Tertiary And Quaternary Activities Class 12 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Tertiary Activities |

|
| Trade and commerce |

|
| Transport |

|
| Communication |

|
| Services |

|
| People Engaged in Tertiary Activities |

|
| Quaternary Activities |

|
| Quinary Activities |

|
| The Digital Divide |

|
Tertiary Activities
- Tertiary activities are linked to the service sector. A key part of this sector is manpower, as many of these activities rely on skilled workers, trained experts, and consultants.
- The main distinction between secondary and tertiary activities is that services depend more on the specialised skills, experience, and knowledge of the workforce rather than on production methods, machinery, or factory processes.
- Tertiary activities focus on the delivery of services rather than the creation of physical products. They do not involve the processing of raw materials directly.

Types of Tertiary Activities
There are four types of tertiary activities. They are trade, transport, communication and services. These include provision of services in exchange of payments.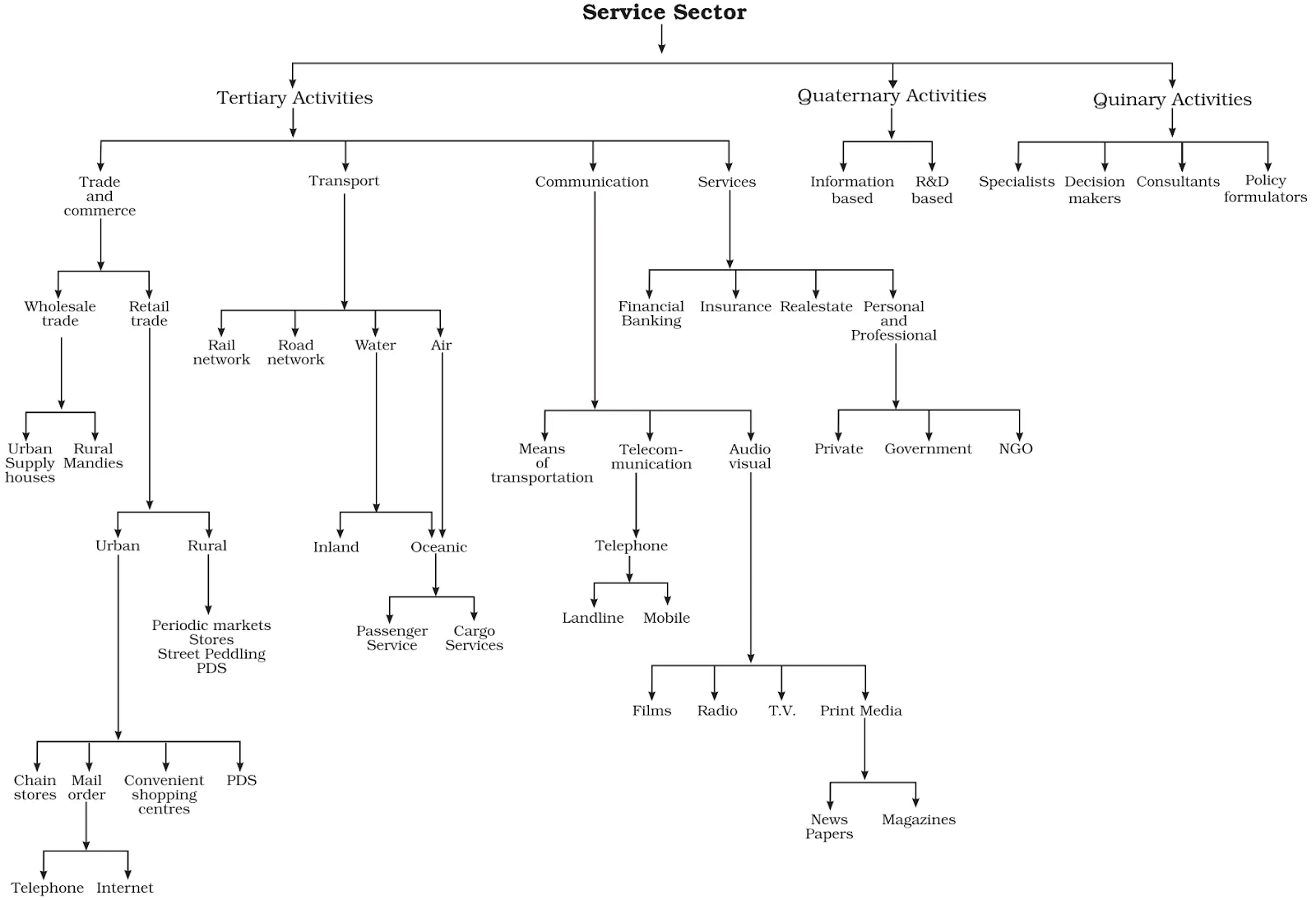
Trade and commerce
Trade and commerce is essentially buying and selling of items produced elsewhere. The collection and distribution points where trading takes place are called trading centres. These centres are divided into:Rural Marketing Centres
- They are quasi urban and cater to local needs and areas.
- Most of these have mandis (wholesale markets) and retail markets.
- In rural areas, there are periodic markets that may be weekly or bi-weekly and people from the nearby areas meet their demands.
- These markets are held on specified dates and shopkeepers move from one place to another.
Periodic Markets
- Periodic markets in rural areas are found where there are no regular markets.
- These markets are organized at different temporal intervals, such as weekly or bi-weekly, to meet the temporally accumulated demand of people from surrounding areas.
- They are held on specified dates and move from one place to another.
- This system keeps shopkeepers busy on all days while serving a large area.
Urban Marketing Centres
- These markets sell ordinary as well as specialised goods and services.
- Markets for labour, housing, semi or finished products exist.
- Services of educational institutions and professionals like teachers, doctors, lawyers also develop.
Retail Trading
- In this type of trading, goods are directly sold to consumers.
- This trading is done through fixed establishments or stores, small shops, consumer cooperatives, big departmental stores, and chain stores.
- The chain stores buy commodities in bulk and then hire skilled specialists for executive tasks.
- Street peddling, handcarts, trucks, door-to-door, mail order, telephone, and Internet are examples of non-store retail trading.
Wholesale Trading
- Wholesale trading constitutes bulk business through numerous intermediary merchants and supply houses and not through retail stores.
- Some large stores including chain stores are able to buy directly from the manufacturers.
- However, most retail stores procure supplies from an intermediary source.
- Wholesalers often extend credit to retail stores to such an extent that the retailer operates very largely on the wholesaler’s capital.
Transport
Transport refers to the services or facilities that move people, materials, and goods from one place to another. It is an organised industry that meets the fundamental need for mobility. In today's world, effective and quick transport systems are essential for producing, distributing, and consuming products. Transportation significantly increases the value of materials at every stage of this intricate process.
When choosing a transport method, factors such as distance, time, and cost are taken into account:
- Distance can be calculated as actual distance (the length of the route in kilometres), time distance (how long it takes to travel that route), and cost distance (the expenses involved).
- Isochrone lines are used on maps to connect locations that take the same amount of time to reach.
Factors Affecting Transport
- Population size influences demand; larger populations increase demand.
- Routes depend on location of cities, towns, villages, industrial centers, raw materials.
- Pattern of trade influences routes.
- Landscape, climate affect feasibility and costs.
- Funds determine ability to overcome obstacles.
Communication
- Communication services involve sharing words, messages, facts, and ideas. Writing allowed for message preservation and made communication reliant on transport methods like hands, animals, boats, roads, rail, and air. Hence, all transport forms are also seen as communication lines.
- Efficient transport networks enable easy communication. Developments like mobile phones and satellites have made some communications independent of transport.
Telecommunications
- The rise of telecommunications is tied to modern technology, speeding up message delivery from weeks to minutes.
- Mobile phones allow immediate communication anytime and anywhere, making older technologies like the telegraph and telex outdated.
- Radio and television broadcast news, images, and calls worldwide, acting as mass media for advertising and entertainment. Satellite communication connects Earth to space, enhancing global communication.
- The Internet has transformed global communication as well.
Services
