Consumer Protection Chapter Notes | Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce PDF Download
Introduction
- Every person is a consumer in some way. It is very important to know about our rights as consumers when we buy goods and services.
- The Consumer Protection Act 2019 was created to help protect consumers and has replaced the old Act from 1986.
- This new law aims to solve many problems consumers face today.
Importance of Being an Informed Consumer:
- Consumers should know their rights to make better choices.
- Awareness helps avoid being cheated by sellers.
Risks of Inadequate Protection:
- If consumers are not protected, they face many risks.
- Unsafe products can cause health issues.
- Adulterated food can harm consumers physically.
- Misleading advertisements can trick consumers into buying bad products.
- Overpricing, hoarding, and black-marketing can lead to unfair costs for consumers.
Transition from Seller Market to Consumer Market:
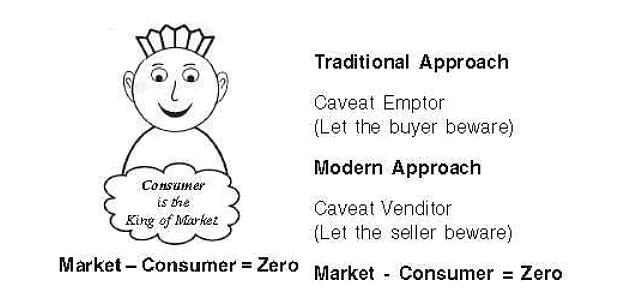
- In the past, consumers had to be very careful (caveat emptor - let the buyer beware).
- Now, businesses must take care of consumers (caveat venditor - let the seller beware).
- This change gives consumers more power in the market.
Consumers as Kings:
- In today’s market, consumers are considered very important.
- Businesses must focus on consumer needs and satisfaction.
Legal Protection Under the Consumer Protection Act 2019:
- The government has created laws to protect consumer interests.
- This law helps prevent businesses from engaging in unfair practices.
- Consumers can seek help and get justice when they are cheated.
Importance of Consumer Protection
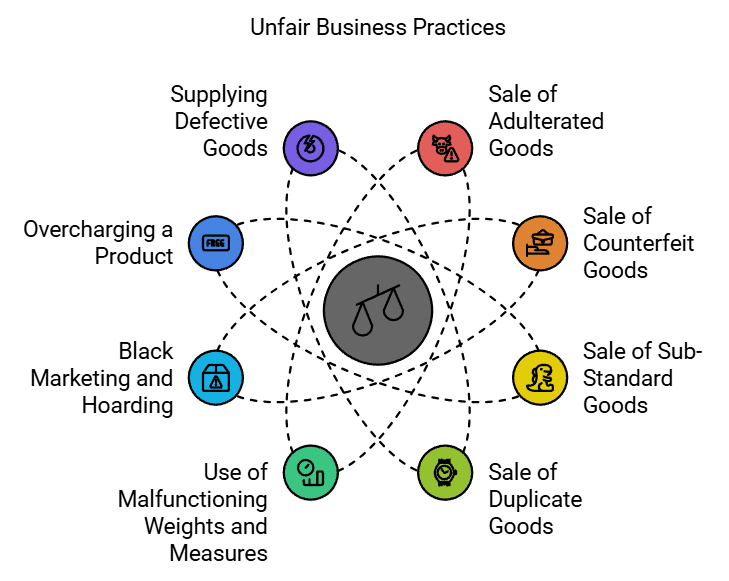
The idea of consumer protection is to keep consumers safe from unfair practices by businesses. It includes rules and actions to help consumers if they face problems with products or services. Here are some key areas of consumer protection:- Sale of Adulterated Goods: This happens when a product is mixed with cheaper or harmful substances. For example, if a food product is sold with added chemicals that make it unsafe to eat.
- Sale of Counterfeit Goods: This refers to selling fake products that look like real ones but are of lower quality. An example is fake designer bags that look like the original but are made from cheap materials.
- Sale of Sub-Standard Goods: These are products that do not meet quality standards. For instance, a toy that breaks easily and is not safe for children is considered sub-standard.
