Marketing Management Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Market
The market traditionally refers to a place where buyers and sellers come together to trade goods and services. This term is often used in everyday language. However, business can also take place through different methods like telephone, mail, and the internet. In modern marketing, the term market encompasses a wider scope. It includes all the real and potential buyers of a product or service. For instance, when a fashion designer creates a new dress, everyone interested in buying it represents the market for that dress. The same applies to fans, bicycles, electric bulbs, or shampoos, referring to all actual and potential buyers of these products.
Additionally, the term "market" can be used in different contexts, such as:
- Product market (e.g., cotton market, gold market, share market)
- Geographic market (e.g., national and international market)
- Type of buyers (e.g., consumer market and industrial market)
- Quantity of goods transacted (e.g., retail market and wholesale market)
A market offering is a complete proposal for a product or service, which includes aspects like size, quality, and taste, at a specified price and available at a certain location. A good 'market offer' is developed by understanding the needs and preferences of potential buyers.
Therefore, marketing is a social process where individuals interact with others to encourage them to take specific actions, such as purchasing a product or service.

Marketer or Seller
If a customer is the seeker of satisfaction the marketer is the provider of satisfaction. A marketer can be a person or an organization that makes products or services available and offers them to the customer with the intention of satisfying the customer's needs and wants.
Important Features of Marketing
- Needs and Wants: Marketing helps people and groups get what they need and want. The main reason people engage in marketing is to meet their needs or desires. Essentially, marketing focuses on satisfying the needs and wants of individuals and organisations. A need is a feeling of lack. For example, when we are hungry, we start looking for food to ease that discomfort.
- Creating a Market Offering:. market offering includes everything about a product or service, like its size, quality, and price, and where it can be found. A strong market offer is created by understanding the needs and preferences of potential customers.
- Customer Value: Marketing helps facilitate the exchange of goods and services between buyers and sellers. Buyers decide what to purchase based on how much they believe a product or service will meet their needs compared to its cost. A product will only be bought if it is seen as providing the best value for the price. Therefore, marketers must enhance the product's value so that customers prefer it over competitors.
- Exchange Mechanism: Marketing operates through exchanges. Buyers and sellers get what they need through this process. For an exchange to happen, two conditions must be met: (i) There must be at least two parties involved, namely the buyer and seller; (ii) Each party must be able to offer something valuable to the other.
What can be Marketed?
Marketing is a social process whereby people exchange goods & services for money or for something of value to them. Anything that is of value to the other can be marketed e.g.
1. Physical Products - T.V., Mobile phone, etc.
2. Services - Insurance, education, etc.
3. Person - Selection for different posts.
4. Place visit - Agra, Taj Mahal, etc.
5. Events - Fashion shows, Films Festivals
Marketing Management
Marketing management means management of the marketing functions. It is the process of organizing, directing, and controlling the activities related to the marketing of goods and services to satisfy customers’ needs & achieve organizational goals.
Marketing management involves the following steps or activities
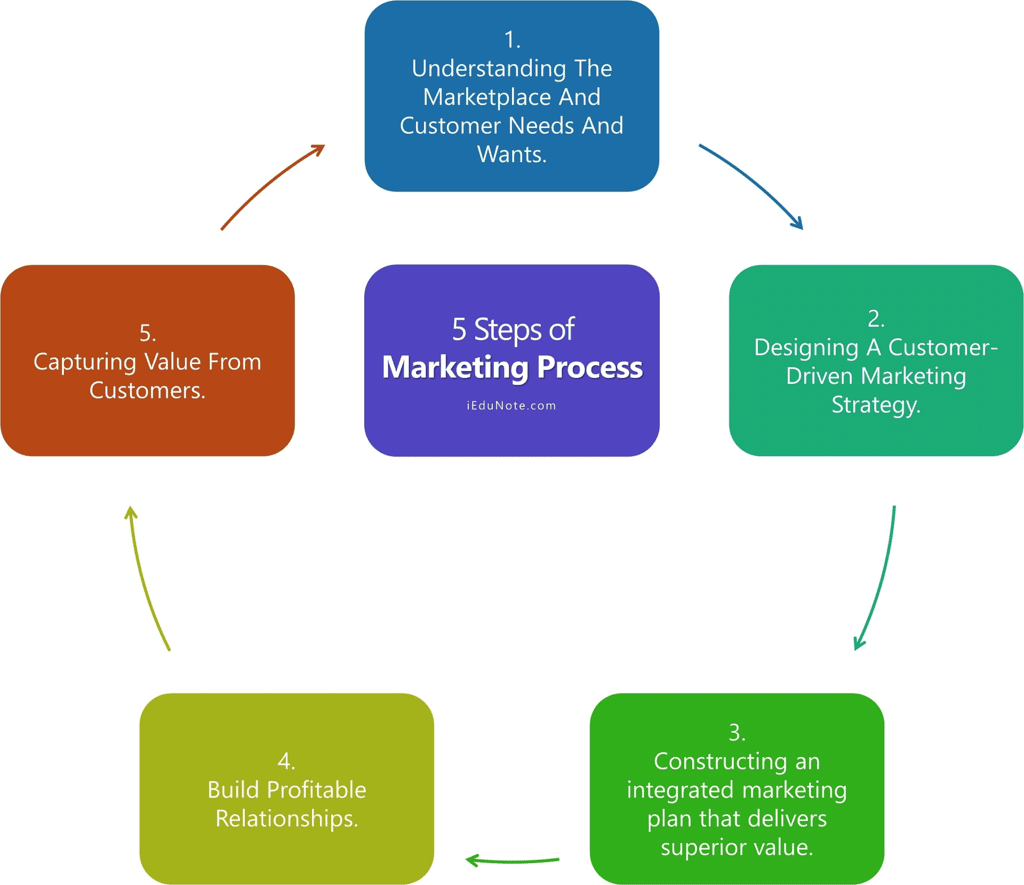
Marketing management involves the process of planning, organizing, implementing, and controlling marketing activities to achieve organizational goals. Here are the five steps of marketing management:
1. Analyzing Market Opportunities:
- Market Research: Conduct research to identify customer needs, preferences, and market trends.
- Segmenting the Market: Divide the market into distinct segments based on demographics, psychographics, and behavior.
- Targeting: Select specific target segments that align with the organization's objectives and resources.
- Positioning: Develop a unique positioning strategy to differentiate the organization's offerings from competitors.
2. Developing Marketing Strategies:
- Product Strategy: Determine the features, benefits, and branding of the product or service.
- Pricing Strategy: Set appropriate pricing levels that consider factors like costs, competition, and customer perceptions.
- Promotion Strategy: Decide on the most effective promotional channels and messages to reach the target audience.
- Distribution Strategy: Develop a distribution plan to ensure the product or service reaches the right customers at the right place and time.
3. Implementing Marketing Plans:
- Marketing Mix: Execute the planned strategies by managing the 4 Ps of marketing - Product, Price, Promotion, and Place.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources effectively to support marketing activities and achieve desired outcomes.
- Timelines and Budgeting: Set timelines and budgets to ensure efficient execution of marketing plans.
- Coordination: Coordinate with various departments within the organization to ensure a seamless implementation of marketing strategies.