- Services can be grouped by their level: low-order services (like grocery shops, laundries) are common, while high-order services (like accountants, consultants, physicians) are specialised.
- Many services are regulated by governments or companies, including highways, bridges, fire services, education, and customer care.
- Professional services such as healthcare, engineering, law, and management are vital for society.
- The location of recreational and entertainment services is determined by market needs (e.g., cinemas near city centres, golf courses in affordable areas).
- Personal services, often provided by unskilled workers migrating from rural regions to enhance daily life of people (e.g., Mumbai's dabbawala(Tiffin) service provided to about 1,75,000 customers all over the city.
People Engaged in Tertiary Activities
Earlier more number of people were employed in the primary and secondary sector as these sectors provided more jobs. But, now there has been a shift of jobs to tertiary or service sector. In developed countries, a higher percentage of workers are employed in providing services as compared to less developed countries.
Some Selected Examples
Tourism
- Travel for recreation rather than business.
- Largest tertiary activity in registered jobs (250 million) and total revenue (40% of total GDP).
- Provides employment in services like accommodation, meals, transport, entertainment, and special shops.
- Fosters growth of infrastructure industries, retail trading, and craft industries (souvenirs).
- Seasonal in some regions due to vacation periods and favorable weather conditions.
- Many regions attract visitors all year round.
 Tourist Regions
Tourist Regions
- Tourism can be seasonal or throughout the year like warmer places around the Mediterranean coast, West coast of India during winters, mountains in summers or winter spots regions found mainly in mountainous areas.
- Historic towns, religious places, heritage sites offer tourism throughout the year.
- Factors Affecting Tourism
- The rise in tourism industry is due to increased demand for it which is thus influenced by improvement in standard of living and increased leisure time.
- Another factor is improvement in transportation that has made travel easier and destinations reachable.
Tourist Attractions
Tourist attractions are specific features of a place that attract people. These are as follows:
- Climate In winter holidays, areas having warm sunny weather is preferred like beaches in Southern Europe, so it attracts more number of tourists there.
- Landscape Mountains, lakes, spectacular sea coasts and landscapes not completely altered by man are good tourist attractions.
- History and Art Ancient or picturesque towns, archaeological sites, historically important places having castles and palaces attract tourists.
- Culture and Economy Areas having rich cultures attract people as they go their to experience ethnic and local customs. Places giving economic benefits are also attractions such as cheap home stays in Goa, Madikere and Coorg in Karnataka.
Medical Services for Overseas Patients in India
- Medical services or tourism takes place when medical treatment is combined with international tourism activity. People from developed countries like US are visiting India for medical tourism or services.
- This brings economic benefits to India and other countries where medical tourism is taking place like Thailand, Singapore and Malaysia.
- Other medical related activities such as outsourcing of medical tests, data interpretation, reading radiology images, interpreting Magnetic Resonance Images (MRIs) and ultrasound tests are taking place in India, Australia and Switzerland.
Quaternary Activities
- Quaternary activities involve the collection, production, and dissemination of information.
- These activities focus on research and development and require specialized knowledge and technical skills.
- The quaternary sector, along with the tertiary sector, has replaced most primary and secondary employment as the basis for economic growth.
- Over half of all workers in developed economies are in the 'Knowledge Sector'.
- There has been significant growth in demand for information-based services, such as those provided by mutual fund managers, tax consultants, software developers, and statisticians.
- Personnel working in office buildings, elementary schools, universities, hospitals, doctors’ offices, theatres, accounting firms, and brokerage firms all belong to this category of services.
- The quaternary activities, like some tertiary functions, can also be outsourced.
- They are not tied to specific resources, are unaffected by the environment, and are not necessarily localized by the market.
Quinary Activities
- Quinary activities involve services that concentrate on creating, reorganising, and interpreting both new and existing ideas, as well as interpreting data and evaluating new technologies.
- These activities differ slightly from the knowledge-based industries that the quinary sector generally encompasses.
- Commonly known as 'gold collar' professions, they represent a subdivision of the tertiary sector, highlighting the specialised and highly paid skills of senior business executives, government officials, research scientists, financial and legal consultants, and others.
- Their role in advanced economies is significantly more important than their numbers suggest.
Outsourcing
Outsourcing, or contracting out, refers to the practice of assigning work to an external agency to enhance efficiency and cut costs.

