Mineral & Energy Resources Class 12 Geography
| Table of contents |

|
| Minerals |

|
| Types of Mineral Resources |

|
| Distribution of Minerals in India |

|
| Energy Resources |

|
| Conservation of Energy Resources |

|
Minerals
Mineral is defined as a “homogenous, naturally occurring substance with a definable internal structure.” Minerals are found in varied forms in nature, ranging from the hardest diamond to the softest talc. Rocks are combinations of homogeneous substances called minerals.Mode of Occurrence of Minerals
Minerals are usually found in “ores”. The term ore is used to describe an accumulation of any mineral mixed with other elements. Minerals generally occur in the following forms:
- In igneous and metamorphic rocks, minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints.
- In sedimentary rocks, a number of minerals occur in beds or layers.
- The decomposition of surface rocks and the removal of soluble constituents also forms the minerals.
- Minerals also occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and the base of hills.
- The ocean waters contain vast quantities of minerals.
Types of Mineral Resources
Minerals can be classified into three types:
- Metallic Minerals
- Non-Metallic Minerals
- Energy Minerals
1. Metallic Minerals
These minerals contain metals.
These are of two types:
(i) Ferrous minerals
- These minerals contain iron.
- It accounts for about three- fourths of the total value of the production of metallic minerals.
- They provide a strong base for the development of metallurgical industries.
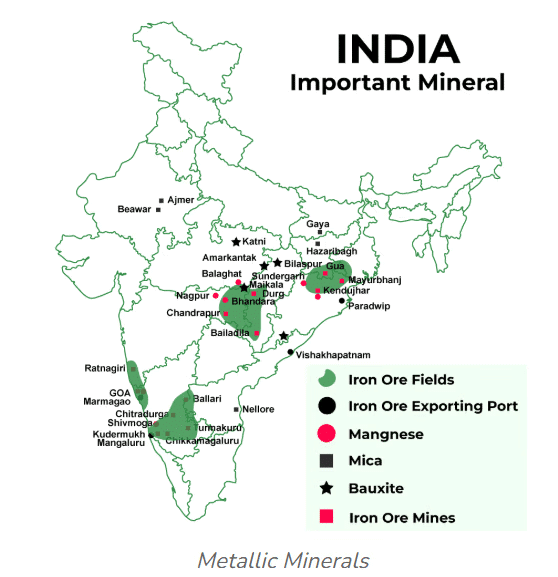
(a) Iron Ore
- This is a fundamental mineral and essential for industrial growth.
- Magnetite is the best iron ore, containing up to 70 percent iron.
- Hematite is the most widely used iron ore, with 50-60 percent iron content.
- India has abundant high-quality iron ores.
- The main iron ore regions in India are:
- Odisha-Jharkhand belt
- Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra
- Bellary-Chitradurga-Chikmaglur-Tumkur belt in Karnataka
- Maharashtra-Goa belt in Goa and Ratnagiri district of Maharashtra.
(b) Manganese
- It is mainly used in the manufacturing of steel and ferro-manganese alloy.
- It is also used in manufacturing bleaching powder, insecticides and paints.
- Orissa is the largest producer of manganese ores in India.
(ii) Non-Ferrous Minerals
- These minerals do not contain iron.
- They play role in a number of metallurgical, engineering and electrical industries.
- Example of Non-ferrous minerals includes copper, bauxite, lead, zinc and gold.
(a) Copper
- It is malleable, ductile and a good conductor, therefore, copper is mainly used in electrical cables, electronics and chemical industries.
- The Balaghat mines in Madhya Pradesh, Khetri mines in Rajasthan and Singhbhum district of Jharkhand are leading producers of copper.
(b) Bauxite
- It is a clay-like substance from which alumina and later aluminium is obtained.
- Aluminium is an important metal because it combines the strength of metals such as iron, with extreme lightness and also with good conductivity and great malleability.
- In India, mainly found in the Amarkantak plateau, Maikal hills and the plateau region of Bilaspur-Katni.
2. Non-Metallic Minerals
These minerals do not contain metal.
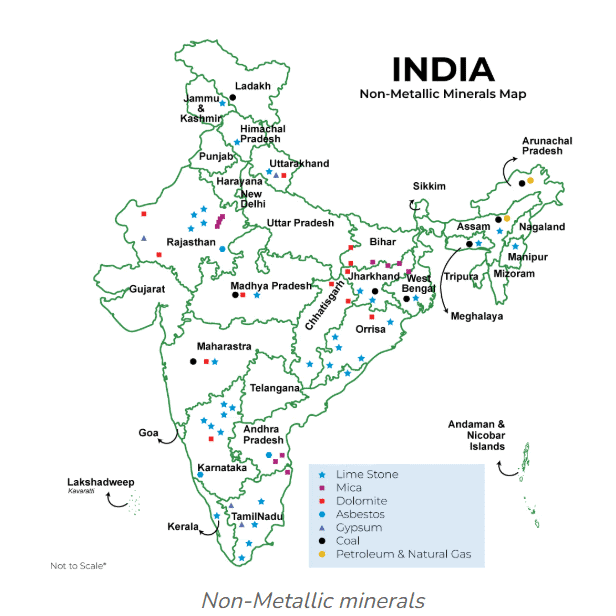
(i) Mica
- Mica consists of layers or plates.
- It can be found in various colours, including clear, black, green, red, yellow, or brown.
- Mica is vital for the electric and electronic industries due to its excellent dielectric strength, low power loss factor, and insulating properties.
