Chabahar Port is a significant strategic asset for India in the region.
- The revocation of the waiver poses challenges for India's economic interests in Afghanistan.
- This move could potentially strain diplomatic relations between India, the U.S., and Iran.
Additional Details
- Chabahar Port: A deep-water port located in the Sistan-Baluchistan province of Iran, on the Gulf of Oman, at the entrance of the Strait of Hormuz. It is notable for being the only Iranian port with direct access to the Indian Ocean.
- Distance: Chabahar is 550 nautical miles from Kandla Port in Gujarat and 786 nautical miles from Mumbai.
- Structure: The port comprises two terminals: Shahid Beheshti and Shahid Kalantari.
- Strategic Importance: Its proximity to Afghanistan and its position on the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) enhance its potential as a major commercial hub, linking the Indian Ocean and Persian Gulf with the Caspian Sea and further to northern Europe via Russia.
The revocation of the sanctions waiver by the U.S. could jeopardize India’s investments in Chabahar, estimated at ₹200 crores, and disrupt future development projects. It also threatens to cut off India’s only direct maritime access to Afghanistan and Central Asia, thereby weakening its strategic position against China’s Gwadar Port in Pakistan. Furthermore, this situation may create diplomatic tensions between India and its strategic partner Iran, as well as with the United States, which is a significant trade partner.
GS1/History & Culture
Sirarakhong Hathei Chilli Festival
Why in News?
The 14th Sirarakhong Hathei Chilli Festival has been inaugurated in Manipur, highlighting its cultural significance and agricultural heritage.
Key Takeaways
- The festival is celebrated annually in Sirarakhong village, Ukhrul district, Manipur.
- It commenced in 2010 to promote the Hathei chilli and its farming traditions.
- The Hathei chilli received Geographical Indication (GI) status in 2021.
Additional Details
- Local Identity: The chilli is also known as Sirarakhong chilli, indigenous to the region.
- Cultivation: It is traditionally grown on slopes using the jhum system.
- Distinct Qualities: Recognized for its bright red color, unique flavor, and medium pungency.
- ASTA Value: It holds a high American Spice Trade Association color value, making it desirable for food coloring.
- Nutritional Benefits: Rich in antioxidants, Vitamin C, and calcium, it also has medicinal properties.
- Uses: Commonly utilized in cooking, pickles, flavoring, food coloring, and in various processing industries.
- Uniqueness: Its exceptional qualities arise from the specific soil and climate of Sirarakhong, making it irreplaceable elsewhere.
This festival not only celebrates the Hathei chilli but also promotes local culture through various activities, including flag hoisting, Tangkhul Naga cultural events, buyer-seller meets, marketing programs, exhibitions, and awareness drives regarding government schemes.
[UPSC 2018]
Consider the following pairs: Tradition - State
1. Chapchar Kut festival — Mizoram
2. Khongjom Parba ballad — Manipur
3. Thong-To dance — Sikkim
Which of the pairs given above is/are correct?
Options: (a) 1 only (b) 1 and 2* (c) 3 only (d) 2 and 3
GS2/Governance
India Needs More Focus to Reach SDG 3, A Crucial Goal
Why in News?
In June 2025, India achieved its best-ever position in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Index, ranking 99 out of 167 countries, a notable improvement from 109 in 2024. This progress reflects a consistent advancement since 2021, particularly in enhancing access to basic services and infrastructure. Despite this achievement, the SDG Report indicates ongoing challenges in health and nutrition, with significant disparities, especially among rural and tribal communities.
Key Takeaways
- India's ranking in the SDG Index improved to 99 in 2025.
- Challenges persist in health and nutrition, particularly affecting rural populations.
- SDG 3 focuses on health and well-being, but progress remains insufficient.
Additional Details
- Maternal Mortality Ratio: Currently at 97 deaths per 100,000 live births, which exceeds the target of 70.
- Under-five Mortality Rate: At 32 per 1,000 live births, surpassing the target of 25.
- Life Expectancy: Stands at 70 years, below the target of 73.63 years.
- Out-of-Pocket Health Expenditure: Accounts for 13% of household consumption, nearly double the target of 7.83%.
- Immunisation Coverage: Strong at 93.23%, yet still shy of the universal target of 100%.
Key barriers to progress include inadequate access to quality healthcare due to weak infrastructure, economic constraints, and non-economic factors such as poor nutrition and sanitation. Cultural practices and stigma further hinder community engagement with healthcare services.
Steps Required to Accelerate Progress on SDG Goal 3
- Universal Health Insurance: Essential for reducing financial burdens and enhancing equitable access, as evidenced by global experiences.
- Robust Primary Health Centres: Improved coordination across healthcare tiers is necessary for early disease detection and cost reduction.
- Leveraging Digital Health Tools: Utilizing telemedicine and integrated health records can help bridge access gaps, particularly in rural areas.