4. Managing Marketing Efforts:
- Monitoring and Control: Regularly monitor and assess marketing performance against set objectives and make necessary adjustments.
- Feedback and Evaluation: Gather feedback from customers, sales teams, and other stakeholders to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing efforts.
- Marketing Metrics: Track key performance indicators (KPIs) such as sales revenue, market share, customer satisfaction, and return on investment (ROI).
5. Reviewing and Adapting:
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously review and adapt marketing strategies based on market dynamics, competition, and customer feedback.
- Market Feedback: Gather insights from customer surveys, focus groups, and market research to identify emerging opportunities and challenges.
- Strategic Planning: Incorporate the learnings from previous marketing efforts into the organization's overall strategic planning process.
By following these five steps, marketing managers can effectively plan, implement, and evaluate their marketing activities to achieve organizational objectives.
Philosophies of Marketing Management
Production Concept
- During the early days of the Industrial Revolution, the need for industrial goods began to grow, but there were only a few producers.
- Because of this, the demand for products was greater than the supply.
- Selling products was easy; anyone who could make the goods was able to sell them.
- Therefore, the main focus of business activities was on making more goods.
- It was thought that companies could make more profits by producing items in large quantities, which would lower the average production cost.
- People assumed that consumers would prefer products that were easily available and at a reasonable price.
- Thus, having products that were both available and affordable was seen as the key to a company's success.
- As a result, more attention was given to improving the efficiency of production and distribution within firms.
Product Concept
- In the past, businesses focused mainly on production capacity, which led to an increase in the supply of products over time.
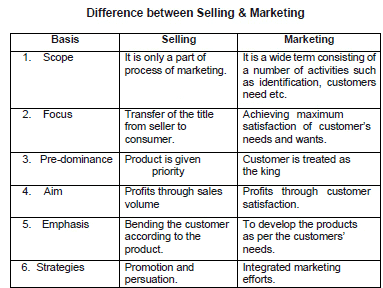
- There is often confusion between marketing and selling. Many people think these two terms mean the same thing.
- Marketing includes a wide range of activities, and selling is just a small part of it.
- For instance, a marketer of televisions will do several things before making a sale, such as:
- Deciding on the type and model of televisions to produce.
- Setting the price for each television.
- Choosing the stores where the televisions will be sold. - The role of selling is limited to promoting goods and services through:
- Salesmanship
- Advertising
- Publicity
- Short-term incentives - The goal of selling is to transfer the title of the product from the seller to the buyer, essentially turning the product into cash.
- Just having a low price for a product does not guarantee more sales or the survival and growth of a business.
- As the supply of products increased, customers began to seek out items that were of higher quality, better performance, and more features.
- Consequently, businesses shifted their focus from producing large quantities to improving the quality of their products.
- This change in focus meant that businesses concentrated on continuously enhancing product quality and adding new features.
- Therefore, product improvement became essential for a firm’s profit maximization, under the idea of product orientation.
Sales Concept
- Over time, the marketing environment changed even more.
- As businesses grew, their ability to supply goods improved, leading to more competition among sellers.
- Simply having good quality products and availability was not enough for companies to survive and grow, as many sellers offered similar quality.
- This situation made it more important for businesses to attract and persuade customers to purchase their products.
- The approach to business changed; it was thought that customers wouldn't buy enough unless they were properly convinced.
- Therefore, companies needed to engage in aggressive selling and promotional activities to encourage purchases.
- Techniques like advertising, personal selling, and sales promotions became essential for selling products.
- As a result, businesses shifted their focus to pushing sales through assertive tactics aimed at persuading customers to buy.
- The emphasis was placed on making sales by any means necessary.
- It was assumed that customers could be manipulated, but what was overlooked was that in the long term, customer satisfaction is what truly matters.
Marketing Concept
- Marketing orientation means that focusing on what customers need is crucial for a company's success in the market.
- It suggests that over time, a company can reach its goal of making more profit by understanding what current and potential customers want and effectively meeting those needs.
- All decisions made within a company are based on the perspective of the customers.
- In simpler terms, customer satisfaction is the center of every decision in the company.
- For instance, decisions about what product to make, what features it should have, how much to charge for it, and where to sell it are all influenced by what customers desire.
- If customers want features like a double door in a refrigerator or a separate space for a water cooler, the company will create a refrigerator with those features and set a price that customers are willing to pay.
- When all marketing choices are made with this customer-focused approach, selling becomes easier and happens naturally.
- Essentially, the main job of a company is to recognize a need and fulfill it.
- This idea means that people buy products and services not just because of their quality, packaging, or brand name, but because they meet a specific need of the customer.
- Therefore, understanding and responding to customer needs is essential for any company's success.
- The marketing concept relies on the following key points:
- Identifying the market or customers who are the focus of the marketing efforts.
- Understanding the needs and wants of these customers in the target market.
- Creating products or services that satisfy the needs of the target market.
- Meeting the needs of the target market better than competitors do.
- Achieving all of this while making a profit.
- So, the marketing concept centers on customer needs, and customer satisfaction is the way to achieve the company's goal of maximizing profit.
- The ultimate aim of marketing is to create value for customers while also making a profit.
Societal Marketing Concept
- The marketing idea discussed earlier is not sufficient when we consider serious social issues like environmental pollution, deforestation, resource shortages, overpopulation, and inflation.
- Activities that meet human needs but harm society as a whole cannot be justified.
- Businesses should not only focus on the immediate needs of consumers but also take into account broader concerns for long-term social welfare.
- The societal marketing concept emphasizes that organizations must understand the needs and wants of their target market.
- It is important for businesses to provide what customers want in an effective and efficient way while also ensuring the long-term well-being of both consumers and society.
- This concept extends the traditional marketing idea by including a focus on the long-term welfare of society.
- In addition to ensuring customer satisfaction, it also addresses important social, ethical, and ecological issues related to marketing.
- Many important issues need to be addressed within this framework.
Functions Of Marketing
- Marketing involves the transfer of goods and services from producers to consumers or users.
- The main goal of marketing is to maximize the satisfaction of customers' needs.
- From a management perspective, marketing includes several activities.
- These activities are essential for ensuring that the marketing process is effective and meets the objectives.