- Sale of Duplicate Goods: This is when a product is sold that is not the original but is made to look like it. For example, a duplicate watch that mimics a famous brand but is not made by the real company.
- Use of Malfunctioning Weights and Measures: This occurs when products are sold using scales or measuring tools that do not work correctly, leading to customers getting less than what they paid for, like being charged for a kilogram but receiving only 800 grams.
- Black Marketing and Hoarding: This is when products are hidden to create a shortage, causing prices to go up. For example, if a seller keeps essential goods like sugar off the market to sell at higher prices later.
- Overcharging a Product: This happens when a product is sold for more than its Maximum Retail Price (MRP). For instance, if a snack that costs $1 is sold for $1.50, that is overcharging.
- Supplying Defective Goods: This means selling items that do not work properly. An example is a phone that has a broken screen or does not turn on correctly.
- Misleading Advertisements: This is when ads make false claims about a product. For example, an ad that says a soap can make you look ten years younger, when it really can't, is misleading.
- Supply of Inferior Services: This refers to services that do not meet what was promised. For example, if you hire a cleaning service that does not clean your home as agreed, you are getting inferior service.
The need for consumer protection comes from the necessity to safeguard consumers against harm, loss, or unfair practices. This includes ensuring:
- Physical safety of consumers.
- Access to information about products and services.
- Corporate Social Responsibility, requiring businesses to provide quality goods in the right amounts and at fair prices.
- Consumer satisfaction, ensuring that buyers are happy with their purchases.
- Social justice and the concept of Trusteeship in the market.
- The survival and growth of businesses.
- Consumer protection is very important because it helps to protect the rights and interests of consumers.
- Consumers often face various kinds of exploitation, such as receiving defective products, being misled by false advertisements, or paying unfair prices.
- To prevent these issues, consumers need to be informed about their rights and how to defend them.
- This is where consumer protection comes into play.
- Consumer protection involves educating consumers about their rights and responsibilities, as well as helping them resolve complaints when things go wrong.
- It requires both legal systems to enforce consumer rights and consumers to come together and form associations that can advocate for their interests.
- In India, there are already consumer organizations working to protect consumers, but these groups need more support to become stronger and more effective.
From the point of view of Consumers
Consumer protection is crucial from the consumer's perspective for several reasons:
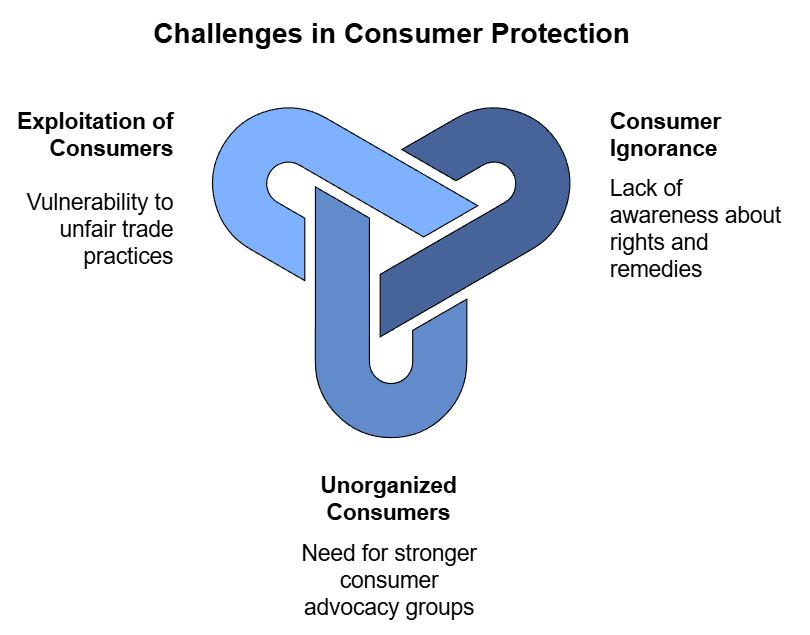
- Consumer Ignorance: Many consumers are unaware of their rights and the remedies available to them. It is essential to educate them about these aspects to raise consumer awareness. For example, consumers should know that they have the right to a refund if a product is defective.
