Class 8 Geography Chapter 5 Notes - Human Resources
| Table of contents |

|
| Human Resource |

|
| Distribution of Population |

|
| Density of Population |

|
| Factors Affecting Distribution of Population |

|
| Population Change |

|
| Patterns of Population Change |

|
| Population Composition |

|
Human Resource
Human resources are considered a nation's most valuable asset. They are essential for transforming natural resources into valuable assets through their demands, skills, and capabilities.

- People are pivotal in converting nature's bounty into useful resources.
- Human resources are the ultimate resource for a nation's development.
Characteristics of Human Resources:
- Healthy, educated, and motivated individuals are crucial for effective resource development.
- Human resources differ in educational levels, age, and sex.
- Human resources are not equally distributed around the world.
- Variations in numbers and characteristics affect resource development and utilization.
Impact on Development: The ability of a nation to develop and utilize its resources is closely linked to the quality and distribution of its human resources.
Distribution of Population
The pattern of how people are dispersed across the Earth's surface is referred to as population distribution.
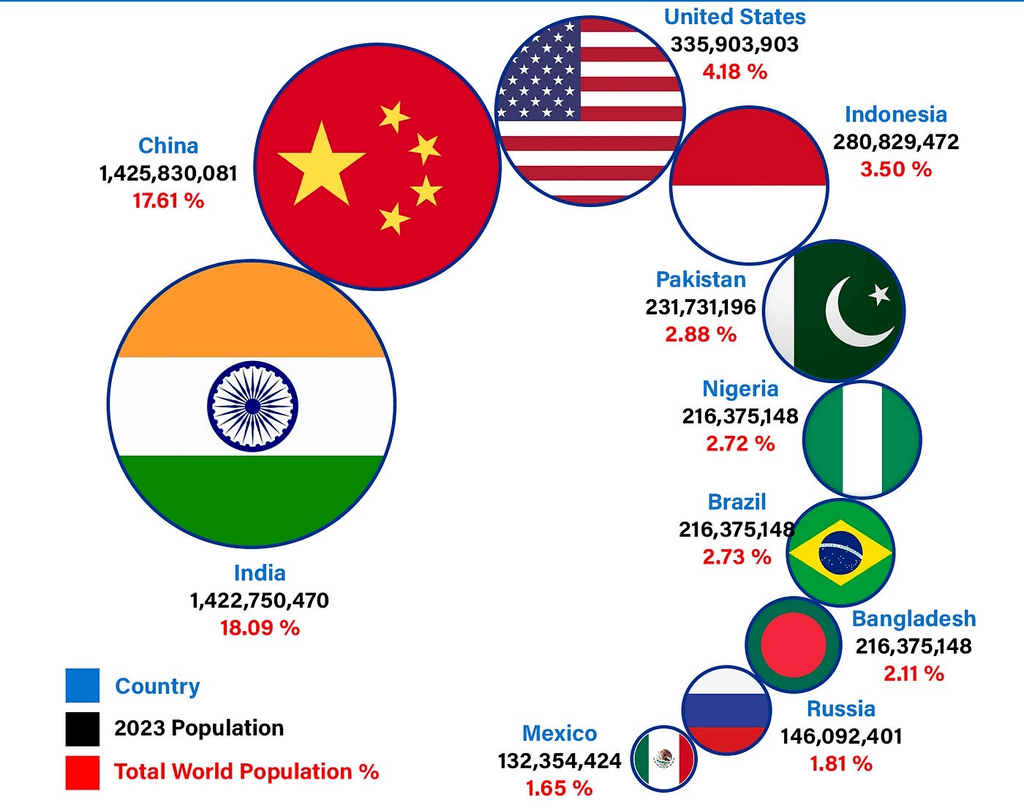 Most Populated Countries of the World
Most Populated Countries of the World
- Over 90% of the global population resides on roughly 30% of the land area.
- Population distribution is highly uneven, with some regions being densely populated while others are sparsely inhabited.
- Crowded Areas: South and Southeast Asia, Europe, and northeastern North America experience high population density.
- Sparsely Populated Areas: Few people live in high-latitude regions, tropical deserts, high mountains, and equatorial forests.
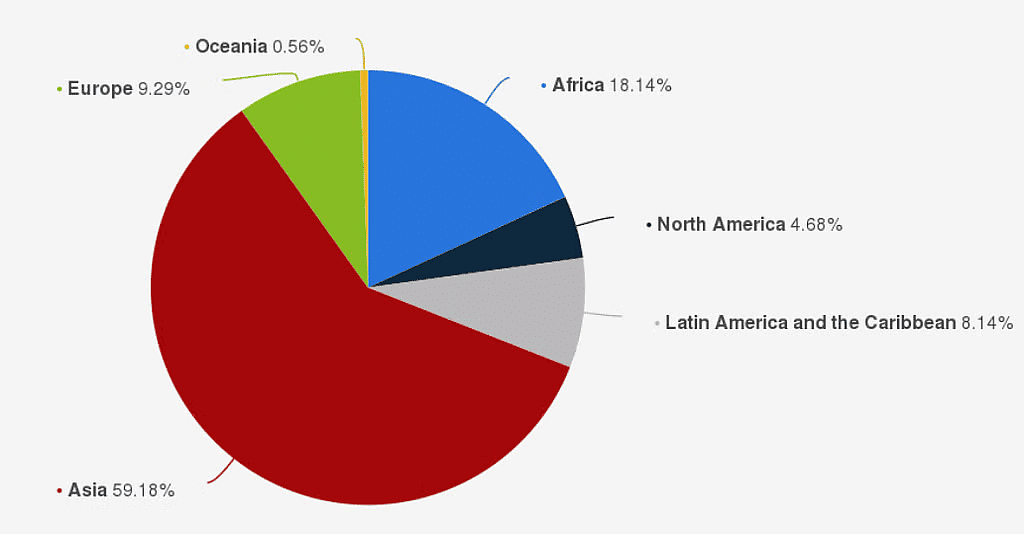
- Population Density:
- There are significantly more people living north of the Equator compared to the south.
- About 75% of the global population is concentrated in two continents: Asia and Africa. - Concentration in Countries: 60% of the world's population is concentrated in just 10 countries, each with over 100 million people.
Density of Population
- A number of people living in the unit area of the earth’s surface are the density of population- normally expressed as per square metre.
