Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Practice Question Answers - How Do Organisms Reproduce
| Table of contents |

|
| Questions: Reproductive Health and Methods |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Questions: Reproductive Health and Methods
Q1. Expand the following terms:
(i) IUCD
(ii) STD
(iii) HIV
(iv) AIDS
Ans:
(i) IUCD - Intrauterine Contraceptive Device
(ii) STD - Sexually Transmitted Disease
(iii) HIV - Human Immunodeficiency Virus
(iv) AIDS - Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome
Q2. How do oral contraceptives function?
Ans: Oral contraceptives work in several ways to prevent pregnancy:
- They stop ovulation, meaning no egg is released from the ovaries.
- They change the cervical mucus, making it harder for sperm to reach an egg.
- They alter the uterine lining, making it less likely to support a fertilised egg.
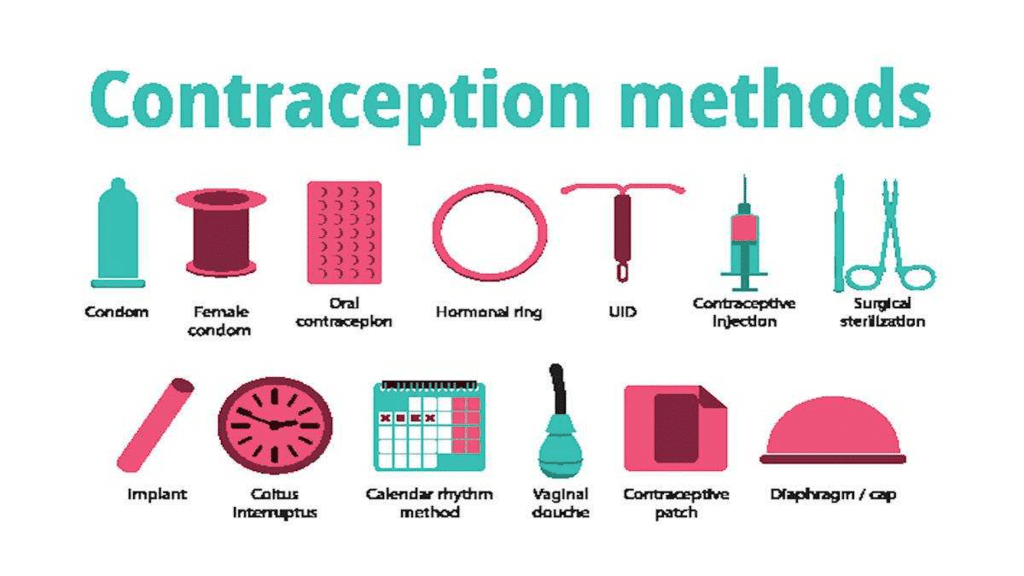
Q3. What is contraception?
Ans: Contraception refers to methods or devices that prevent pregnancy by disrupting the normal processes involved in fertilisation, implantation, or ovulation.
- Mechanical barriers: These prevent sperm from reaching the egg. Examples include condoms and vaginal coverings.
- Hormonal methods: These alter the body's hormonal balance to stop egg release and fertilisation. Commonly taken as oral pills, they may have side effects.
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs): Devices like the loop or copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy, but they can also cause irritation and side effects.
- Surgical methods: Procedures can block the vas deferens in males or the fallopian tubes in females, preventing sperm transfer or egg movement, respectively. While generally safe, surgery carries risks of infection.
Contraceptive methods are essential for family planning and maintaining a healthy society, as they help manage population growth and prevent unwanted pregnancies.
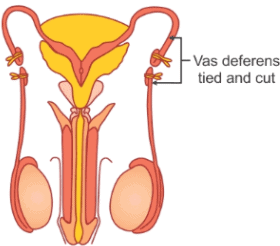
Q4. What is a vasectomy?
Ans: A vasectomy is a surgical procedure designed for male sterilisation or permanent contraception. It involves:
- Cutting and sealing the vas deferens.
- Preventing sperm from entering the semen.
This procedure is considered a safe and effective method of contraception.