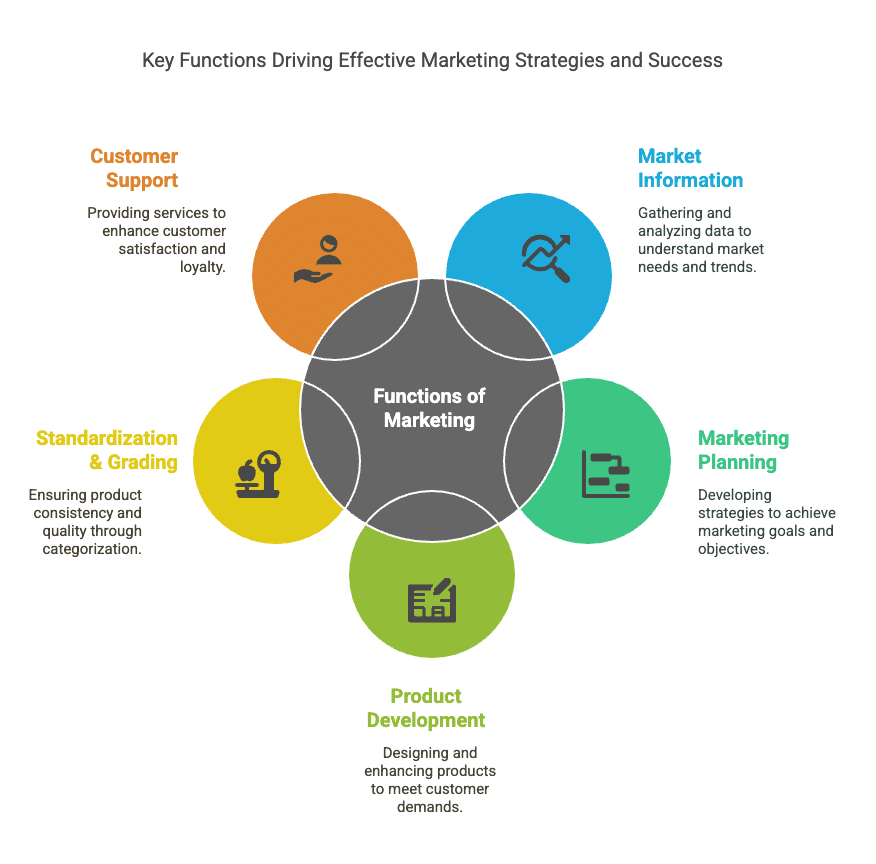
1. Gathering and Analysing Market Information
- One key role of a marketer is to collect and analyze market data.
- This process helps in understanding the needs of customers, which is essential for making effective decisions regarding marketing products and services.
- Analyzing market information is crucial for evaluating available opportunities and threats, as well as the strengths and weaknesses of a business.
- Such analysis aids in determining which opportunities the organization should pursue.
- For instance, there is forecasted rapid growth in various sectors of the Indian economy, such as the use of the Internet and the cellphone market.
- Businesses must carefully assess their strengths and weaknesses to decide which of these growing areas they should enter or expand into.
- With the rise of computers, a new trend has developed in gathering market information.
- More companies are now using interactive websites to collect customer feedback and opinions before making significant business choices.
- For example, a popular Hindi TV news channel asks its viewers to vote via SMS on which of the day’s main news stories they want to see presented in detail during prime time.
- This approach ensures that viewers can listen to the news story that interests them the most.
2. Marketing Planning
- An essential task for a marketer is to create suitable marketing plans that help meet the organization's marketing goals.
- For instance, if a marketer sells colour TVs and currently holds a 10 percent market share in the country, their goal might be to increase this to 20 percent within the next three years.
- To achieve this goal, the marketer needs to develop a comprehensive marketing plan that addresses several key areas.
- This plan should include strategies for:
- Boosting the production levels
- Enhancing product promotion - Additionally, the marketer must outline specific action programs that detail how these objectives will be accomplished.
3 . Product Designing and Development
- Another key area in marketing involves product design and development.
- The design of a product plays a significant role in attracting its intended customers.
- A well-designed product can enhance its performance and provide a competitive edge in the market.
- For instance, when considering the purchase of a product, such as a motorbike, we evaluate various aspects.
- We look at features like price and fuel efficiency, but we also pay attention to the design elements.
- These design elements include aspects such as the shape and style of the motorbike.
4. Standardisation and Grading
- Standardisation means creating products that meet set specifications. This helps achieve uniformity and consistency in what is produced.
- It assures buyers that the products meet certain standards for quality, price, and packaging.
- Standardisation also reduces the need for inspection, testing, and evaluation of products.
- Grading is the method of sorting products into different categories based on key features like quality and size.
- Grading is especially important for items that do not follow set specifications, such as agricultural products like wheat and oranges.
- Grading helps ensure that products are of a certain quality and can lead to higher prices for high-quality goods.
5. Packaging and Labelling
- Packaging involves creating and developing the container for products.
- Labelling is the process of designing and creating the label that goes on the package.
- The label can range from a basic tag to intricate designs.
- Both packaging and labelling are crucial in today's marketing, often seen as the foundations of marketing strategies.
- Packaging serves two main purposes:
- It protects the products.
- It acts as a promotional tool to attract customers. - Customers often judge the quality of a product based on its packaging.
- Many well-known consumer brands, like Lays and Uncle Chips for potato wafers, Clinic Plus for shampoos, and Colgate for toothpaste, have successfully used packaging to enhance their brand image.
6. Branding
- A key choice for marketing many consumer products is whether to sell them under a generic name (which is the name of the product category, like Fan or Pen) or under a brand name (such as Pollar Fan or Rottomac Pen).
- Using a brand name helps to create product differentiation, meaning it provides a way to tell the products of one company apart from those of competitors.
- This differentiation is important because it helps to build customer loyalty and can boost sales.
- Important decisions regarding branding include determining the branding strategy. This involves deciding if each product will have its own unique brand name or if the same brand name will be used for all products made by the company.
- For example, a company like Phillips may use the same brand name for its bulbs, tubes, and televisions, while Videocon may use it for its washing machines, televisions, and refrigerators.
- The choice of brand name is a crucial factor in the success of a product.
7. Customer Support Services
- Marketing management plays a crucial role in creating services that assist customers.
- These services include:
- After-sales support
- Handling customer complaints
- Adjustments
- Credit services
- Maintenance services
- Technical support
- Consumer information
- All these services aim to provide the highest level of satisfaction to customers.
- Customer satisfaction is essential for achieving marketing success today.
- Effective customer support services help to:
- Encourage repeat sales from customers.
- Build brand loyalty for products.
8. Pricing of Product
- The price of a product is the amount of money that customers need to spend to buy it.
- Importance of Price: The price is a key factor that can influence whether a product does well or poorly in the market.
- Demand and Price Relationship: There is a clear connection between the demand for a product or service and its price.
- General Rule: Usually, if the price is lower, the demand for the product will be higher, and if the price is higher, the demand will be lower.
- Marketers' Responsibilities: It is essential for marketers to carefully examine the factors that influence a product's price.
- Key Decisions: Marketers need to make several important choices regarding pricing, which include:
- Setting Pricing Objectives: Establishing goals for how pricing should work.
- Choosing Pricing Strategies: Deciding on methods to set prices effectively.
- Determining the Price: Figuring out the actual price of the product.
- Adjusting Prices: Making changes to prices as necessary.
9. Promotion
- The goal of promoting products and services is to inform customers about what the company offers, including its features, and to encourage them to make a purchase.
- There are four main ways to promote products:
- Advertising
- Personal Selling
- Publicity
- Sales Promotion
- A marketer needs to make several important decisions regarding the promotion of products and services, such as:
- Determining the promotion budget
- Selecting the promotion mix, which refers to the combination of different promotional tools that will be used
- Managing the overall promotion strategy
10. Physical Distribution
- Managing physical distribution is a crucial part of marketing goods and services.
- There are two main areas to focus on in this function:
- The first area involves deciding on channels of distribution, which refers to the marketing intermediaries like wholesalers and retailers that will be used.
