Continuity & Differentiability
Question 1: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Then,
Question 2: Find the second order derivatives of the function. x20
Answer
Let y = x20
Then,
Question 3: Find the second order derivatives of the function. x.cos x
Answer
Let y = x.cos x
Then,
Question 4: Find the second order derivatives of the function. log x
Answer
Let y = log x
Then,
Question 5: Find the second order derivatives of the function. x3 log x
Answer
Let y = x3 log x
Then,
Question 6: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Question 7: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Then,
Question 8: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Then,
Question 9: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Then,
Question 10: Find the second order derivatives of the function.
Answer
Let y =
Then,
Question 11: If
Answer
It is given that,
Then,
Hence, proved.
Question 12:
If in terms of y alone.
Answer
It is given that,
Then,
Question 13:
If
Answer
It is given that,
Then,
Hence, proved.
Question 14:
If 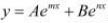 , show that
, show that 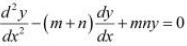
Answer
It is given that, 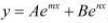
Then,
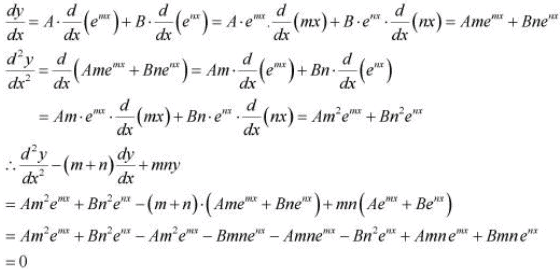
Hence, proved.
Question 15:
If 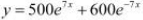 , show that
, show that 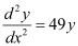
Answer
It is given that, 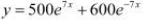
Then,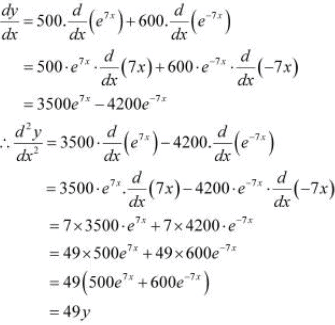
Hence, proved.
Question 16:
If 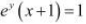 , show that
, show that 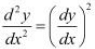
Answer
The given relationship is 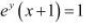
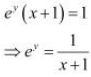
Taking logarithm on both the sides, we obtain
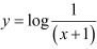
Differentiating this relationship with respect to x, we obtain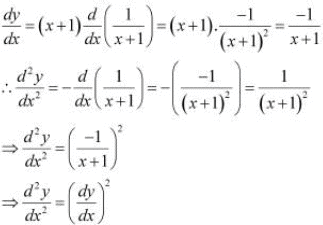
Hence, proved.
Question 17:
If  , show that
, show that 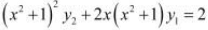
Answer
The given relationship is 
Then,
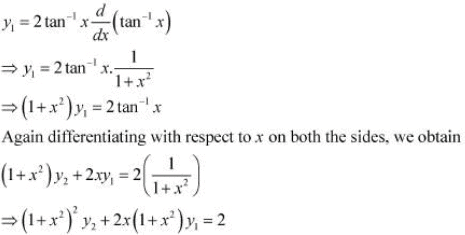
Hence, proved.
FAQs on NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths Chapter 5 - Continuity & Differentiability
| 1. What is continuity in calculus? |  |
| 2. What is differentiability in calculus? |  |
| 3. How do you determine if a function is continuous? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between continuity and differentiability? |  |
| 5. What are the applications of continuity and differentiability in real life? |  |




















