NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Judiciary
Q1: What are the different ways in which the independence of the judiciary is ensured? Choose the odd ones out.
(i) The Chief Justice of the Supreme Court is consulted in the appointment of other judges of the Supreme Court.
(ii) Judges are generally not removed before the age of retirement.
(iii) A judge of a High Court cannot be transferred to another High Court.
(iv) Parliament has no say in the appointment of judges.
Ans:  Judiciary should be independentThe independence of the judiciary is maintained in the following ways:
Judiciary should be independentThe independence of the judiciary is maintained in the following ways:
(i) Chief Justice consultation: True.
The consultation of the Chief Justice in judicial appointments (collegium system) limits executive interference, ensuring independence.
(ii) Security of tenure: True.
Judges cannot be removed except by a rigorous impeachment process, safeguarding judicial autonomy.
(iii) High Court transfer restriction: False.
High Court judges can be transferred under Article 222; this statement does not reflect judicial independence.
(iv) Parliament has no say: False.
Parliament has an indirect role (e.g., impeachment process, constitutional amendments); thus, this is not entirely correct.
Conclusion:
- Ways in which judicial independence is ensured: (i) and (ii)
- Odd ones out (not ways of ensuring independence): (iii) and (iv)
Q2: Does independence of the judiciary mean that the judiciary is not accountable to anyone? Write your answer in not more than 100 words.
Ans:
The independence of the judiciary does not mean it is unaccountable. It ensures that no other organ of the government—executive or legislature—can interfere with its functioning. Judges perform their duties impartially, without fear, favour, or external pressure.
Simultaneously, the judiciary remains accountable to the Constitution of India, which defines its powers and limitations, to the people of India, the ultimate sovereign, and to the democratic traditions that guide all state institutions. This balance maintains judicial independence while ensuring responsible exercise of judicial authority.
Q3: What are the different provisions in the Constitution to maintain the independence of the judiciary?
Ans:  The different provisions in the Constitution to maintain the independence of the judiciary are:
The different provisions in the Constitution to maintain the independence of the judiciary are:
- The independence of the judiciary ensures that other organs of the government do not interfere in its functioning, and judges can perform their duties without fear or favour.
- Parliament has no direct role in the appointment of judges to avoid political influence, affirmed by the collegium system.
- Judges enjoy a fixed tenure and hold office until retirement, with removal possible only through a difficult impeachment procedure.
- Judicial actions and decisions are protected from personal criticism to maintain dignity and impartiality.
- Salaries and allowances of judges cannot be altered to influence their functioning or be subjected to legislative approval.
- The judiciary can penalise individuals for contempt of court to maintain its authority and dignity.
- The Constitution bars Parliament from discussing the conduct of judges except during impeachment proceedings, preserving judicial independence.
Q4: Read the news report below and identify the following aspects:
- What is the case about?
- Who has been the beneficiary in the case?
- Who is the petitioner in the case?
- Visualise what would have been the different arguments put forward by the company.
- What arguments would the farmers have put forward?
Supreme Court orders REL to pay Rs 300 crore to Dahanu farmers:
Our Corporate Bureau 24 March 2005:
Mumbai: The Supreme Court has ordered Reliance Energy to pay Rs. 300 crore to farmers who grow the chikoo fruit in the Dahanu area outside Mumbai. The order comes after the chikoo growers petitioned the court against the pollution caused by Reliance's thermal power plant.
Dahanu, which is 150 km from Mumbai, was a self-sustaining agricultural and horticultural economy known for its fisheries and forests just over a decade ago, but was devastated in 1989 when a thermal power plant came into operation in the region. The next year, this fertile belt saw its first crop failure. Now, 70 per cent of the crop of what was once the fruit bowl of Maharashtra is gone. The fisheries have shut down and the forest cover has thinned. Farmers and environmentalists say that fly ash from the power plant entered groundwater and polluted the entire ecosystem. The Dahanu Taluka Environment Protection Authority ordered the thermal station to set up a pollution control unit to reduce sulphur emissions, and in spite of a Supreme Court order backing the order, the pollution control plant was not set up even by 2002. In 2003, Reliance acquired the thermal station and resubmitted a schedule for the installation process in 2004. As the pollution control plant is still not set up, the Dahanu Taluka Environmental Protection Authority asked Reliance for a bank guarantee of Rs. 300 crores.