- Unorganized Consumers: Consumers need to be organized into consumer groups that can advocate for their interests. While India has some consumer organizations, they need more support and power to effectively protect and promote consumer interests. For instance, a strong consumer organization can help individuals file complaints against unfair businesses.
- Widespread Exploitation of Consumers: Consumers are vulnerable to exploitation through unfair trade practices such as selling defective products, adulteration of goods, false advertising, hoarding, and black-marketing. Consumer protection is necessary to safeguard against these malpractices. For example, if a company falsely advertises a product as safe when it is not, consumers need protection from such deceitful practices.
From the point of view of Business
- Long-term Interest of Business
Enlightened businesses understand that satisfying customers is crucial for their long-term success. Satisfied customers lead to repeat sales and positive word-of-mouth, which helps expand the customer base. For example, a restaurant that consistently delivers great food and service will have loyal customers who recommend it to others, leading to increased profits over time. - Business Uses Society’s Resources
Businesses rely on resources that belong to society, such as natural resources, labour, and infrastructure. Therefore, they have a responsibility to provide products and services that serve the public interest and maintain public confidence. For instance, a company that pollutes the environment harms society and undermines its own resource base. - Social Responsibility
Businesses have social responsibilities towards various stakeholders, including consumers. Since businesses make money by selling goods and services to consumers, it is essential to prioritize their interests. For example, a company that prioritizes ethical sourcing and fair labour practices not only benefits consumers but also enhances its reputation and long-term viability. - Moral Justification
It is morally imperative for businesses to protect consumer interests and avoid exploitation. Unfair trade practices such as selling defective products, adulteration, false advertising, hoarding, and black marketing are unethical and harmful. For instance, a company that engages in false advertising misleads consumers and damages trust, which can have long-term repercussions. - Government Intervention
Engaging in exploitative trade practices can attract government intervention, which damages a company’s image and credibility. For example, companies involved in black marketing or selling unsafe products may face legal actions and fines, harming their reputation. It is advisable for businesses to proactively adopt practices that prioritize customer needs and interests to avoid such interventions.
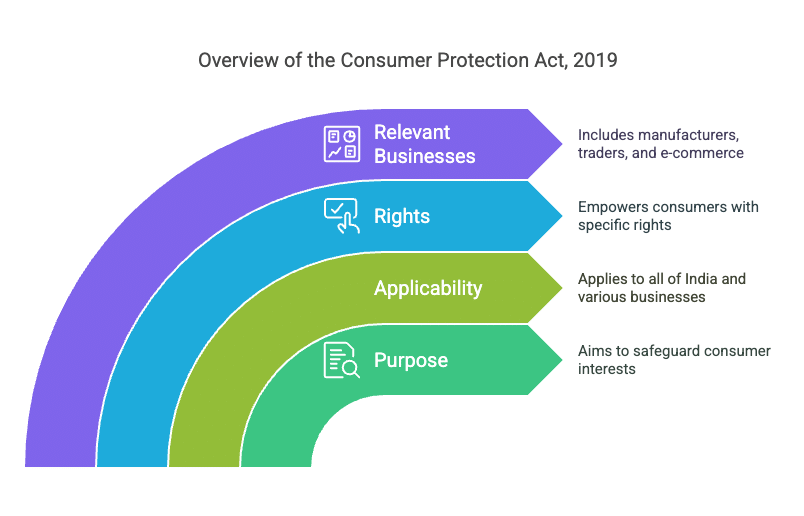
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019
- The Consumer Protection Act 2019 aims to safeguard and promote the interests of consumers.
- It allows for quick and affordable solutions to customer complaints.
- This law applies to all of India.
- It is relevant to all kinds of businesses, including:
1. Manufacturers
2. Traders
3. E-commerce companies - The Act gives specific rights to consumers to empower them.
- Its purpose is to ensure that consumers' interests are protected.
Who is A Consumer?
