NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics - Parliament and the Making of Laws
Page No. 45
Exercises
Ans:
- People from various backgrounds joined the struggle for freedom. They were inspired by the ideas of freedom, equality and participation in decision making.
- Under colonial rule, the people had to live in fear of the British Government. The British forced people to follow their orders and decisions which were at times very harsh. People were severely punished even if they tried to criticize these decisions.
- Because of the continuous demand of the Indian National Congress, the Government of India Act 1909 was passed, which allowed for some elected representation. Still, the British Government did not allow all adults to vote.
- The bitter experience of colonial rule and struggle for freedom movement left little doubt in the minds of the nationalists that all persons in independent India would be able to participate in decision making.
- These are the reasons because of which, I think, the nationalist movement supported the idea that all adults (above 18 years of age) have a right to vote.
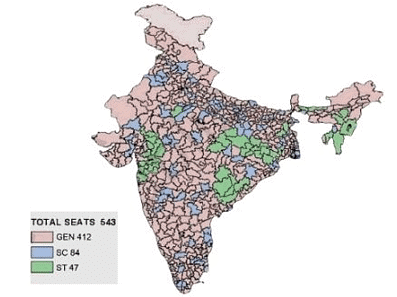
Ans:
| My state | Jharkhand |
| My constituency | Ranchi |
| M.P. from my constituency | Ram Tahal Chaudhary |
| Number of MPs in our state | 14 |
| Green Constituencies | Reserved for Scheduled Tribes (ST) |
| Blue Constituencies | Reserved for Scheduled Castes (SC) |
Q3: You have read in Chapter 1 that the ‘Parliamentary form of government’ that exists in India has three tiers. This includes the Parliament (central government) and the various State Legislatures (state governments). Fill in the following table with information on the various representatives from your area:
| State Government(Uttar Pradesh) | Central Government | |
Which political party/parties is/are currently in power? | ||
Who (name) is the current representative from your area? | ||
Which political parties currently form the Opposition? | ||
When were elections last held? | ||
When will the next elections be held? | ||
How many women representatives are there (from your state)? |
Ans:
| State Government | Central Government | |
| Which political party/parties is/are currently in power? | BJP | BJP Led NDA |
| Who (name) is the current representative from your area? | Satyadev Pachauri (BJP) from Kanpur | - |
| Which political parties currently form the Opposition? | Indian National Congres, Samajwadi Party and Baahujan Samajwadi Party | Indian National Congress |
| When were elections last held? | March-April 2022 | In 2019 |
| When will the next elections be held? | Scheduled for 2027 | In 2024 |
| How many women representatives are there (from your state)? | Find yourself | Find yourself |
Q4: Re-read the storyboard on how a new law on domestic violence got passed. Describe in your own words the different ways in which women’s groups worked to make this happen.
Ans:
Women's groups worked together to make this happen. Here's how they did it:
- Talking about the Problem: They talked about how serious domestic violence is. They held meetings and told people about it.
- Finding Information: They collected facts and stories about how many people were facing this problem. This helped them explain why a new law was needed.
- Speaking to Important People: They talked to important people like politicians and government leaders. They told them about the new law they wanted.
- Marches and Protests: They organized marches and protests, where many people walked together to show they cared about this issue. This made the leaders notice and listen.
- Sharing Stories: Women's groups gave chances for people who faced domestic violence to tell their stories. This made the issue more real and urgent.
|
69 videos|431 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Civics - Parliament and the Making of Laws
| 1. What is the role of Parliament in making laws? |  |
| 2. How does a bill become a law in Parliament? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of debates in the making of laws in Parliament? |  |
| 4. How are laws made in Parliament influenced by public opinion? |  |
| 5. Can laws made in Parliament be challenged or changed in the future? |  |

