- The second area is about the physical movement of products from where they are made to where customers need them for use or consumption.
- Key decisions in physical distributioninclude:
- Managing inventory: This means keeping track of the stock levels of goods.
- Storage and warehousing: This involves finding suitable places to keep the products until they are needed.
- Transportation: This is about moving goods from one location to another efficiently.
11. Transportation
- Transportation refers to the physical movement of goods from one location to another.
- The users of products, especially consumer goods, are often spread out and located far from where these goods are made.
- It is important to move these products to the areas where they are needed for use or consumption.
- For instance, tea that is produced in Assam must be transported not only within the state but also to distant places such as Tamil Nadu, Punjab, Jammu and Kashmir, Haryana, and Rajasthan, where it is consumed.
- A marketing firm needs to evaluate its transportation requirements by considering various factors, including:
- Type of product
- Cost
- Location of the target market
- The firm must then make decisions regarding:
- Mode of transportation to be used
- Other related aspects of transportation
12. Storage or Warehousing
- There is often a delay between when goods are made or bought and when they are sold or used.
- This delay can happen because of:
- Unpredictable demand: For example, products like woollen clothes or raincoats may not be needed all the time.
- Unreliable supply: Some items, like agricultural products such as sugarcane, rice, wheat, and cotton, are produced only in certain seasons.
- To ensure that products are available in the market without interruptions, it is essential to have good storage facilities.
- It is also important to keep enough stock of goods to:
- Handle unexpected delays in delivery.
- Meet sudden increases in demand.
- In marketing, various parties like manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers are responsible for the storage of products.
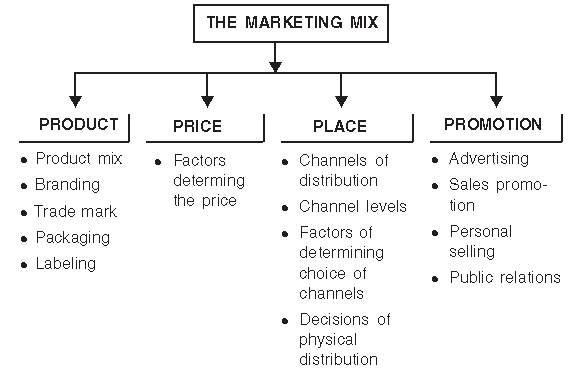
Marketing Mix
Marketing mix refers to ingredients or the tools or variables which the marketeer mixes in order to interact with a particular market. 11.8.1 Elements of Marketing Mix: The four main elements of the marketing mix as classified by McCarthy are:
A. Product
B. Price
C. Promotion
D. Place/Physical Distribution
These elements are more popularly known four Ps of marketing.
1. Product Mix
- Product means goods or services, or anything valuable, offered for sale.
- In marketing, a product includes both tangible and intangible features that can be exchanged for value and meet customer needs.
2. Price Mix
- The demand for a product or service is linked to its price.
- Typically, a lower price leads to higher demand, and vice versa.
- Marketers must set pricing objectives and analyse various factors to determine prices.
- Considerations include after-sales services, complaint handling, spare parts availability, and credit terms to ensure customer satisfaction.
3. Promotion Mix
- Promotion involves informing customers about the firm's products and persuading them to buy.
- The key methods of promotion include advertising, personal selling, publicity, and sales promotion.
4. Place Mix
- The fourth element is the physical distribution of products and services.
- This ensures goods are available at the right place and time for the right customers.
- Once products are manufactured, packaged, priced, and promoted, they must be accessible to customers in appropriate quantities.
Role of Marketing: By adopting a marketing-oriented approach, any organisation, whether profit or non-profit, can effectively meet its goals. Furthermore, marketing plays a crucial role in a country's economic growth and enhances people's living standards.
Products
- From the customer's perspective, a product is a collection of features that is bought for its ability to meet specific needs.
- A buyer purchases a product or service for what it offers or the advantages it brings.
- There are three main types of benefitsa customer may look for when buying a product:
- Functional benefits: These are practical advantages, like the utility of a product.
- Psychological benefits: These relate to how a product makes a person feel, such as feelings of prestige or satisfaction.
- Social benefits: These involve the acceptance or recognition a person gains from others when using a product.
- For instance, buying a motorcycle offers the functional benefit of transportation. At the same time, it can fulfill a psychological need for status and provide a social benefit by helping the rider be accepted within a community of motorbike enthusiasts.
- Therefore, when designing a product, all these factors—functional, psychological, and social—should be taken into account.
Classification of Products
Products can be divided into two main types:
- Consumer Products
- Industrial Products
1. Consumer Products
These are the items bought by individuals for their personal use and to meet their needs and wants. Examples include: soap, edible oil, food items, clothes, toothpaste, and fans.
Consumer products can be further categorized into three groups:
- 1. Convenience Products:These are items that people buy frequently, quickly, and with little effort.
- Examples include: cigarettes, ice cream, medicine, newspapers, stationery, and toothpaste.
- These products usually have a low price and are bought in small quantities.
- 2. Shopping Products:These are items where buyers spend time comparing factors like quality, price, style, and suitability at different stores before making a purchase.
- Examples include: clothes, shoes, jewelry, furniture, radios, and televisions.
- 3. Specialty Products:These are unique items that have special features, leading people to make extra efforts to buy them.
- These products often have loyal customers who are willing to go out of their way to purchase them.
- Examples include rare artworks or antiques; people might travel long distances to acquire these items.
- In daily life, we notice people frequently visiting specific hair salons, restaurants, or tailors.
- The demand for these products tends to be stable, meaning that even if prices rise, people will still want to buy them.
2. Industrial Products
Industrial products are items used as inputs to create other products.
- Examples of industrial products include:
- Raw materials
- Engines
- Lubricants
- Machines
- Tools
These products are intended for business and non-personal use in the production of other goods.
- The market for industrial products includes:
- Manufacturers
- Transport agencies
- Banks
- Insurance companies
- Mining companies
- Public Utilities
Classification of Industrial Goods
Industrial goods are classified into three main categories:
1. Materials and Parts:
These are items that are completely used in the manufacturing of products. They can be divided into:
- Raw materials: This includes farm products like cotton, sugar cane, and oil seed, as well as natural products like minerals (e.g., crude petroleum, iron ore), fish, and lumber.
- Manufactured materials and parts: This includes
- Component materials like glass, iron, and plastic
- Component parts such as tyres, electric bulbs, steering wheels, and batteries.
2. Capital Items:
These are goods used in producing finished products, including:
- Installations: Such as elevators and mainframe computers.
- Equipment: Such as hand tools, personal computers, and fax machines.
3. Supplies and Business Services:
These are goods and services that are short-lasting and help in developing or managing the final product. They include:
- Maintenance and repair items: Such as paint and nails.
- Operating supplies: Such as lubricants, computer stationery, and writing paper.