- Consumer Definition under the Act: The consumer is someone who buys goods or avails services for a price that is paid, promised, or partly paid and partly promised, or under a deferred payment plan.
- Inclusion of Users and Beneficiaries: The definition includes any user of goods or beneficiary of services if such use is made with the approval of the buyer.
- Applicability: The Act applies to both offline and online transactions, including those made through electronic means, teleshopping, direct selling, or multilevel marketing.
- Exclusion: Individuals who obtain goods or avail services for resale or commercial purposes are not treated as consumers and are outside the scope of the Act.
Consumer Rights
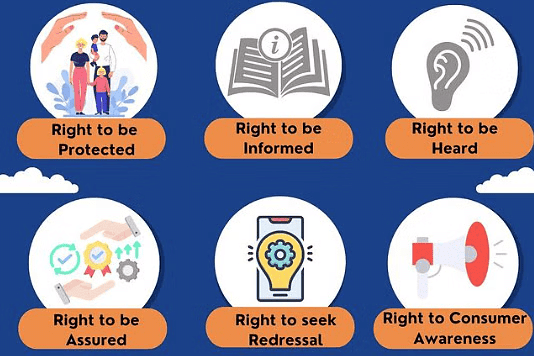 The Consumer Protection Act of 2019 outlines six essential rights for consumers to safeguard their interests and ensure fair treatment in the marketplace.
The Consumer Protection Act of 2019 outlines six essential rights for consumers to safeguard their interests and ensure fair treatment in the marketplace.1. Right to Safety: Consumers have the right to be protected from goods and services that pose risks to their lives, health, and property. For instance, using electrical appliances that are substandard or do not meet safety standards can lead to serious injuries. To ensure safety, consumers are advised to use ISI-marked electrical appliances, which indicate compliance with quality specifications.
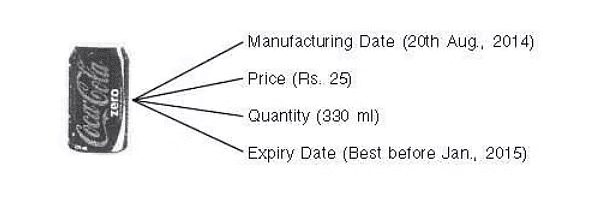
2. Right to be Informed: Consumers have the right to receive complete information about products they intend to purchase, including details such as ingredients, date of manufacture, price, quantity, and instructions for use. This is why Indian law requires manufacturers to provide such information on product packaging and labels.
3. Right to be Assured: Consumers should have access to a variety of products at competitive prices. Marketers are expected to offer a wide range of products in terms of quality, brand, price, and size, allowing consumers to make informed choices.
4. Right to be Heard: Consumers have the right to file complaints and be heard if they are dissatisfied with a product or service. Many progressive businesses have established their own consumer service and grievance cells, and consumer organizations are also working to help consumers resolve their complaints.
5. Right to Seek Redressal: Consumers are entitled to seek relief against unfair trade practices, restrictive trade practices, or exploitation if a product or service does not meet their expectations. The Consumer Protection Act 2019 provides various forms of redressal, including product replacement, defect removal, and compensation for loss or injury.
6. Right to Consumer Education: Consumers have the right to acquire knowledge and be informed about their rights throughout their lives. They should be aware of the available remedies if a product or service falls short of their expectations. Many consumer organizations and progressive businesses are actively involved in educating consumers about their rights and remedies.