- The average density of population in the whole world is 51 persons per square km. South-Central Asia has the highest density of population followed by East and South East Asia.
Factors Affecting Distribution of Population
1. Geographical Factors
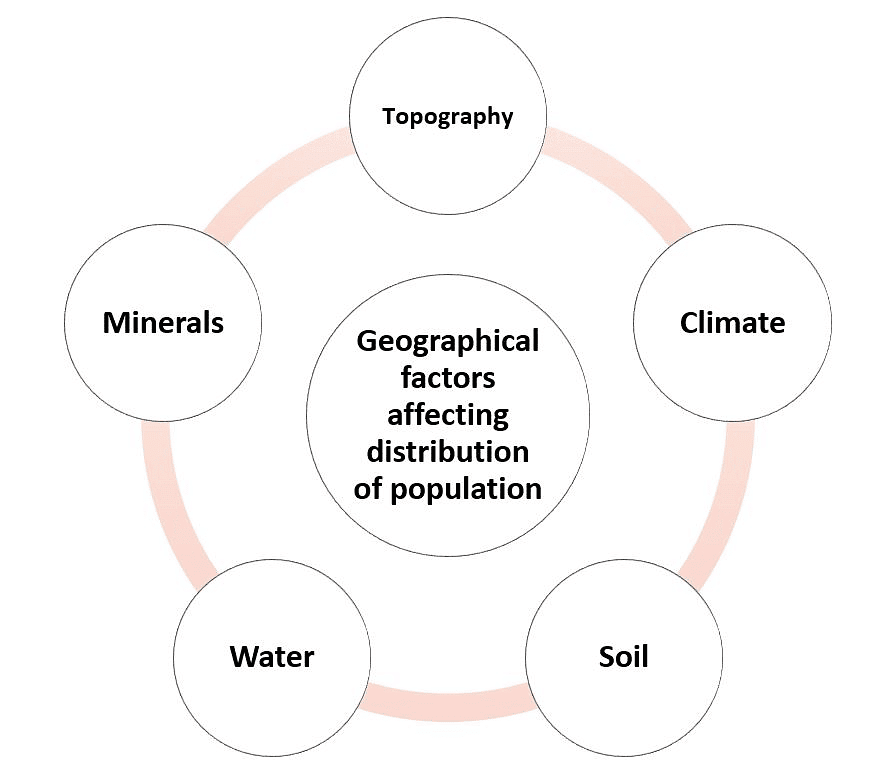
- Topography: People prefer to live on plains rather than mountains and plateau as these areas are suitable for farming, manufacturing and service activities.
(i) The Ganga plains- most densely populated areas of the world
(ii) Andes, Alps and Himalayas- sparsely populated. - Climate: People usually avoid extreme climates that are very hot or very cold.
Examples: Sahara desert, polar regions of Russia, Canada and Antarctica. - Soil: Fertile soils provide suitable land for agriculture.
Examples: Densely populated fertile plains such as Ganga and Brahmaputra in India, Hwang-He, Chang Jiang in China and the Nile in Egypt. - Water: People prefer to live in areas where freshwater is easily available. River valleys of the world are densely populated while deserts have spare population.
- Minerals: Areas with mineral deposits are more populated.
Example: Diamond mines of South Africa and the discovery of oil in the Middle East lead to settling of people in these areas.
2. Social, Cultural and Economic Factors
- Social: Areas of better housing, education and health facilities are more densely populated
Example: Pune. - Cultural: Places with religion or cultural significance attract people.
Example: Varanasi, Jerusalem and Vatican city. - Economic: Industrial areas provide employment opportunities so it attracts a large number of people.
Example: Osaka in Japan and Mumbai in India are two densely populated areas.
Population Change
Population change refers to variations in the number of people over time, influenced by birth rates, death rates, and migration.
- Historical Trends:
- For centuries until the 1800s, population growth was slow due to high birth and death rates, limited healthcare, and inadequate food supply.
- In 1804, the global population reached 1 billion. By 1959, it had surged to 3 billion, marking a period of rapid growth known as the "population explosion."