Branding
Giving a name/a sign; a symbol etc. to a product e.g.: Pepsi, Nike:
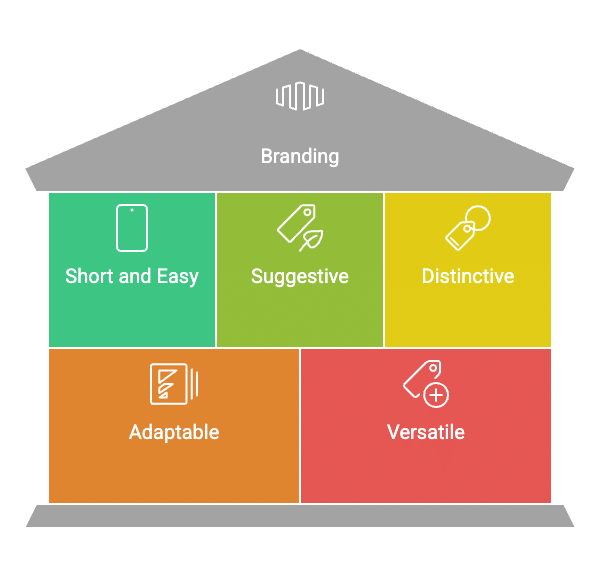
Qualities of a Good Brand Name
- Short and Easy: The brand name should be brief and simple to say, spell, recognise, and remember, such as Ponds, VIP, Rin, and Vim.
- Suggestive:. good brand should hint at the product's benefits and features, being suitable for its purpose.
- Distinctive: The brand name must be unique, helping it stand out from the competition.
- Adaptable: It should be flexible enough for packaging, various advertising methods, and multiple languages.
- Versatile: The name should be broad enough to fit new products added to the range.
- Legally Protectable: It should be able to be registered and legally defended.
- Staying Power: The selected name should endure over time, avoiding becoming outdated.
Advantages of Branding
- Branding helps marketers to set their products apart from those of competitors.
- It provides various benefits to both sellers and consumers.
- Branded products are easily recognizable for consumers.
- Branding encourages customer loyalty, leading to repeat purchases.
- It maintains a certain level of quality: if quality changes, customers can complain to the manufacturer.
- A major benefit of branding is the legal protection it offers, allowing companies to secure exclusive rights to their brand names and marks, stopping competitors from using them without permission.
- Good brand names are distinctive, adaptable, and enduring. They should be short, easy to say, spell, recognise, and remember. A brand should also hint at the product's benefits and qualities, be suitable for various advertising media and languages, and be flexible enough to include new products in the line.
 |
Download the notes
Chapter Notes - Marketing Management
|
Download as PDF |
Packaging
Act of designing and producing the container or wrapper of a product. Good packaging often helps in selling the product so it is called a silent salesman.
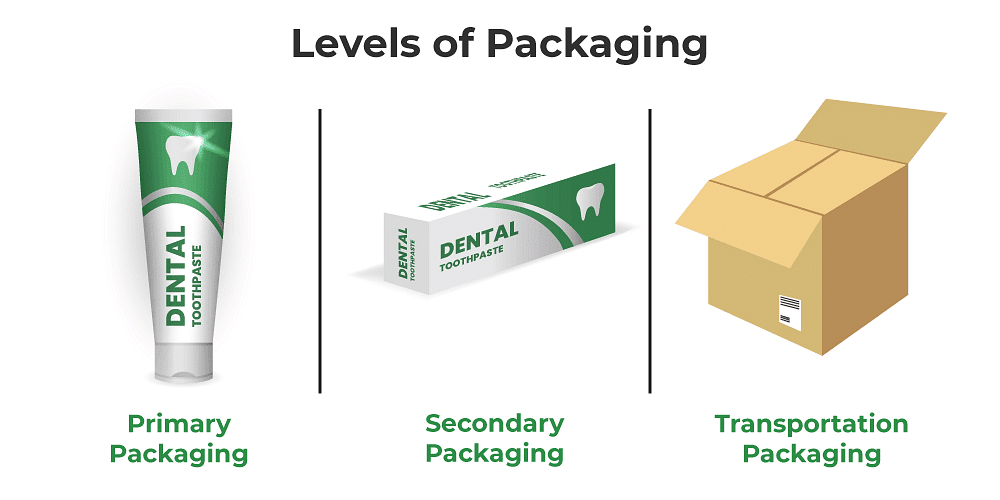
Levels of Packaging
- Primary Package: refers to the product’s immediate container e.g. toffee in a wrapper, or a matchbox.
- Secondary Package: refers to additional layers of protection that are kept till the product is ready for use e.g. a Colgate toothpaste usually comes in a cardboard box.
- Transportation Package: refers to further packaging components necessary for storage, identification, and transportation e.g. package of toffees are put into corrugated boxes for storing at a manufacturer’s warehouse and for transportation.
Functions of Packaging
1. Product Identification:
Packaging helps consumers easily identify products, such as the red packaging of Colgate or the design of a Ponds cream jar.
2. Product Protection:
It safeguards products from spoilage, breakage, leakage, theft, damage, and weather effects during storage, distribution, and transport.
3. Facilitating Use of the Product:
The design of the package should allow for easy opening, handling, and use, which is essential for items like cosmetics, medicines, and toothpaste tubes.
4. Convenience:
Packaging enhances convenience, improving the overall experience for consumers when using the product.
5. Product Promotion:
Packaging can serve as a promotional tool, using eye-catching colours, images, or fonts to grab attention at the point of sale, sometimes more effectively than traditional advertising.
6. Innovational Opportunity:
Recent advancements in packaging have transformed marketing, allowing products like milk to be stored without refrigeration for several days. Innovations in pharmaceuticals and soft drinks have also expanded marketing possibilities.
7. Product Differentiation:
Packaging plays a critical role in differentiating products, as aspects like colour, size, and material influence customer perceptions of quality. For instance, the packaging of paint or hair oil can indicate the expected quality of the product inside.
8. Labelling:
Designing product labels is an essential marketing task, providing important information about the product, its contents, usage instructions, and other details. For example, a toothpaste package might list the "Ten Teeth and Gum Problems" it aims to address.
Advantages of Packaging
- Rising Standards of Health and Sanitation: As living standards improve, more people prefer packaged goods because they are less likely to be adulterated.
- Self-Service Outlets: The popularity of self-service stores, especially in larger cities, has shifted some promotional roles from personal selling to packaging.
- Innovational Opportunity: Recent packaging advancements have transformed marketing. For example, milk can now be kept fresh for several days without refrigeration due to new materials.
- Product Promotion: Packaging also serves promotional purposes, using eye-catching colours, images, or fonts to draw attention at the point of sale. In self-service environments, this aspect of packaging is particularly critical.
Labelling
Labelling means putting identification marks on the package. The label is a carrier of information & provides information like - the name of the product, name of the manufacturer, contents of the product, expiry, and manufacturing date, general information for use, weight, etc. Labels perform the following functions:
1. Identify the product: It helps the customers to identify the product from the various types available. For example, We can easily identify Cadbury chocolate from the various chocolates by the purple color of its label.
