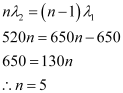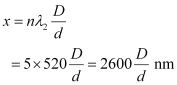NCERT QUESTION
(Wave Optics)
Q10.1: Monochromatic light of wavelength 589 nm is incident from air on a water surface. What are the wavelength, frequency and speed of (a) reflected, and (b) refracted light? Refractive index of water is 1.33.
Ans: Wavelength of incident monochromatic light,
λ = 589 nm = 589 × 10−9 m
Speed of light in air, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Refractive index of water, μ = 1.33
(a) The ray will reflect back in the same medium as that of incident ray. Hence, the wavelength, speed, and frequency of the reflected ray will be the same as that of the incident ray.
Frequency of light is given by the relation,
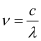
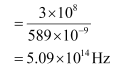
Hence, the speed, frequency, and wavelength of the reflected light are 3 × 108 m/s, 5.09 ×1014 Hz, and 589 nm respectively.
(b) Frequency of light does not depend on the property of the medium in which it is travelling. Hence, the frequency of the refracted ray in water will be equal to the frequency of the incident or reflected light in air.
∴ Refracted frequency, ν = 5.09 ×1014 Hz
Speed of light in water is related to the refractive index of water as:
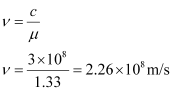
Wavelength of light in water is given by the relation,
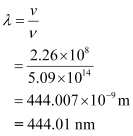
Hence, the speed, frequency, and wavelength of refracted light are 2.26 ×108 m/s, 444.01nm, and 5.09 × 1014 Hz respectively.
Q10.2: What is the shape of the wavefront in each of the following cases:
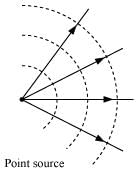
(a) Light diverging from a point source.
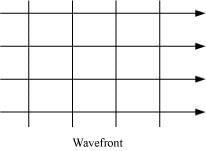
(b) Light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus.
(c) The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star intercepted by the Earth.
Ans: (a) The shape of the wavefront in case of a light diverging from a point source is spherical. The wavefront emanating from a point source is shown in the given figure.
(b) The shape of the wavefront in case of a light emerging out of a convex lens when a point source is placed at its focus is a parallel grid. This is shown in the given figure.
(c) The portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star intercepted by the Earth is a plane.
Q10.3: (a) The refractive index of glass is 1.5. What is the speed of light in glass? Speed of light in vacuum is 3.0 × 108 m s−1)
(b) Is the speed of light in glass independent of the colour of light? If not, which of the two colours red and violet travels slower in a glass prism?
Ans: (a) Refractive index of glass, μ = 1.5
Speed of light, c = 3 × 108 m/s
Speed of light in glass is given by the relation,
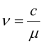
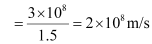
Hence, the speed of light in glass is 2 × 108 m/s.
(b) The speed of light in glass is not independent of the colour of light.
The refractive index of a violet component of white light is greater than the refractive index of a red component. Hence, the speed of violet light is less than the speed of red light in glass. Hence, violet light travels slower than red light in a glass prism.
Q10.4: In a Young’s double-slit experiment, the slits are separated by 0.28 mm and the screen is placed 1.4 m away. The distance between the central bright fringe and the fourth bright fringe is measured to be 1.2 cm. Determine the wavelength of light used in the experiment.
Ans: Distance between the slits, d = 0.28 mm = 0.28 × 10−3 m
Distance between the slits and the screen, D = 1.4 m
Distance between the central fringe and the fourth (n = 4) fringe,
u = 1.2 cm = 1.2 × 10−2 m
In case of a constructive interference, we have the relation for the distance between the two fringes as:
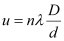
Where,
n = Order of fringes = 4
λ = Wavelength of light used
∴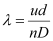
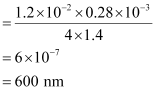
Hence, the wavelength of the light is 600 nm.
Q10.5: In Young’s double-slit experiment using monochromatic light of wavelengthλ, the intensity of light at a point on the screen where path difference is λ, is K units. What is the intensity of light at a point where path difference is λ /3
Ans: Let I1 and I2 be the intensity of the two light waves. Their resultant intensities can be obtained as:
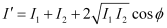
Where,
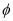 = Phase difference between the two waves
= Phase difference between the two waves
For monochromatic light waves,
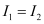
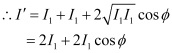
Phase difference = 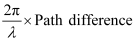
Since path difference = λ,
Phase difference, 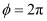
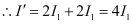
Given,
I’ = K

When path difference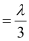 ,
,
Phase difference, 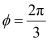
Hence, resultant intensity, 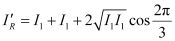
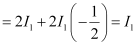
Using equation (1), we can write:
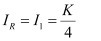
Hence, the intensity of light at a point where the path difference is 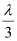 is
is 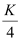 units.
units.
Q10.6: A beam of light consisting of two wavelengths, 650 nm and 520 nm, is used to obtain interference fringes in a Young’s double-slit experiment.
(a) Find the distance of the third bright fringe on the screen from the central maximum for wavelength 650 nm.
(b) What is the least distance from the central maximum where the bright fringes due to both the wavelengths coincide?
Ans: Wavelength of the light beam, 
Wavelength of another light beam, 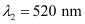
Distance of the slits from the screen = D
Distance between the two slits = d
(a) Distance of the nth bright fringe on the screen from the central maximum is given by the relation,
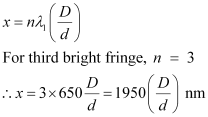
(b) Let the nth bright fringe due to wavelength 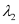 and (n − 1)th bright fringe due to wavelength
and (n − 1)th bright fringe due to wavelength 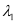 coincide on the screen. We can equate the conditions for bright fringes as:
coincide on the screen. We can equate the conditions for bright fringes as:
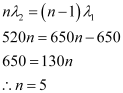
Hence, the least distance from the central maximum can be obtained by the relation:
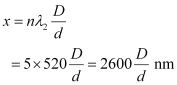
Note: The value of d and D are not given in the question.
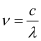
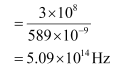
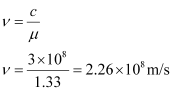
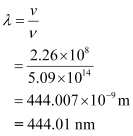


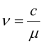
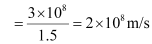
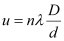
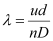
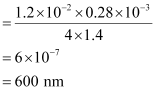
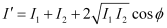
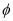 = Phase difference between the two waves
= Phase difference between the two waves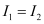
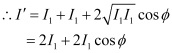
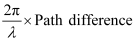
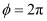
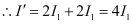

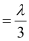 ,
,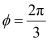
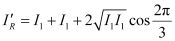
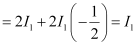
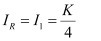
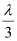 is
is 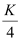 units.
units.
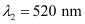
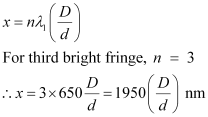
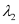 and (n − 1)th bright fringe due to wavelength
and (n − 1)th bright fringe due to wavelength 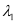 coincide on the screen. We can equate the conditions for bright fringes as:
coincide on the screen. We can equate the conditions for bright fringes as: