NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Determination of Income and Employment
Q1. What is the marginal propensity to consume? How is it related to the marginal propensity to save?
Ans: Marginal propensity to consume (MPC) is the proportion of any change in disposable income that is spent on consumption. It indicates how much consumption increases when income rises. The formula for MPC is:
MPC 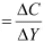
- ΔC = Change in consumption
- ΔY = Change in income
For example, a person's income rises from Rs 200 crores to Rs 250 crores and consumption increases from Rs 20 crores to Rs 40 crores.
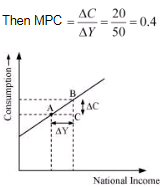
This means that 40% of the increase in income is spent on consumption. Additionally, the relationship between MPC and marginal propensity to save (MPS) can be expressed as:
- Y = C S (Income is either consumed or saved)
- ΔY = ΔC ΔS
Dividing both sides by ΔY gives:
- 1 = MPC MPS
- MPC = 1 - MPS
- MPS = 1 - MPC
This shows that the sum of MPC and MPS always equals 1. Thus, if MPC increases, MPS decreases, and vice versa.
Q2. What is the difference between ex-ante investment and ex-post investment?
Ans: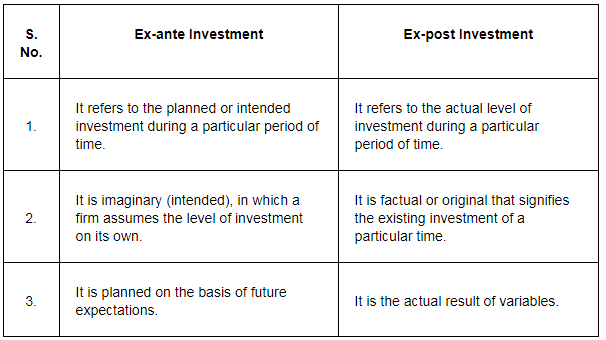
Q3. What do you understand by ‘parametric shift of a line’? How does a line shift when its (i) slope decreases, and (ii) its intercept increases?
Ans: The parametric shift of a line refers to how a line on a graph changes position based on alterations in its parameters, specifically the slope and intercept.
- Slope Decrease: When the slope of a line decreases, it rotates downward around the same vertical intercept. This means the line becomes flatter.
- Intercept Increase: When the intercept increases, the line shifts upward in parallel. This means the entire line moves higher on the graph without changing its slope.
In summary:
- A decrease in slope results in a downward rotation of the line.
- An increase in intercept leads to a parallel upward shift of the line.
Q4. What is ‘effective demand’? How will you derive the autonomous expenditure multiplier when price of final goods and the rate of interest are given?
Ans: Effective demand refers to a situation where the equilibrium output is determined entirely by the level of aggregate demand. This occurs under the assumption that supply is infinitely elastic. If there is a discrepancy between aggregate demand (AD) and aggregate supply (AS), equilibrium output will be influenced solely by AD. The concept can be illustrated with a diagram where:
- The x-axis represents income/output level.
- The y-axis represents the level of aggregate demand.
- The equilibrium point (E) is where the AS and AD curves intersect.
- EG indicates effective demand, with output determined by AD.
The autonomous expenditure multiplier can be derived as follows:
- At equilibrium: Y = AD
- Substituting: Y = A cY
- Rearranging gives: Y - cY = A
- Thus, Y(1 - c) = A
Where:
- A = Autonomous expenditure
- c = Marginal propensity to consume (MPC)
- Y = Level of income
Therefore, the autonomous expenditure multiplier depends on the level of income and the MPC.
Q5. Measure the level of ex-ante aggregate demand when autonomous investment and consumption expenditure (A) is Rs 50 crores, MPS is 0.2 and level of income (Y) is Rs 4000 crores. State whether the economy is in equilibrium or not (cite reasons).
Ans: Consumption expenditure (A) is Rs 50 crores, with a MPS of 0.2. This means the MPC is calculated as:
- MPC = 1 - MPS = 1 - 0.2 = 0.8
The level of income (Y) is Rs 4000 crores. The formula for aggregate demand (AD) is:
- AD = A cY
Substituting the values:
- AD = 50 0.8 × 4000
- AD = 50 3200 = Rs 3250 crores
Since Rs 3250 crores is less than Rs 4000 crores, we conclude:
- AD < Y
- This indicates that the economy is not in equilibrium.
Q6. Explain the ‘Paradox of Thrift’.
Ans: The Paradox of Thrift describes a situation where individuals save more money, but this collective behaviour can lead to a decrease in overall savings for the economy.
- When everyone increases their savings, aggregate demand falls because consumption decreases.
- This reduction in demand can result in lower employment and income levels.
- Consequently, total savings for the economy may decline or remain unchanged.
- This concept was introduced by Keynes, highlighting that increased individual savings can slow down economic growth.
|
139 videos|431 docs|128 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Economics - Determination of Income and Employment
| 1. How is income determined in the context of national income accounting? |  |
| 2. What is the relationship between income and employment? |  |
| 3. How does government spending impact income and employment levels? |  |
| 4. What role does the business cycle play in determining income and employment? |  |
| 5. How do economists measure national income and employment levels? |  |

