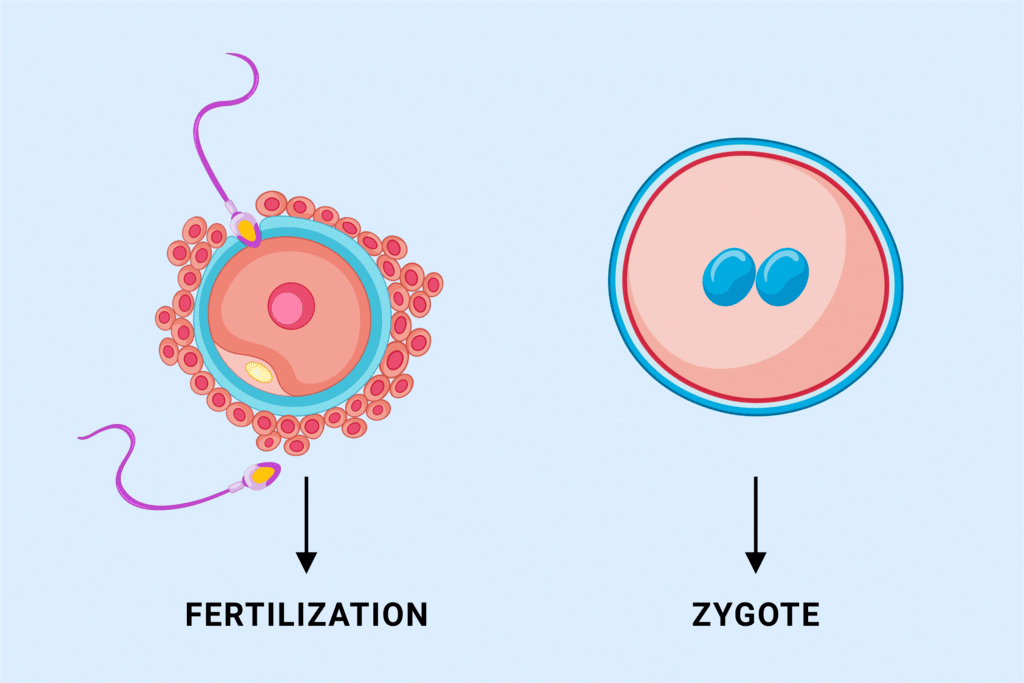
Q5. What do you understand by fertilization?
Ans: Fertilization is the process where a sperm cell and an ovum (egg cell) combine to form a zygote, marking the beginning of a new individual’s development.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. Where does fertilization take place?
Ans: Fertilization occurs in the fallopian tube of the female reproductive system.
Q2. How is an embryo produced?
Ans: An embryo is formed when a zygote undergoes multiple cell divisions, evolving into a multicellular organism.
Q3. What is a zygote?
Ans: A zygote is the first cell formed when a sperm fertilises an ovum. It marks the start of a new organism's development.
- The zygote contains genetic material from both parents.
- It undergoes cell division to form an embryo.
- The embryo eventually implants in the uterus, where it continues to grow.
- This process is crucial for the development of specialised tissues and organs.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. What are the parts of a male reproductive system?
Ans: The male reproductive system consists of:
- Testes - Produce sperm.
- Vas deferens - Transports sperm.
- Prostate gland - Adds fluid to sperm.
- Seminal vesicles - Provide nutrients to sperm.
- Urethra - Common passage for sperm and urine.
- Penis - Delivers sperm to the female reproductive system.
The testes are located in the scrotum to maintain a lower temperature, essential for sperm production.
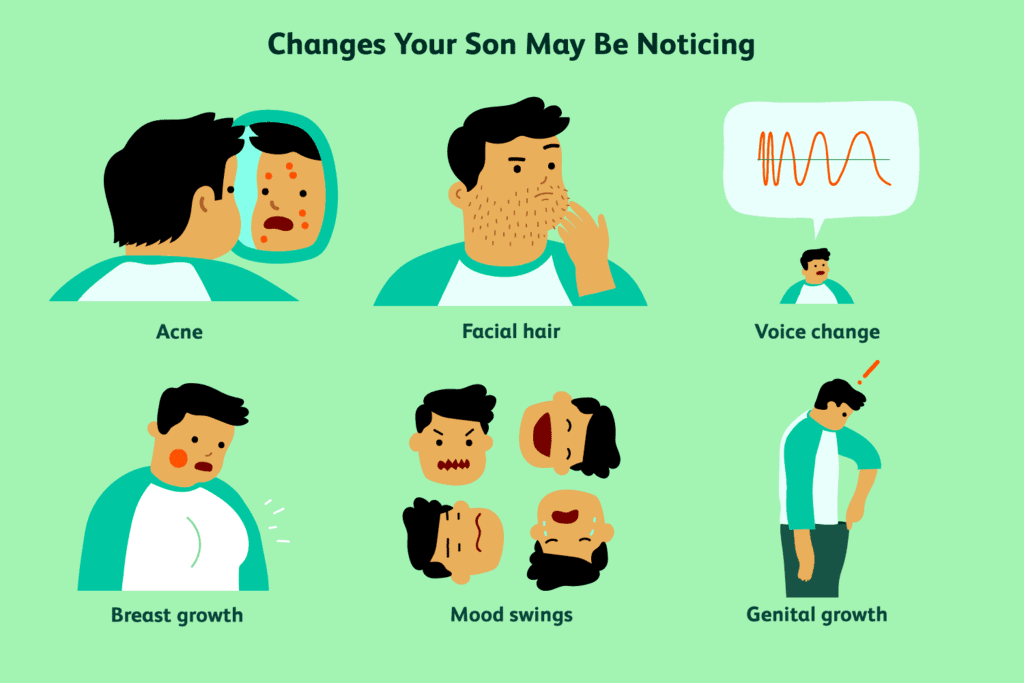
Q2. What is puberty?
Ans: Puberty is the stage of development when a person becomes sexually mature. It involves various physical and hormonal changes, including:
- The body grows larger and changes shape.
- New features appear, such as body hair in areas like the armpits and genital region.
- Skin may become oilier, leading to pimples.
- In girls, breast development begins, and menstruation starts.
- In boys, facial hair grows, and the voice may deepen.
These changes occur gradually over months or years and can vary widely among individuals. They signal that the body is preparing for reproduction, with specific changes indicating sexual maturity.
Q3. What happens if the mature ovum is not fertilized in a female?
Ans: If the ovum is not fertilised, it has a lifespan of about one day. Each month, the ovary releases an egg, while the uterus prepares itself to receive a fertilised egg by thickening its lining.
When fertilisation does not occur:
- The uterine lining, which is no longer needed, begins to break down.
- This lining is expelled from the body through the vagina, mixed with blood and mucus.
- This process is known as menstruation, which typically lasts between two to eight days.
Q4. What is internal fertilization? Give an example.
Ans: Internal fertilization occurs when fertilization takes place inside the female body. This process is exemplified in humans.
Q5. What happens if the mature ovum is not fertilized in a female?
Ans: If the ovum is not fertilised, it undergoes the following process:
- The ovum survives for about one day.
- Each month, the ovary releases one egg while the uterus prepares for a potential pregnancy.
- The uterine lining becomes thick and spongy, ready to nourish a fertilised egg.
- If fertilisation does not occur, this lining is no longer needed.
- The lining gradually breaks down and is expelled through the vagina as blood and mucous.
- This monthly cycle is known as menstruation and typically lasts between two to eight days.
Long Answer Type Questions
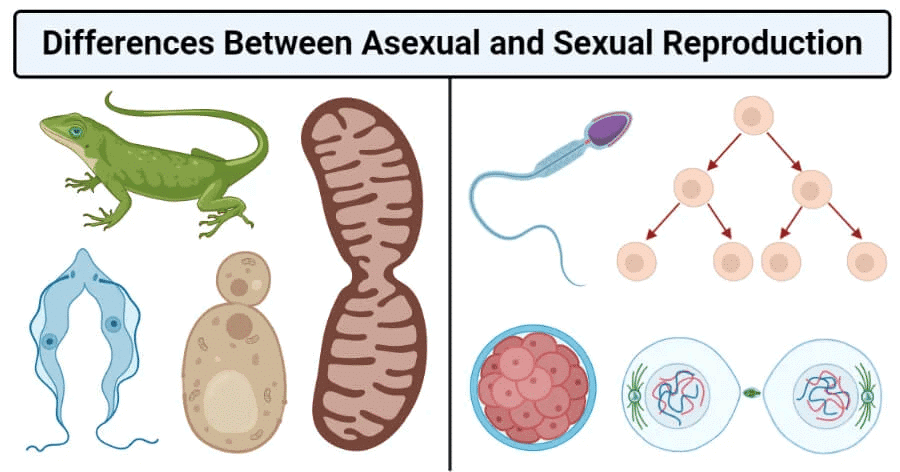
Q1. "Sexual reproduction is more advanced than asexual reproduction" - why?
Ans: Sexual reproduction is regarded as more advanced than asexual reproduction for several reasons:
- It involves the combination of genetic material from two individuals, resulting in genetic variation.
- Offspring inherit traits from both parents, creating a unique blend of characteristics.
- This genetic diversity enhances a population's ability to adapt to changes in the environment.
- It improves resistance to diseases and increases survival chances in various habitats.
- In contrast, asexual reproduction produces genetically identical offspring, making the population vulnerable to environmental threats.
- Thus, sexual reproduction fosters evolutionary adaptability and resilience, crucial for long-term survival.
Q2. In which female reproductive organ does the embryo get embedded and why?
Ans: The embryo gets embedded in the uterus, a muscular organ in the female reproductive system. This is essential for several reasons:
- The uterus provides a stable and nutrient-rich environment for the embryo's growth and development.
- After fertilisation in the fallopian tube, the fertilised egg, now called a zygote, travels to the uterus.
- In the uterus, the zygote undergoes cell division to form a blastocyst.
- The blastocyst attaches to the uterine lining, known as the endometrium, in a process called implantation.
- The endometrium thickens each month, preparing for potential pregnancy, and is rich in blood vessels to nourish the embryo.
- The uterus also protects the embryo from external threats and expands to accommodate the growing foetus until birth.
Thus, the uterus is crucial for the successful development and sustenance of a pregnancy.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Science Chapter 7 Practice Question Answers - How Do Organisms Reproduce
| 1. What are the main types of reproduction in organisms? |  |
| 2. How do organisms reproduce asexually? |  |
| 3. What is the role of gametes in sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. Can organisms reproduce both sexually and asexually? |  |
| 5. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction? |  |