- This has led to the establishment of many call centres in countries like India, China, Eastern Europe, Israel, the Philippines, and Costa Rica.
- It has generated new job opportunities in these regions, attracting businesses looking for affordable and skilled labour.
- As work continues to be outsourced, there may be a decrease in migration for these roles.
- However, countries that engage in outsourcing are experiencing pushback from young people seeking jobs locally.
New Trends in Quinary Services
- Knowledge Processing Outsourcing (KPO): Involves highly skilled workers, distinct from BPO.
- Home shoring: Alternative to outsourcing.
- KPO is information-driven and enables companies to create additional business opportunities.
- Examples of KPOs: Research and Development (R&D), e-learning, business research, intellectual property (IP) research, legal profession, and the banking sector.
The Digital Divide
- The benefits and opportunities arising from Information and Communication Technology (ICT) based development are not distributed evenly across the globe. There are significant economic, political, and social differences among countries that affect how quickly they can provide ICT access and its benefits to their citizens.
- Developed countries have generally made rapid progress in this area, while developing countries have fallen behind, creating what is known as the digital divide.
- Additionally, digital divides also exist within countries. For instance, in large nations like India or Russia, urban centers tend to have better connectivity and access to the digital world compared to rural areas on the periphery.
|
50 videos|366 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Tertiary And Quaternary Activities Class 12 Geography
| 1. What are tertiary activities and why are they important? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between quaternary and quinary activities? |  |
| 3. How does the digital divide impact tertiary and quaternary activities? |  |
| 4. What types of jobs are typically found in the tertiary and quaternary sectors? |  |
| 5. How can countries bridge the digital divide to enhance tertiary and quaternary activities? |  |





