- Major producers are located in the northern part of the Chota Nagpur plateau, including the Koderma-Gaya-Hazaribagh belt in Jharkhand, as well as Ajmer in Rajasthan and the Nellore mica belt in Andhra Pradesh.
(ii) Limestone
- Limestone is found in association with rocks composed of calcium carbonates or calcium and magnesium carbonates.
- It is the basic raw material for the cement industry and essential for smelting iron ore in the blast furnace.
Agencies involved in the exploration of minerals
- Geological survey of India
- Oil and natural gas commission
- Mineral exploration corporation ltd
- National mineral development corporation
- Indian bureau of mines
- Bharat gold mines
- Hindustan copper ltd
- National aluminum ltd
- Dept. Of mining and geology
Distribution of Minerals in India
- Most metallic minerals in India are found in the peninsular plateau region, located in old crystalline rocks.
- Over 97 percent of coal reserves are in the valleys of Damodar, Sone, Mahanadi, and Godavari.
- Petroleum reserves are within the sedimentary basins of Assam, Gujarat, and the Mumbai High (offshore in the Arabian Sea).
- New reserves have also been discovered in the Krishna-Godavari and Kaveri basins.
- The majority of major mineral resources are found east of a line connecting Mangaluru and Kanpur.
Mineral Belts in India:
- The main belts are: The North-Eastern Plateau Region, South-Eastern Plateau Region, and the Peninsular Region.
North-Eastern Plateau Region:
- This region includes West Bengal, Odisha, and parts of Chhattisgarh. Minerals found here are iron, coal, manganese, bauxite, and mica.
South-Eastern Plateau Region:
- This area covers Karnataka, Goa, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. Minerals found here include ferrous metals, limestone, bauxite, iron ore, manganese, and coal deposits.
North Western Region
- Covers Rajasthan (RAJ) and Gujarat (GUJ).
- Minerals include copper, lead, zinc, cobalt, wolfram, sandstone, granite, marble, gypsum, fuller's earth, dolomite, and limestone. Petroleum is specifically found in Gujarat.
Energy Resources
Energy resources can be classified as
- Conventional Sources: It includes firewood, cattle dung cake, coal, petroleum, natural gas and electricity.
- Non-Conventional Sources: It includes solar, wind, tidal, geothermal, biogas and atomic energy
1. Conventional Sources of Energy
(i) Coal: There are three types of coal
- Anthracite: Found in the Himalayan region.
- Bituminous: Located in Gondwana fields, DVC, Godavari Valley, Sone Valley, Jharia, Raniganj, Mahanadi Valley, Chanda, and Wardha Valley.
- Lignite: Found in Tamil Nadu.
- Tertiary coal: Found in Assam, Arunachal Pradesh (ARP), Meghalaya (MEG), Nagaland (NAG), and Jammu & Kashmir (J&K).
(ii) Petroleum
- Used to make energy resources, petrochemical industries, fertilizers, synthetic rubber, wax, lubricants, soap, and cosmetics.
- Also known as liquid gold.
- Found in Digboi, Naharkatia, and Moran in Assam; Ankaleshwar, Kalol, Mehasana, and Nawagam in Gujarat; and Mumbai High.
- Krishna Godavari Basin.
- Oil refineries include two types: (i) field-based and (ii) market-based.
- There are a total of 18 oil refineries.
(iii) Natural Gas
- Found in Gujarat, Rajasthan, Tripura, Krishna Godavari, and Cauvery Basin.
- Nuclear energy resources: Uranium and thorium are important minerals.
- Uranium deposits occur in the Dharwar rocks.
- Found in Singhbhum in Bihar, Udaipur, Alwar, Jhunjhunu of Rajasthan, Durg of Chhattisgarh, and Bhandara of Maharashtra.
- Thorium is mainly obtained from monazite and ilmenite in the beach sands along the coast of Kerala and Tamil Nadu.
- World's richest monazite deposits occur in Palakkad and Kollam districts of Kerala, near Vishakhapatnam in Andhra Pradesh, and Mahanadi river delta in Odisha.
- Monazite sands of Kerala.
- The Atomic Energy Commission was established in 1948.
- Nuclear power stations include: Tarapur in Maharashtra, Rawatbhata in Rajasthan, Kalpakkam in Tamil Nadu, Narora in Uttar Pradesh, Kaiga in Karnataka, and Kakarapara in Gujarat.
2. Non-conventional resources: The renewable energy sources like solar energy, wind, tide, biomass and energy from waste material are called Non-Conventional Energy Sources.
- Nuclear or Atomic Energy: Nuclear Energy is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. Uranium and Thorium are used for generating atomic or nuclear power.
- Solar Energy: Solar energy is produced by the Sun’s light. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity.
- Wind Energy : Wind Energy or Power is the use of wind to generate electricity. Wind turbines are used for this purpose. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai.
- Tidal Energy or Wave Energy: Tidal energy is the form of hydropower that converts the energy obtained from tides into useful forms of power, mainly electricity. In India, the Gulf of Khambhat, the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat on the western coast and Gangetic delta in Sunderban regions of West Bengal provide ideal conditions for utilising tidal energy.
- Geo-Thermal Energy: When heat and electricity are produced by using the heat from the interior of the earth, it is known as Geo-Thermal Energy. In India, geothermal energy is harnessed from Parvati valley near Manikarn in Himachal Pradesh and from Puga Valley, Ladakh.
In 1880, Boise, Idaho (USA) successfully tapped underground heat for the first time using a hot water pipe system to warm nearby buildings, and this plant is still operational.
- Bio-energy : It is derived from biological waste like agricultural residues, municipal, and industrial waste. It can be converted into electricity, heat, or cooking gas while also processing waste. This helps rural economies, reduces pollution, promotes self-reliance, and lowers fuel wood dependence. Bio-energy projects, like the one in Okhla, Delhi, efficiently convert waste into energy.
Conservation of Energy Resources
Every part of our economy—like agriculture, industry, transport, commercial, and domestic sectors—requires energy. The challenge we face in achieving sustainable development is to connect economic growth with taking care of our environment. There is an urgent need to conserve resources and find a sustainable way to save energy. Here are some ways we can all help:
- Using public transport instead of personal vehicles
- Switching off electrical appliances when not in use
- Utilising energy-saving devices
- Exploring alternative energy sources like solar, wind, wave, and geothermal energy
It is crucial to protect our resources for future generations, ensuring a balance between our energy demands and environmental sustainability.
|
50 videos|353 docs|37 tests
|
FAQs on Mineral & Energy Resources Class 12 Geography
| 1. What are the main types of minerals and how are they classified? |  |
| 2. What are the primary energy resources derived from minerals? |  |
| 3. How do minerals impact the economy and the environment? |  |
| 4. What is the importance of mineral resources in daily life? |  |
| 5. How can we conserve mineral and energy resources? |  |
