2. Describe the product and specify its contents: The manufacturer prints all the information related to the product.
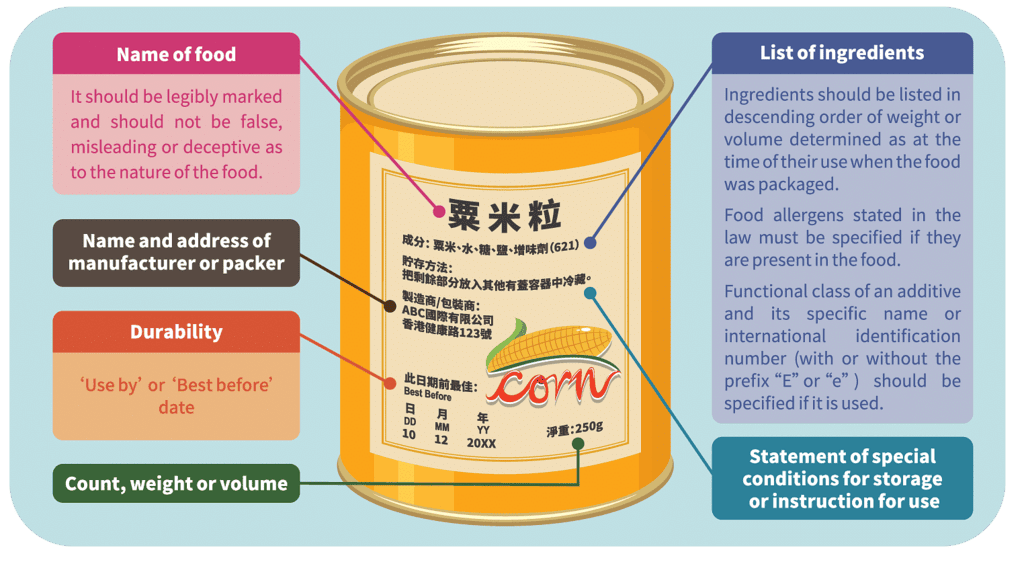
3. Grading of products: With the help of labels, products can be graded in different categories for example Brook Bond Red Label, Brook Bond Yellow Label, Green Label, etc.
4. Helps in the promotion of products: Attractive and colorful labels excite the customers and induce them to buy the products. For example, 40% extra free is mentioned on detergent etc.
5. Providing information required by law: There is a legal compulsion to print batch no, contents, max retail price, weight/volume on all the products, and statutory warning on the packet of cigarettes, “Smoking is injuries of health”: In case of hazard on/poisonous material appropriate safety, warnings need to be put.
Price Mix
Meaning and Concept of Price
Price may be defined as the amount of money paid by a buyer (or received by a seller) in consideration of the purchase of a product or a service. Pricing is crucial for manufacturers, customers, and intermediaries. A customer will buy a product only when he perceives that the value of a product is at least equal to the value of money, which he has to pay in the form of price. Before framing any pricing policy following factors should be considered:
1. Pricing Objectives
(a) to maximize profits in the short term-tend to charge maximum price.
(b) Obtain a large share of the market i.e., by maximizing sales it will charge a lower price.
(c) Firm is operating in a competitive market it may charge a low price for it.
2. Cost of Production: This needs to be fully realized before fixing prices.
3. Demand: High Demand and less supply may permit an increase in price while low demand and more supply may not allow an increase in price.
4. Competition in the Market: Prices of competitors need to be considered before fixing prices.
5. Government Policies: Products regulated by government pricing regulations need to be priced as per government policies.
Place Mix/Physical Distribution Mix
Covers all the activities required to physically move goods from manufacturers to the customer Important activities include.
1. Order Processing:
- In a typical buyer-seller relationship, the first step is placing an order.
- Products travel from producers to customers through various channels, while orders go back from customers to producers.
- An efficient physical distribution system ensures orders are processed accurately and quickly.
- If not, goods may arrive late or with incorrect quantities or specifications, leading to customer dissatisfaction and potential loss of business.
2. Transportation:
- Transportation is the method of moving goods and raw materials from where they are made to where they are sold.
- It is a vital part of physical distribution and gives companies flexibility in setting prices.
3. Inventory Control:
- Good inventory control is essential for managing stock levels effectively.
- It ensures there is enough inventory to meet demand without having too much, which helps reduce storage costs and avoid stock shortages.
4. Warehousing:
- Warehousing is necessary to bridge the time gap between product creation and when it is needed for sale.
- Proper storage is crucial to maintain a smooth market flow and to protect against delays in delivery or unexpected demand increases.
Channels of Distribution
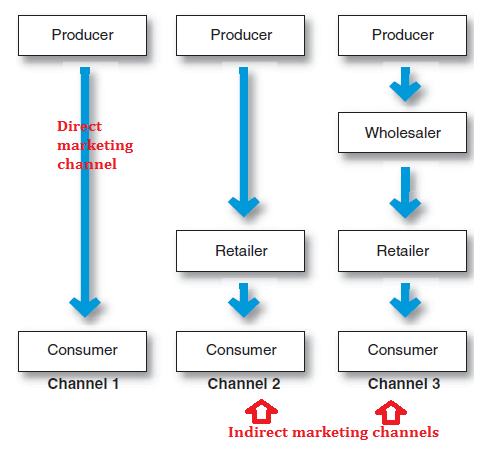
Direct Channel — Manufacturer-Customer
Indirect Channel —
1. Manufacturer-Retailer-Customer.
2. Manufacture-Wholesaler-Retailer-customer.
3. Manufacture → Agent → Wholesaler → Retailer → Customer
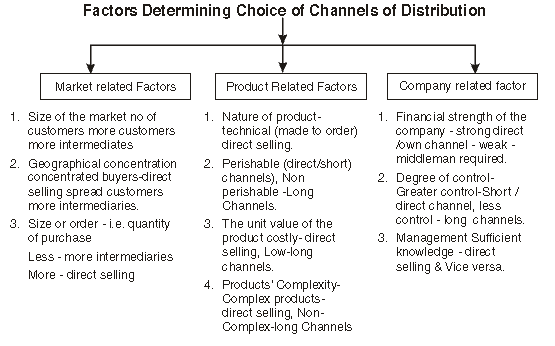
Factors Determining Choice of Channels of Distribution
The choice of the appropriate channel of distribution is a very important marketing decision, which affects the performance of an organization. Whether the firm will adopt direct marketing channels or long channels involving a no. of intermediaries is a strategic decision.
Promotion Mix
The promotion mix is the set of promotional tools that an organisation uses to meet its communication goals. It involves various methods of communication to inform and convince customers about a company’s products. These methods can be combined in different ways to achieve promotional aims.

Tools/Elements of Promotion Mix
1. Advertising: Most commonly used tool of promotion. It is an impersonal form of communication, which is paid by the marketers (sponsors) to promote goods and services. Common mediums are newspapers, magazines, television & radio.
Role of Importance of Advertising:
1. Enhancing customer satisfaction and confidence.
2. Helpful in increasing the demand for existing products.
3. Helpful to increase the market share.
4. Helpful in generating more employment.
5. Helpful in the economic development of the country.
6. Knowledge of various products.
7. No fear of exploitation.
Objections against Advertising
Though advertising is one of the most frequently used mediums for the promotion of goods & services it attracts a lot of criticism/objections against it, which are as follows:
- Increased Product Price: Advertising costs can unnecessarily raise product prices, which consumers ultimately pay. For instance, a TV ad can cost marketers several lakhs of rupees, while print ads in newspapers or magazines also require significant investment. However, this spending can drive demand for the product, as more potential buyers become aware of it. Increased demand can lead to higher production, which can lower the per-unit cost as the total cost is spread over more units.