Consumer Responsibilities
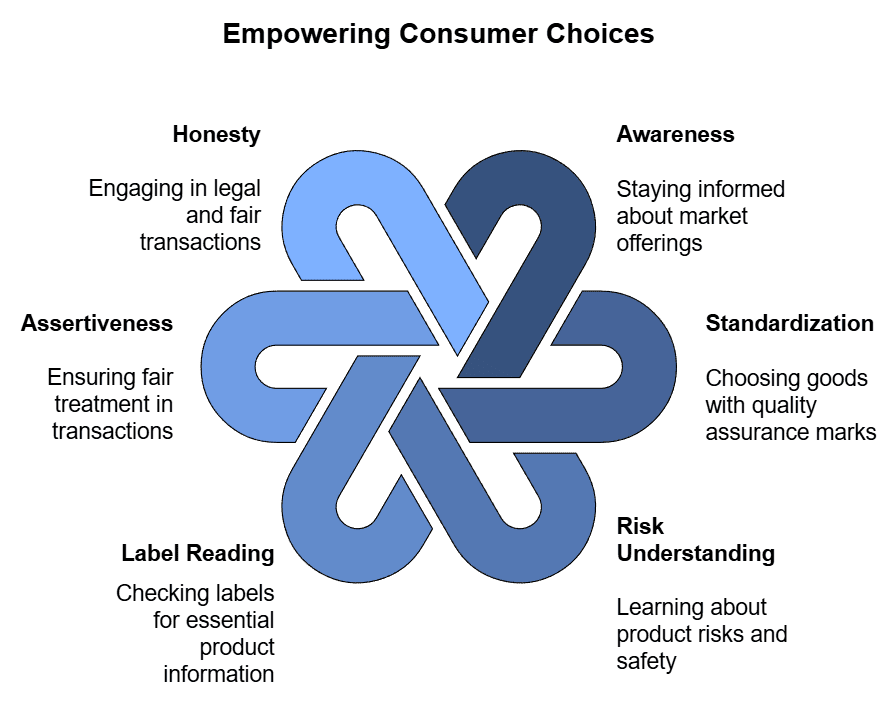
The Consumer Protection Act gives power to consumers to fight against unfair and exploitative trade practices by sellers. However, consumer rights alone are not enough for effective protection. Consumers also need to understand their responsibilities. Here are some important responsibilities consumers should keep in mind when buying, using, and consuming goods and services:- Be informed: Stay aware of the various goods and services available in the market to make intelligent and wise choices.
- Buy standardized goods: Look for quality assurance marks like ISI on electrical goods, FPO on food products, and Hallmark on jewellery.
- Understand risks: Learn about the risks associated with products and services, follow manufacturer’s instructions, and use products safely.
- Read labels carefully: Check labels for important information such as prices, net weight, manufacturing and expiry dates, etc.
- Assert yourself: Ensure you get a fair deal and do not hesitate to speak up.
- Be honest: Engage only in legal transactions and discourage practices like black-marketing and hoarding.
- Ask for a cash memo: Request a cash memo when purchasing goods or services as proof of purchase.
- File complaints: If you experience a shortcoming in the quality of goods or services, file a complaint in the appropriate consumer forum, regardless of the amount involved.
- Form consumer societies: Join or form consumer societies that educate consumers and safeguard their interests.
- Respect the environment: Avoid waste, littering, and contributing to pollution.
Ways and Means of Consumer Protection
Consumer protection aims to ensure that consumers are treated fairly and have access to safe and reliable products and services. While consumer awareness is important, there are various other ways to achieve this objective.- Self-regulation by Business: Many socially responsible firms follow ethical standards and practices in their dealings with customers. These companies understand that it is in their long-term interest to serve customers fairly. To address consumer problems and grievances, numerous firms have established customer service and grievance cells.
- Business Associations: Trade, commerce, and business associations like the Federation of Indian Chambers of Commerce and Industry (FICCI) and the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) have created codes of conduct for their members. These codes provide guidelines for members on how to interact with customers.
- Consumer Awareness: Informed consumers who know their rights and available remedies are better equipped to challenge unfair trade practices and exploitation. Understanding their responsibilities also helps consumers protect their interests. The Department of Consumer Affairs, Government of India, runs the Jago Gharak Jago campaign to raise consumer awareness.
- Consumer Organisations: Consumer organisations play a crucial role in educating consumers about their rights and offering protection. These organisations can pressure businesses to avoid malpractice and mistreatment of consumers.