Health education in schools is crucial for prevention, which is more cost-effective than treatment. Educating children on nutrition, hygiene, and mental health can lead to improved long-term behaviors. This can significantly impact maternal health and child mortality rates. Global examples, such as Finland's and Japan's health education reforms, showcase the potential benefits of a structured curriculum in India.
Need for Collective Action to Achieve SDG Goals
- Policymakers should integrate health education into curricula and strengthen universal health coverage.
- Parents must advocate for comprehensive health education in schools.
While India's SDG ranking shows promise, only 17% of global targets are currently on track for 2030. Educating youth on healthy behaviors, combined with robust healthcare systems, can establish a foundation for sustained progress towards the vision of a healthier and stronger Viksit Bharat by 2047.
GS3/Economy
What is PM MITRA Park?
Why in News?
The Prime Minister recently laid the foundation stone for India's first PM MITRA (Mega Integrated Textile Region and Apparel) Park in Dhar, Madhya Pradesh, marking a significant development in the textile sector.
Key Takeaways
- The PM MITRA scheme was introduced by the Ministry of Textiles in 2021.
- The objective is to establish 7 world-class integrated parks to strengthen India's textile sector.
Additional Details
- Overview: The PM MITRA scheme focuses on creating integrated parks that encompass the entire textile value chain, from spinning to garment-making, within a single ecosystem.
- Selected Sites: Parks will be developed in Tamil Nadu (Virudhunagar), Telangana, Karnataka, Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh (Dhar), and Uttar Pradesh (Lucknow).
- Timeline: All parks are expected to be established by 2026-27, each covering around 1,000+ acres.
- Implementation Structure: Each park will be developed by a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) that is jointly owned by the Centre and State Governments, operating under a Public-Private Partnership (PPP) model.
- Financial Support: The Centre will provide up to ₹500 crore per park in Development Capital Support (DCS) and ₹300 crore per park in Competitive Incentive Support (CIS) to encourage rapid implementation.
- Key Features: Integrated parks will reduce transport costs and delays, include world-class infrastructure like incubation centres and logistics facilities, and are expected to generate approximately 1 lakh direct and 2 lakh indirect jobs, particularly benefiting women and rural youth.
- Investment Potential: The scheme aims to attract over ₹70,000 crore in investments toward the textile sector.
In summary, the PM MITRA Park initiative represents a comprehensive approach to enhancing the Indian textile industry by ensuring an integrated and efficient production ecosystem, thereby promoting growth and employment opportunities.
GS2/International Relations
Highlights of the Global Innovation Index, 2025
Why in News?
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has recently published the Global Innovation Index (GII) for the year 2025, which assesses the innovative capacities of various economies around the world.
Key Takeaways
- The GII ranks 139 economies based on their innovation capabilities.
- Switzerland leads the index, followed by Sweden and the United States.
- India holds the 38th position globally, with a notable score among lower-middle-income countries.
Additional Details
- About the Global Innovation Index (GII): The GII is an annual report that evaluates and ranks economies based on their innovation performance, utilizing over 80 metrics divided into seven pillars.
- Indicators: The GII includes two main sub-indices: the Innovation Input Sub-Index (comprising institutions, human capital and research, infrastructure, market sophistication, and business sophistication) and the Innovation Output Sub-Index (including knowledge and technology outputs as well as creative outputs).
- R&D Growth: The growth rate for Research and Development has slowed, registering at 2.9% in 2024 and projected to decrease to 2.3% in 2025—marking the lowest growth since the 2010 financial crisis.
- Regional Trends: Europe showcases strong performance with 15 of the top 25 economies, while the Southeast, East Asia, and Oceania region contributes 6 economies to this group.
- India's Performance: India ranks 38th with a score of approximately 40.5, demonstrating strengths in knowledge and technology outputs but facing challenges in business sophistication and infrastructure.
The Global Innovation Index serves as a vital tool for governments to evaluate their effectiveness in translating research and development, education, and infrastructure investments into tangible innovation outcomes. The evolving trends highlighted in the GII 2025 reflect the dynamic landscape of global innovation and the need for continuous improvement in various sectors.
|
38 videos|5258 docs|1111 tests
|
FAQs on UPSC Daily Current Affairs: 19th September 2025 - Current Affairs & Hindu Analysis: Daily, Weekly & Monthly
| 1. What are the main challenges faced by the onion sector in India regarding price distress? |  |
| 2. How does the PM MITRA Park initiative aim to enhance the textile industry in India? |  |
| 3. What role does technology play in governance as suggested by the concept of "Technology as the Grammar of Governance"? |  |
| 4. What are the implications of the US revoking the sanctions waiver on Chabahar Port for India? |  |
| 5. Why is achieving Sustainable Development Goal 3 (SDG 3) critical for India? |  |





