- Confusion to Customers: The sheer volume of advertisements for similar products can confuse consumers. Competing brands of detergent, for example, may make similar claims, making it hard for customers to decide which to trust. However, proponents of advertising argue that consumers are rational and can use the information provided to make informed purchasing decisions.
- Encouraging the Sale of Inferior Products: Advertising does not always differentiate between high-quality and low-quality products, potentially misleading consumers about what they are buying. This can lead to the promotion of inferior products, making it seem like consumers are making informed choices when they may not be.
- Advertisement of Bad Tastes: Some advertisements promote lifestyles that may not be socially acceptable, which can harm human dignity. This is often seen in the portrayal of events or models that clash with societal values.
- Undermines Social Values and Promotes Materialism: Advertising can lead to dissatisfaction as people become aware of new products, prompting them to want more and distorting social relationships. Yet, advertising can also inform consumers about better alternatives. Ultimately, the choice to buy rests with consumers, who may feel motivated to work harder to afford what they desire.
Personal Selling
Personal selling consists of contacting prospective buyers of the product personally i.e. face to face interaction between seller and buyer for the purpose of sale.
Features of the Personal Selling
1. Personal contact is established under personal selling.
2. Oral conversation.
3. Quick solution to queries.
4. Receipt of additional information.
5. Development of relationships with prospective customers which may become important in making sales.
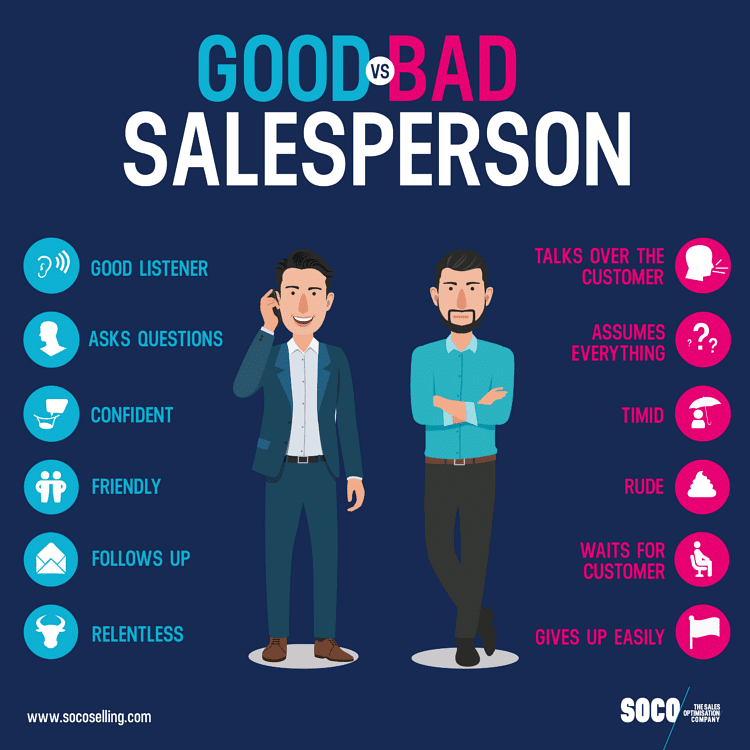
Qualities of a Good Salesman
1. Physical Qualities: Physical qualities include personality health, stamina, and tolerance. A salesman can instantly connect with customers if he is good-looking and smart.
2. Mental Qualities: These include mainly skills, mental alertness, imagination, and self-confidence.
3. Technical Qualities: He should have full and updated knowledge about the product he is selling-Its features, price, and variety available. He should be aware of the nature of work carried on by the firm, he is working for.
4. Good communication skills: He should be able to develop a good conversation with the customer. He should be confident while he is communicating and should be able to answer all the queries of the customer satisfactorily.
5. Honesty: It is a very important quality of a good salesman. In order to establish the goodwill of the firm he must be honest and sincere in performing his duty. A salesman who resorts to selling inferior goods, charging higher rates, providing wrong information, giving exaggerated claims, etc. will cause a decline in the goodwill of the firm in the long run.
6 . Courtesy: A Salesman who is polite and courteous generates buyer’s confidence selling a product becomes easy for him.
7. Persistent: “Never give up”, is the spirit that a salesman should have. Making the customer buy the maximum amount of a product is the ultimate task given to him.
8. Capacity to inspire trust: The salesman should have the convincing power to develop the belief in a customer that the product he is buying is the best product in the market.
Sales Promotion
Techniques
Short-term incentives are designed to encourage buyers to make immediate purchases of a product/service.
Sales promotion techniques in business studies refer to various strategies and activities implemented by businesses to stimulate sales, attract customers, and promote their products or services. These techniques are designed to create immediate customer interest and encourage purchasing behaviour. Here are some commonly used sales promotion techniques:
1. Coupons and Discounts: Offering coupons or discounts on products or services is a popular sales promotion technique. This involves providing customers with a price reduction or a specific discount code that they can use during their purchase. Coupons and discounts can attract new customers, encourage repeat purchases, and create a sense of urgency.
2. Free Samples: Providing free samples of a product allows potential customers to try it without any cost. This technique aims to generate interest, create a positive brand experience, and ultimately increase sales. Free samples can be distributed at stores, through mailings, or online.
3. Contests and Sweepstakes: Organizing contests or sweepstakes can generate excitement and engagement among customers. Participants have a chance to win prizes by completing certain actions, such as making a purchase, submitting an entry, or sharing content on social media. Contests and sweepstakes help increase brand awareness, attract new customers, and encourage customer loyalty.
4. Buy One, Get One (BOGO) Offers: BOGO offers involve giving customers an additional product or service for free or at a discounted price when they purchase one. This technique incentivizes customers to make a purchase by offering extra value. It can also help clear out excess inventory or introduce new products.
5. Loyalty Programs: Loyalty programs are designed to reward and retain existing customers. Customers earn points or rewards based on their purchases or engagement with the business. These rewards can be redeemed for discounts, free products, exclusive offers, or other incentives. Loyalty programs encourage repeat purchases and build customer loyalty.
6. Bundling: Bundling involves combining multiple products or services together and offering them at a discounted price. This technique encourages customers to purchase more items than they initially intended, as they perceive greater value in the bundled offer. Bundling can help increase sales and introduce customers to new products.
7. Flash Sales: Flash sales are limited-time promotions that offer significant discounts or exclusive deals for a short period. These sales create a sense of urgency and encourage immediate purchases. Flash sales are often conducted online, with a countdown timer or limited quantities available, to maximize the sense of urgency.
8. Referral Programs: Referral programs incentivize customers to refer their friends, family, or acquaintances to the business. Customers are rewarded with discounts, credits, or other incentives when their referrals make a purchase or become customers themselves. Referral programs leverage the power of word-of-mouth marketing and can expand the customer base.