- By 1999, the population doubled again to 6 billion, driven by improved healthcare and food supplies that reduced death rates while birth rates remained high.
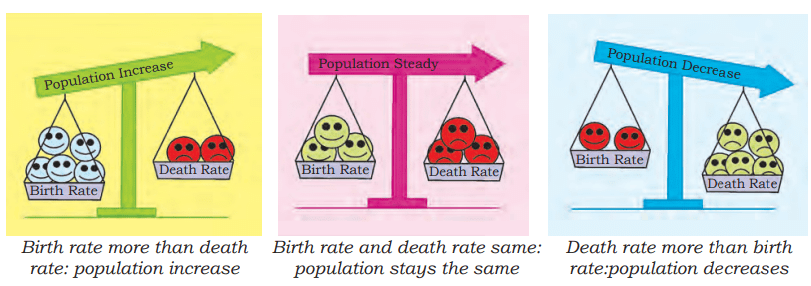
- Key Measurements:
- Birth Rate: Number of live births per 1,000 people.
- Death Rate: Number of deaths per 1,000 people.
- Natural Growth Rate: The difference between the birth rate and the death rate.
 Balance of Population
Balance of Population
- Migration:
- Emigrants: People who leave a country.
- Immigrants: People who enter a country.
- Countries like the USA and Australia have seen population increases due to immigration, while Sudan has experienced population declines due to emigration.
- Migration Patterns:
- International migration often occurs from less developed to more developed countries in search of better opportunities.
- Internal migration frequently involves people moving from rural areas to urban centers for better employment, education, and healthcare.
Patterns of Population Change
- Rates of population growth vary across the world- Even if, the world’s total population is rising rapidly, not all countries are experiencing this growth.
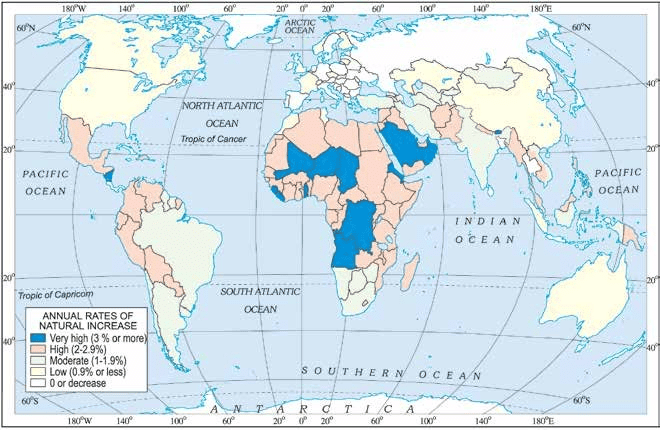 World: Differing rates of population growth
World: Differing rates of population growth
- Kenya has a high population growth rate, as well as high birth rates and death rates. With improving health care, death rates have reduced, but birth rates still remain high leading to high growth rates.
- In other countries like the United Kingdom, population growth is slowing because of both low death and low birth rates.
Population Composition
- Economic development has little to do with how crowded a place is. Bangladesh and Japan-densely populated. But, Japan is more economically developed than Bangladesh. People vary in age, sex, literacy level, health condition, occupation and income level. Population composition refers to the structure of the population.
- The composition of the population helps to know- the number of males or females, age group they belong to, how educated they are and what type of occupations they are employed in, what their income levels and health conditions are. People can study the population composition of a country by looking at the population pyramid or the age-sex pyramid.
Population Pyramid
- The total population divided into various age groups, e.g., 5 to 9 years, 10 to 14 years.
- The percentage of the total population, subdivided into males and females, in each of those groups. age-sex pyramid (population composition pyramid).
 Population Pyramid
Population Pyramid
- The numbers of children (below 15 years) are shown at the bottom and reflect the level of births.
- The size of the top shows the numbers of aged people (above 65 years) and reflects the number of deaths.
- The population pyramid also tells us how many dependents there are in a country.
- There are two groups of dependents — young dependents (aged below 15 years) and elderly dependents (aged over 65 years). Those of the working-age are economically active.
Population pyramid of Kenya
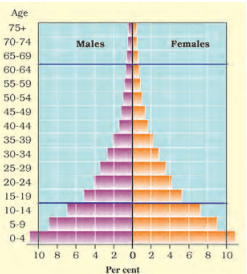
- The population pyramid shown above for Kenya has birth and death rates both high, hence it is broad at the base and rapidly narrows towards the top.
- This is because although many children are born, a large percentage of them die in their infancy, relatively few become adults and there are very few old people.
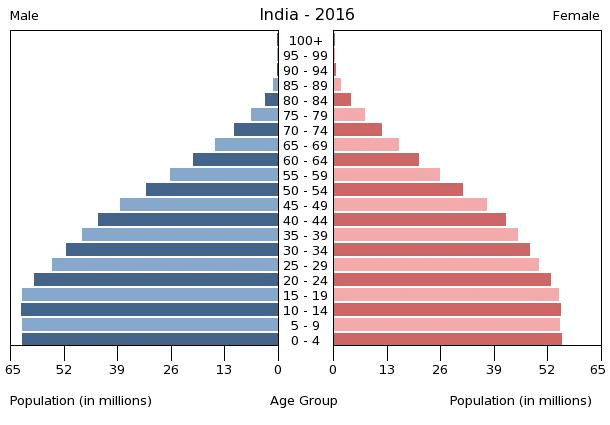
Population Pyramid of India
- In countries like India where death rates (especially amongst the very young) are decreasing, the pyramid is broad in the younger age groups, because more infants survive to adulthood.
- This can be seen in the pyramid above for India. Such populations contain a relatively large number of young people and which means a strong and expanding labour force.
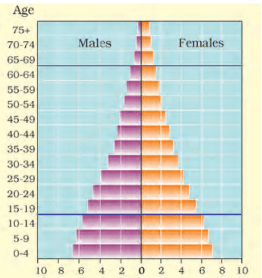
Population Pyramid of Japan
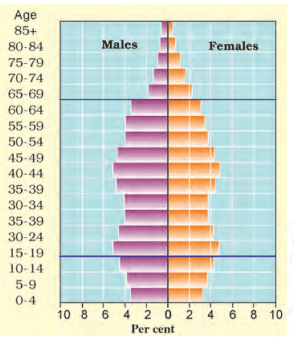
- In countries like Japan, low birth rates make the pyramid narrow at the base. Decreased death rates allow numbers of people to reach old age.
- Skilled, spirited and hopeful young people endowed with a positive outlook are the future of any nation.
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 5 Notes - Human Resources
| 1. What is the role of human resources in an organization? |  |
| 2. How can effective human resource management impact employee performance? |  |
| 3. What are the key functions of human resource management? |  |
| 4. How does human resource planning contribute to organizational success? |  |
| 5. What are the challenges faced by human resource managers today? |  |
