Ans:
1. What is the case about?
The case concerns pollution caused by Reliance Energy’s thermal power plant in Dahanu, which damaged agriculture, horticulture, fisheries, and forests. Chikoo farmers petitioned the Supreme Court seeking compensation for environmental and economic losses caused by the plant.
2. Who has been the beneficiary in the case?
The farmers of Dahanu, particularly those growing chikoo fruit, have been the beneficiaries, as the Supreme Court ordered Reliance Energy to pay Rs. 300 crore in compensation.
3. Who is the petitioner in the case?
The chikoo growers/farmers of Dahanu were the petitioners who approached the Supreme Court against the environmental damage caused by the thermal power plant.
4. Visualise what would have been the different arguments put forward by the company (Reliance Energy):
- They may have argued that they acquired the plant only in 2003 and were following a schedule to install the pollution control unit.
- They could have claimed that the pollution was pre-existing before their acquisition.
- They might have emphasised financial or technical difficulties in immediately setting up the pollution control unit.
5. What arguments would the farmers have put forward?
- The farmers would have highlighted the loss of crops, fisheries, and forests due to pollution.
- They could have argued that fly ash contaminated groundwater, affecting agriculture and health.
- They may have stressed that orders by the Dahanu Taluka Environment Protection Authority and the Supreme Court to control pollution were not implemented.
- They would likely demand adequate compensation for long-term environmental and economic damage.
Q5: Read the following news report and,
- Identify the governments at different levels
- Identify the role of the Supreme Court
- What elements of the working of the judiciary and executive can you identify in it?
- Identify the policy issues, matters related to legislation, implementation and interpretation of the law involved in this case.
Centre, Delhi join hands on CNG issue
By Our Staff Reporter, The Hindu 23 September 2001:
NEW DELHI, SEPT. 22. The Centre and the Delhi Government today agreed to jointly approach the Supreme Court this coming week for phasing out of all non-CNG commercial vehicles in the Capital. They also decided to seek a dual fuel policy for the city instead of putting the entire transportation system on the single-fuel mode “which was full of dangers and would result in disaster.”
It was also decided to discourage the use of CNG by private vehicle owners in the Capital. Both governments would press for allowing the use of 0.05 per cent low sulphur diesel for running buses in the Capital. They also pleaded before the Court that all commercial vehicles meeting Euro-II standards should be allowed to ply in the city. Though both the Centre and the State would file separate affidavits, these would contain common points. The Centre would also support the Delhi Government's position on the issues concerning CNG.
These decisions were taken at a meeting between Delhi Chief Minister, Ms. Sheila Dikshit, and the Union Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister, Mr. Ram Naik.
Ms. Dikshit said the Central Government would request the court to extend the deadline, as it was not possible to convert the entire 10,000-odd bus fleet into CNG within the prescribed time. The Mashelkar Committee, appointed under Dr. R.A. Mashelkar to suggest an “Auto Fuel Policy” for the country, is expected to submit its report within six months.
The Chief Minister said time was needed to implement court directives. Referring to coordinated work on the issue, Ms. Dikshit said this would consider vehicle numbers, eliminating queues at CNG stations, CNG fuel requirements, and ways to implement the court directive.
The Supreme Court had refused to relax the only CNG norm for buses but clarified it did not insist on CNG for taxis and auto rickshaws. Mr. Naik said the Centre would insist on allowing low sulphur diesel use for buses in Delhi, as putting the entire system on CNG could be disastrous. The Capital relied on pipeline supply for CNG, and any disruption would stall public transport.