These sales promotion techniques are just a few examples of the strategies businesses use to boost sales and attract customers. The choice of techniques depends on the target audience, product or service offering, marketing objectives, and budgetary considerations of the business.
Public Relations
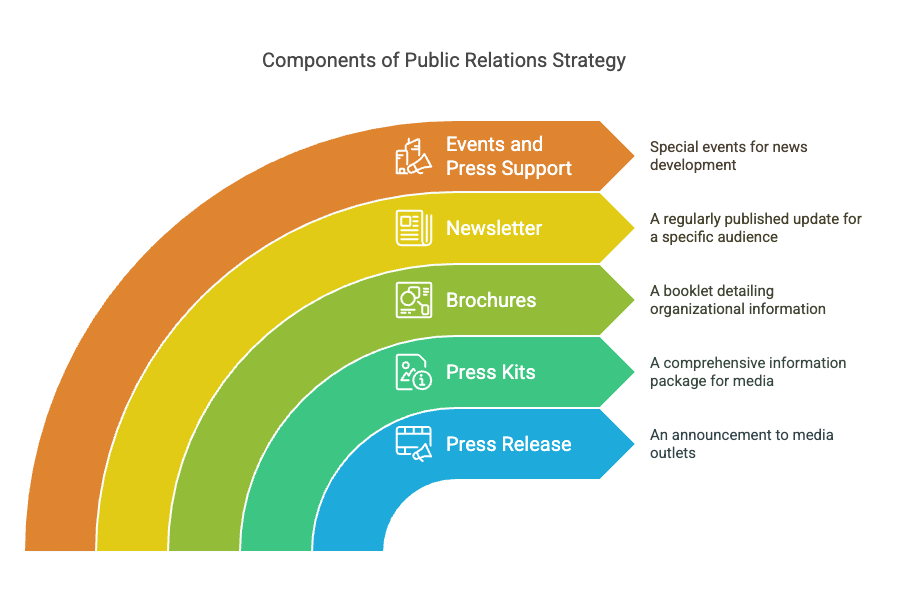
“The Chartered Institute of Public Relations” defines Public Relations as a strategic management function that adds value to an organization by helping it to manage its reputation Public relations covers a wide range of tactics, usually involving providing information to independent media sources in the hope of gaining favorable coverage. It also involves a mix of promoting specific products, services, and events and promoting the overall brand of an organization which is an ongoing tact. Public Relations tools include:
1. Press Release: A press release is an announcement of an event, performance, or other newsworthy item that is issued to the press by a public relations professional of an organization. It is written in the form of a story with an attractive heading so that the media newspaper/radio/television/internet.
2. Press Kits: It is a comprehensive package of information outlining a company’s quick grasp and circulating the message through products and services most frequently sent to members of the press. It includes A brief company biography. Information of senior management. Comments from customers. Reprints of newspaper and magazine articles. Photos of products.
3. Brochures: It is a booklet published by the organization which contains the organization’s background, ethics, vision, mission, past, present, and future projects, its CISP, etc. E.g.: a brochure was given to new employees to give them a gist of the organization.
4. Newsletter: It is a printed publication produced at regular intervals focusing on a particular set of people. The content of a newsletter is presented in a writing style that is less formal and letter-like. For example, a newsletter published by a college consists of information about activities conducted during a particular period, special achievements by students or teachers, etc.
5. Events and Press support: Special events are acts of news development. The ingredients are time, place, people, activities, drama, and showmanship; one special event may have many subsidiary events, such as luncheons, banquets, contests, speeches, and many others as part of the buildup.
6. Conferences and Seminars: Conferences and seminars are conducted for making people aware of the organization. For example, travel companies generally call prospective clients and offer travel packages. The members are contacted by telephone and asked to attend the seminar.
7. Websites: A website acts as a window for the outside world to know an organization. So it is designed not just to serve as a resource for members, but also to present a positive message to non-members who are browsing through.
Role of 'PR' in an Organisation
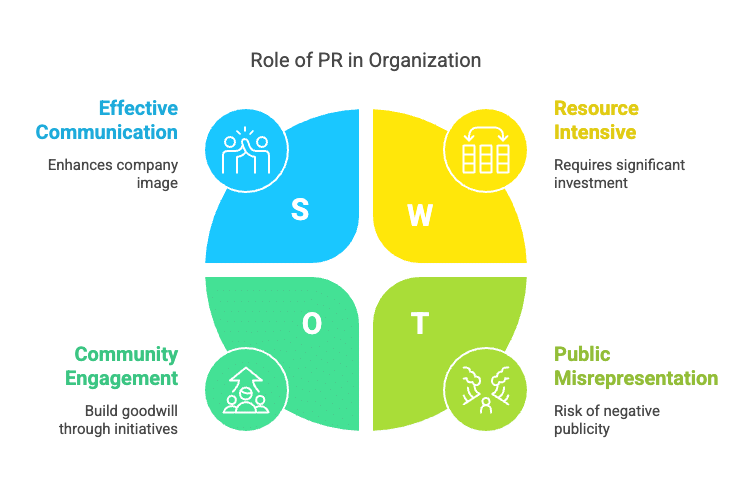
The role of public relations can be understood through the various functions performed by the department. Public relations serves as a vital tool for the marketing department, benefiting the overall business. The public relations department carries out five key functions:
- Publicity: Publicity is akin to advertising but is a non-paid form of communication. It occurs when positive news about a product or service is shared in the mass media. For instance, if a manufacturer develops a car engine that operates on water rather than petrol, and this is reported by the media, it is regarded as publicity, benefiting the manufacturer.
- Corporate Communication: To enhance its image, the organisation must communicate effectively with the public and its employees. This is achieved through newsletters, annual reports, brochures, articles, and visual materials. These resources help companies reach and influence their target audiences. Speeches by executives at trade meetings or fairs can significantly enhance the company's image, as can media interviews and responses to inquiries.
- Lobbying: The organisation engages with government officials and ministers regarding policies that impact business and the economy. The government also aims to maintain good relations with business associations and seeks input from key stakeholders when creating policies. The public relations department must actively promote and interpret regulations that affect the organisation.
- Counselling: Public relations professionals advise management on issues affecting the public and the company's stance on these matters. The organisation can enhance its goodwill by investing in community initiatives.
- Publicity Management: The public relations department works with the media to present accurate information about the company. This is essential, as news can be misrepresented if sourced elsewhere. Creating news stories requires skill in both development and research, and getting the media to accept press releases can be challenging.
Managing the public's perception of an organisation is crucial for the marketing department. Effective communication with customers, suppliers, and dealers is key to boosting sales and profits. Additionally, other members of the public, who may have an interest in the company and its products, can influence the business's ability to reach its goals. Therefore, it's vital to manage public opinion and maintain a positive relationship with the public consistently. Public relations encompass a range of activities aimed at sustaining a good image and building goodwill.
|
50 videos|195 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Marketing Management Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the meaning of marketing? |  |
| 2. What is the role of a marketer or seller in marketing? |  |
| 3. What are the important features of marketing? |  |
| 4. What are the functions of marketing or marketing activities? |  |
| 5. What are the concepts and philosophies of marketing? |  |






