- Government: The government protects consumer interests by enacting various measures. For instance, the Government of India has established a toll-free national consumer helpline (1800 11 4000) to assist consumers. The legal framework in India includes several legislations that safeguard consumers, with the most significant being the Consumer Protection Act, 2019. This Act establishes a central authority, the Central Consumer Protection Authority (CCPA), to regulate issues related to consumer rights violations, unfair trade practices, and misleading advertisements. Additionally, a three-tier system at the district, state, and national levels is in place to address consumer grievances.
Redressal Agencies Under The Consumer Protection Act
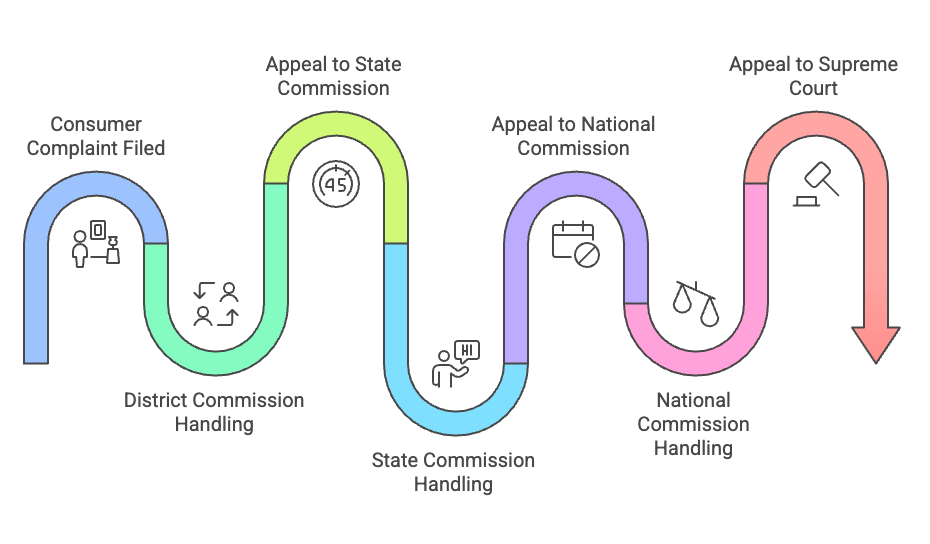
The Consumer Protection Act, 2019 provides for the establishment of a three-tier enforcement mechanism at the District, State, and National levels for the redressal of consumer grievances. This mechanism includes the District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, and the National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission, commonly referred to as the District Commission, State Commission, and National Commission, respectively.
1. District Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- This commission handles complaints where the value of goods or services does not exceed one crore rupees.
- It has the authority to mediate disputes and can refer cases for mediation if both parties agree.
- If mediation fails, the commission proceeds with the complaint.
- In cases involving defective goods that require analysis, the commission can obtain samples and refer them for testing.
- For service disputes, the commission relies on evidence provided by the complainant and can request additional information from the service provider.
- Parties unsatisfied with the district commission's decision can appeal to the state commission within 45 days.
2. State Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- Established by the state government, this commission typically operates from the state capital.
- It handles complaints where the value of goods or services exceeds one crore but does not exceed ten crore rupees.
- Parties dissatisfied with the state commission's decision can appeal to the national commission within 30 days.
3. National Consumer Disputes Redressal Commission
- This commission has jurisdiction over the entire country and deals with complaints where the value of goods or services exceeds ten crore rupees.
- Parties unhappy with the national commission's decision can appeal to the Supreme Court of India within 30 days.
Relief Available
Consumer Protection Act 2019: The Consumer Protection Act, 2019, is a legislation in India that aims to protect the interests of consumers by establishing authorities to address their grievances and ensuring fair trade practices.- Orders Issued by Commissions: When a District, State, or National Commission finds a defect in goods, deficiency in services, unfair trade practice, or product liability claim, they can issue various orders to protect consumers.
- Removal of Defects: The commission may order the removal of defects in goods or deficiencies in services.
- Replacement of Products: Defective products may be ordered to be replaced with new, defect-free ones.
- Refunds: Consumers may be entitled to refunds for products or services that do not meet standards.
- Compensation for Losses: Commissions can order compensation for losses or injuries caused by negligence.