Ans:
1. Governments at different levels:
- Central Government (Union Government): Represented by the Union Petroleum and Natural Gas Minister, Mr Ram Naik.
- State Government (Delhi Government): Represented by Delhi Chief Minister, Ms Sheila Dikshit.
2. Role of the Supreme Court:
- The Supreme Court issued directives regarding the use of CNG in Delhi’s public transport.
- It refused to relax the CNG norm for buses but clarified it did not insist on CNG for taxis and auto rickshaws.
- Both the Centre and Delhi Government approached the Court seeking modifications or exemptions in view of practical and safety concerns.
3. Elements of the working of the judiciary and executive:
Judiciary:
- Provides directives to ensure environmental protection (CNG implementation).
- Ensures compliance by monitoring government action.
Executive:
- Implements court directives considering practical feasibility, safety, and public interest.
- Coordinates between the Central and State levels for policy implementation.
- Files affidavits in the Supreme Court presenting its stance.
4. Policy issues, matters related to legislation, implementation, and interpretation of law:
Policy Issues:
- Environmental protection via clean fuel (CNG) in public transport.
- Safety concerns regarding exclusive reliance on CNG.
- Dual fuel policy for public transport balancing environmental and operational needs.
Legislation Matters:
- Compliance with the Supreme Court directive on CNG usage.
- Reference to Euro-II emission standards for commercial vehicles.
Implementation Issues:
- Converting the bus fleet to CNG within the prescribed deadline.
- Ensuring adequate fuel supply and avoiding long queues at filling stations.
Interpretation of Law:
- Supreme Court’s clarification that CNG is mandatory only for buses, not taxis or auto rickshaws.
- Coordination between the Centre and State in presenting arguments to the Court regarding feasibility and safety.
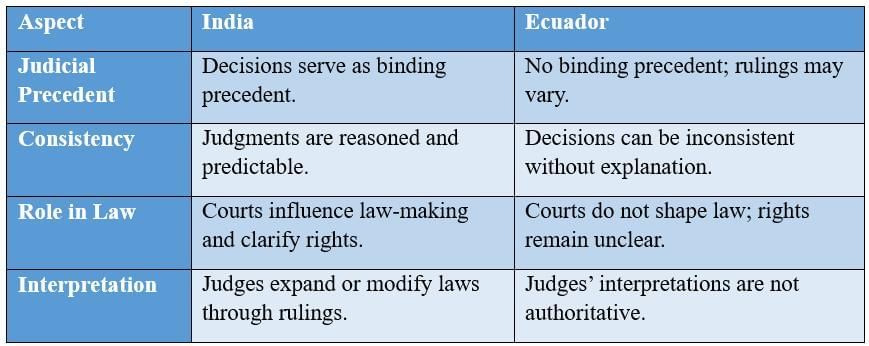
Q6: The following is a statement about Ecuador. What similarities or differences do you find between this example and the judicial system in India?
“It would be helpful if a body of common law, or judicial precedent, existed that could clarify a journalist's rights. Unfortunately, Ecuador's courts don't work that way. Judges are not forced to respect the rulings of higher courts in previous cases. Unlike the US, an appellate judge in Ecuador (or elsewhere in South America, for that matter) need not provide a written decision explaining the legal basis of a ruling. A judge may rule one way today and the opposite way, in a similar case, tomorrow, without explaining why.”
Ans:
No similarity is found between Ecuador and India in this example because:
- In India, judicial decisions are an important source of law and play a significant role in law-making.
- Judges provide their own interpretations to decide cases, often expanding or modifying existing laws.
- The rulings of the Supreme Court and High Courts are frequently cited by lawyers with authority and effect.
- In the given example, it is noted that Ecuador lacks a system of common law or judicial precedent to clarify rights.
- In Ecuador, judicial decisions do not serve as binding precedents, and a judge may rule one way today and the opposite way tomorrow without explaining the reasoning.
