NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History Chapter 6 - Civilising the “Native”, Educating the Nation
| Table of contents |

|
| Let's Recall |

|
| Let's Discuss |

|
| Let's Do |

|
| Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) |

|
Chapter "Civilising the "Native", Educating the Nation" is a part of the Class 8 History curriculum. It focuses on the different approaches taken by the British in India towards education and the role it played in colonialism. Let's have a look at some NCERT Solutions of the chapter.

Let's Recall
Q1: Match the following:
Ans: 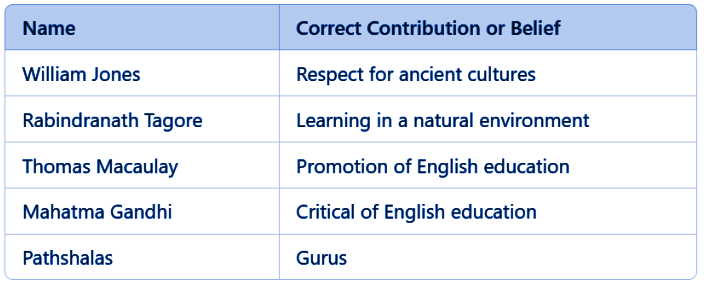
- William Jones: British scholar who promoted the study of ancient Indian cultures.
- Rabindranath Tagore: Emphasized learning in a natural environment, and established Santiniketan school.
- Thomas Macaulay: Introduced English education in colonial India.
- Mahatma Gandhi: Criticized English education, and advocated for Indian traditions and practical skills.
- Pathshalas: Traditional Indian schools with gurus guiding students.
Q2: State whether true or false:
(a) James Mill was a severe critic of the Orientalists.
Ans: True
(b) The 1854 Despatch on Education was in favor of English being introduced as a medium of higher education in India.
Ans: True
(c) Mahatma Gandhi thought that the promotion of literacy was the most important aim of education.
Ans: False
Mahatma Gandhi thought that the promotion of literacy was the most important aim of education.
(d) Rabindranath Tagore felt that children ought to be subjected to strict discipline.
Ans: False
Rabindranath Tagore felt that children ought to be subjected to strict discipline.
Let's Discuss
Q3: Why did William Jones feel the need to study Indian history, philosophy and law?
Ans: William Jones believed studying Indian history, philosophy, and law would help rediscover India’s cultural heritage and establish British control as guardians of Indian traditions.
 William Jones.
William Jones.
Q4: Why did James Mill and Thomas Macaulay think that European education was essential in India?
Ans: James Mill and Thomas Macaulay thought the knowledge about the East was wrong and not scientific. They believed Eastern literature was not serious.
Macaulay felt India was not civilized and needed to become civilized. They wanted to teach English so that Indians could read great literature and learn about Western science and philosophy.
 Thomas Macaulay.
Thomas Macaulay.
Q5: Why did Mahatma Gandhi want to teach children handicrafts?
Ans: Gandhi believed handicrafts taught dignity of labor, improved mental and physical development, and encouraged self-reliance and appreciation for practical skills.
 Mahatma Gandhi
Mahatma Gandhi
Q6: Why did Mahatma Gandhi think that English education had enslaved Indians?
Ans: Gandhi felt English education created a sense of inferiority among Indians, making them favor Western civilization and alienating them from their own culture and traditions.
Let's Do
Q7: Find out from your grandparents about what they studied in school.
Ans: It would be interesting to learn about our grandparents' education. From what they have shared so far, they studied Urdu/Hindi language, Mathematics, Social Studies, and Drawing. It would be great to hear more about their experiences and how their education has impacted their lives.
Q8. Find out about the history of your school or any other school in the area you live.
Ans: My school is St. Peter's Academy, the oldest educational institution in this region. Founded by a Christian missionary in 1980, it has a rich history of academic excellence and outstanding achievements. The school's principal is always appointed by the missionary and is known for their high academic repute and administrative quality. The teachers are also highly talented and committed to their students' success. St. Peter's Academy currently has around five thousand students, who have brought great pride to the school and the region through their excellent results in board examinations. As a student of St. Peter's Academy, I am proud of its history and traditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What is the main focus of the chapter "Civilising the "Native", Educating the Nation"?
Ans: The main focus of the chapter is on the different approaches taken by the British in India towards education and how it played a role in colonialism.
Q2. What was the Orientalist approach towards education in India?
Ans: The Orientalist approach towards education in India focused on teaching Western values, language, and culture to Indian students. The British believed that it was their duty to "civilize" the natives and establish English-medium schools and colleges.
Q3. Who were the key figures promoting the Orientalist approach in India?
Ans: William Jones and Colebrooke were the key figures promoting the Orientalist approach in India.
Q4. What was the perspective of James Mill towards education in India?
Ans: James Mill was critical of the Orientalist approach towards education in India. He believed that Indians should be made familiar with the scientific and technical advances that the West had made, and not the sacred literature of the Orient.
Q5. What was Mahatma Gandhi's view on English education in India?
Ans: Mahatma Gandhi believed that English education in India had enslaved Indians by creating a sense of inferiority in their minds. He advocated for an education that could help Indians recover their sense of dignity and self-respect and focused on Indian languages as the medium of teaching.
|
40 videos|88 docs|23 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 History Chapter 6 - Civilising the “Native”, Educating the Nation
| 1. What was the main objective of colonial education in India as discussed in the article? |  |
| 2. How did the British justify their educational policies in India? |  |
| 3. What impact did colonial education have on Indian society and culture? |  |
| 4. In what ways did Indian nationalists respond to colonial education? |  |
| 5. What role did women play in the context of education during the colonial period? |  |