- Punitive Damages: In certain cases, punitive damages may be awarded to deter future misconduct.
- Discontinuation of Unfair Practices: Commissions can order the discontinuation of unfair or restrictive trade practices.
- Prohibition of Hazardous Goods: Authorities may prohibit the sale of hazardous goods and withdraw them from the market.
- Cease Manufacture of Hazardous Goods: Manufacturers may be ordered to cease the production of hazardous goods and services.
- Product Liability Actions: Consumers can seek compensation for injuries caused by hazardous products under product liability actions.
- Finality of Orders: Orders by district, state, or national commissions are deemed final if no appeals are made by the parties involved.
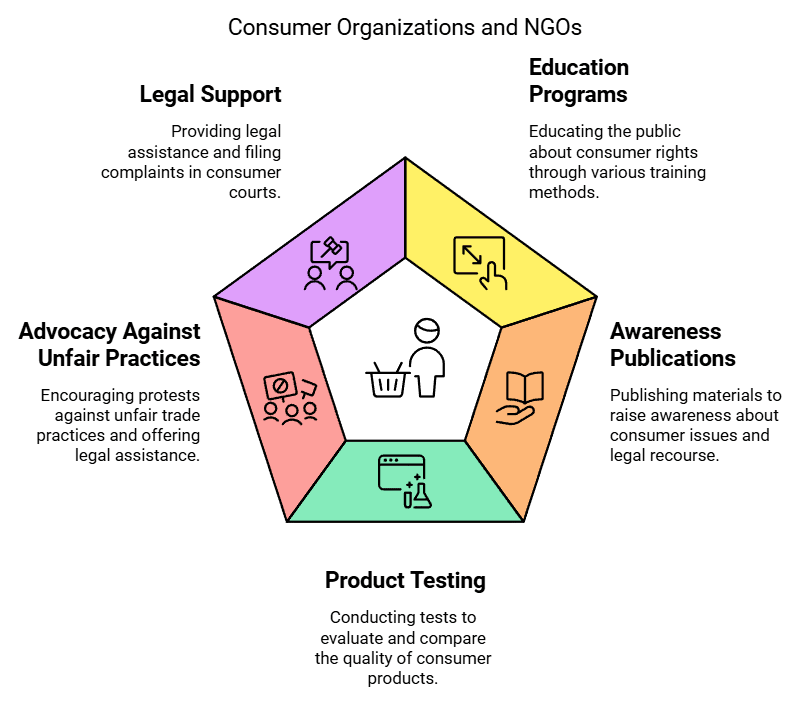
Role of Consumer Organisations And Ngos
- In India, various consumer organizations and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) have been established to safeguard and promote consumers' interests.
- NGOs are nonprofit entities focused on enhancing people's welfare, operating under their own constitution and without government interference.
- Consumer organizations and NGOs undertake several functions to protect and promote consumer interests, including:
1. Educating the public about consumer rights through training programs, seminars, and workshops.
2. Publishing periodicals and other materials to raise awareness about consumer issues, legal recourse, and matters of interest.
3. Conducting comparative testing of consumer products in accredited laboratories to evaluate the relative quality of competing brands and sharing the results with consumers.
5. Encouraging consumers to protest against unfair and exploitative trade practices by sellers.
6. Offering legal assistance to consumers in seeking legal remedies.
7. Filing complaints in consumer courts on behalf of consumers.
8. Initiating cases in consumer courts in the public interest, not for individual gain. - Consumer Unity and Trust Society (CuTS), Jaipur.
|
51 videos|230 docs|49 tests
|
FAQs on Consumer Protection Chapter Notes - Business Studies (BST) Class 12 - Commerce
| 1. What is the main purpose of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019? |  |
| 2. Who qualifies as a consumer under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019? |  |
| 3. What are the key rights of consumers as per the Consumer Protection Act? |  |
| 4. What responsibilities do consumers have under the Consumer Protection Act? |  |
| 5. What are the redressal agencies established under the Consumer Protection Act, 2019? |  |






