Q7: Read the following statements: Match them with the different jurisdictions the Supreme Court can exercise - Original, Appellate, and Advisory.
1. The government wanted to know if it could pass a law about the citizenship status of residents of Pakistan-occupied areas of Jammu and Kashmir.
Ans: Advisory Jurisdiction
The Supreme Court advises the President or Government on legal questions referred under Article 143.
2. To resolve the dispute about the river Cauvery, the government of Tamil Nadu wants to approach the court.
Ans: Original Jurisdiction
The Supreme Court hears disputes between states or between the Centre and states under Article 131.
3. The court rejected the appeal by the people against the eviction from the dam site.
Ans: Appellate Jurisdiction
The Supreme Court hears appeals against judgments of High Courts or lower courts under Articles 132–136.
Q8: In what way can public interest litigation help the poor?
Ans:
Public interest litigation (PIL) can help the poor in the following ways:
- Since 1979, the court has provided relief for the poor in cases filed by others on behalf of aggrieved persons.
- Such cases involve public interest issues that improve the living conditions of the poor.
- Voluntary organisations have sought judicial intervention to protect the rights of the poor.
- PIL is a tool of judicial activism, addressing environmental protection, trafficking prohibition, bonded labour, grievances of weaker sections, and relief for undertrial prisoners.
- Example: In Hussainara Khatoon vs. Bihar, a petition led to the release of many prisoners detained for long periods without trial.
- The diverse problems of the poor can be addressed through the Supreme Court's intervention via PIL.
Q9: Do you think that judicial activism can lead to a conflict between the judiciary and the executive? Why?
Ans:  Yes, judicial activism can lead to conflicts between the judiciary and the executive because it significantly impacts the political system.
Yes, judicial activism can lead to conflicts between the judiciary and the executive because it significantly impacts the political system.
- Judicial activism facilitates a free and fair electoral system by guiding candidates to disclose assets, income, and educational qualifications, enhancing transparency.
- This often dissatisfies some political candidates, as judicial intervention blurs the division between the executive, legislature, and judiciary.
- The judiciary sometimes resolves issues traditionally belonging to the executive, such as pollution control, corruption investigation, and electoral reforms.
- Since these functions are typically executive responsibilities, judicial activism may cause conflicts between the two organs.
Q10: How is judicial activism related to the protection of fundamental rights? Has it helped in expanding the scope of fundamental rights?
Ans:
Judicial Activism and Protection of Fundamental Rights
Fundamental Rights in India:
- Right to Equality
- Right to Freedom
- Right against Exploitation
- Right to Freedom of Religion
- Cultural and Educational Rights
- Right to Constitutional Remedies (Articles 32 & 226)
Role of Judiciary:
- Can declare laws unconstitutional under Article 13.
- Protects citizens’ rights through judicial review.
- Expands the scope of rights via Public Interest Litigation (PIL).
Writs under the Right to Constitutional Remedies:
- Habeas Corpus: Orders authorities to produce a person illegally detained before the court.
- Mandamus: Directs a public authority or lower court to perform a duty owed to the petitioner.
- Quo Warranto: Challenges an individual unlawfully holding public office.
- Prohibition: Issued by a higher court to restrain a lower court from acting beyond its jurisdiction.
- Certiorari: Orders a lower court to send case records to a higher court for review, often issued with prohibition.
Through these powers and writs, judicial activism has expanded the scope of fundamental rights, ensuring effective protection of citizens and upholding the Constitution.
|
151 videos|780 docs|202 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 11 Political Science - Judiciary
| 1. What is the role of the judiciary in India? |  |
| 2. How is the Indian judiciary structured? |  |
| 3. What are the key functions of the Supreme Court of India? |  |
| 4. What is judicial review and its significance? |  |
| 5. How can a citizen approach the judiciary for justice? |  |






















