Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
Q1. Name the different major physiographic divisions of India. Write a note on any one of the physiographic divisions of India. (Important)
Ans: The major physiographic divisions of India are:
- The Himalayan Mountains
- The Northern Plains
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Indian Desert
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands
The Coastal Plains:
- The Coastal Plains are narrow strips of flat land along the eastern and western coasts of India, lying between the Peninsular Plateau and the seas.
- The Western Coastal Plain lies along the Arabian Sea, between the Western Ghats and the sea. It includes the Konkan Coast (from Mumbai to Goa), the Kannad Coast (central part), and the Malabar Coast (southern part).
- The Eastern Coastal Plain lies along the Bay of Bengal, between the Eastern Ghats and the sea. It is wider and more level than the western plain and includes the Northern Circar (northern part) and the Coromandel Coast (southern part).
- These coastal plains are important for agriculture, trade, and fishing.
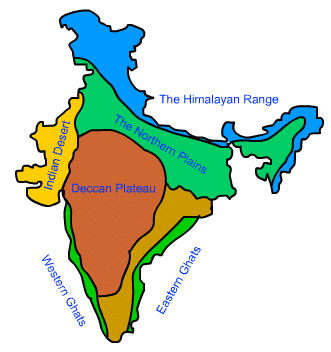 Physiographic divisions of India
Physiographic divisions of India
Q2. Where are the Western and the Eastern Ghats situated? Write a small note on each.
Ans: The Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats are situated in the Peninsular Plateau region of India.
Western Ghats:
- Form the western edge of the Deccan Plateau.
- Run parallel to the western coast.
- Continuous range crossed only through passes like Thal, Bhor, and Pal Ghats.
- The average elevation ranges from 900 to 1600 metres.
- The highest peaks include Anai Mudi (2,695 metres) and Doda Betta (2,637 metres).
Eastern Ghats:
- Mark the eastern edge of the Deccan Plateau.
- Stretch from the Mahanadi Valley to the Nilgiri Hills.
- The average elevation is lower, around 600 metres.
- The highest peak is Mahendragiri (1,501 metres).
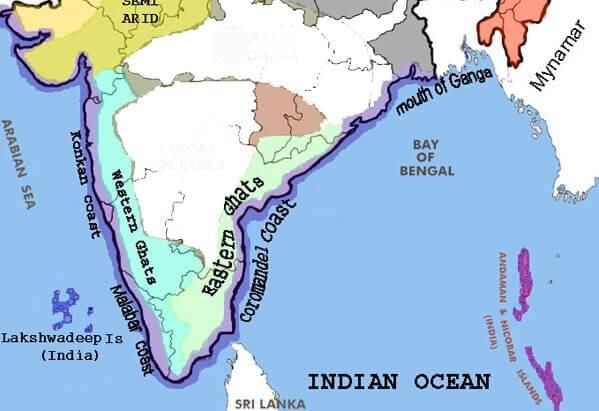 Western and Eastern ghats of India
Western and Eastern ghats of India
Q3. What is the Great Himalaya? Write two characteristics of it.
Ans: The Great Himalaya, also known as the Inner Himalayas or Himadri, is the northernmost range of the Himalayas.
- Highest Peaks: This range is the most continuous and features the highest peaks, averaging around 6,000 metres. It includes all the major Himalayan peaks.
- Geological Features: The folds of the Great Himalaya are asymmetrical, with a core made of granite rock. This range is always snow-covered and contains numerous glaciers.
Q4. Which plateau lies between the Aravali and the Vindhya range? Write a brief note on this plateau.
Ans: The Malwa Plateau is situated between the Aravali hills and the Vindhya range, with the Aravali to the west and the Vindhya to the south. It is mainly found in Madhya Pradesh and is characterised by:
- Extensive lava flows form its foundation.
- The rolling plains are interspersed with flat-topped hills.
- Ravines, especially near the Chambal Valley in the east.
The northern section of the plateau, located above the Narmada River, is referred to as the Central Highlands.
Q5. What do you understand by 'duns'? Where are they situated in our country?
Ans: Duns are longitudinal valleys found between the Lesser Himalayas and the Shivaliks.
They are characterised by:
- A width of 10-50 km
- An altitude ranging from 900 to 1100 metres
- Composition of unconsolidated sediments
- Examples of notable Duns include Dehra Dun, Kotli Dunand Patli Dun
Q6. Describe 'Bhabar' and 'Terai'.
Ans: Bhabar is a region at the base of the Himalayas, characterised by a formation of pebbles. Key features include:
- A narrow belt, approximately 8 to 16 km wide, runs parallel to the Shiwaliks.
- Streams that disappear into the ground within this area.
Terai lies south of Bhabar and is known for:
- It's sloping land at the foothills of the Nepal Himalayas.
- Heavy rainfall results in a lush, swampy environment.
- Once densely forested, but now largely cleared for agriculture.
Q7. Name any three divisions of the Himalayas on the basis of regions from West to East, and also write one main feature of each.
Ans:
- Punjab Himalayas: Located between the Indus and Sutlej rivers, this region is also known as the Kashmir Himachal Himalaya.
- Kumaon Himalayas: This area lies between the Sutlej and Kali rivers.
- Assam Himalayas: Defined by the Kali and Teesta rivers, this region extends from the Teesta to the Dihang rivers.
Q8. Why are the Himalayas called young fold mountains?
Ans: The Himalayas are known as young fold mountains for several key reasons:
- They are geologically young, having formed relatively recently in Earth's history.
- These mountains were uplifted from the Tethys Sea during the Tertiary period.
- Their landscape features high peaks, deep valleys, and fast-flowing rivers, indicating a youthful topography.
- Overall, the Himalayas are one of the most rugged and dynamic mountain ranges in the world.
 The Himalayan mountains
The Himalayan mountains
Q9. The relief of India displays a great physical variation. Explain.
Ans: India's landscape is characterised by a wide range of physical features:
- Mountains: The Himalayas are young, folded mountains that run along the northern border, featuring high peaks and deep valleys.
- Plains: The northern plains are made up of alluvial deposits, making them fertile and ideal for agriculture.
- Plateaus: The Peninsular Plateau consists of ancient igneous and metamorphic rocks, with gently rising hills.
- Deserts: The Indian Desert in the west is known for its arid conditions.
- Islands: India includes various islands that enjoy a tropical climate and rich biodiversity.
This diverse geography has been shaped by geological processes over time, including weathering, erosion, and deposition.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 1 Question Answers - Contemporary India - I
| 1. What are the major physical features of India? |  |
| 2. How do the Himalayas influence the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the Indo-Gangetic plains in India? |  |
| 4. What role do rivers play in the physical geography of India? |  |
| 5. How does the Thar Desert affect the lifestyle of people living in its vicinity? |  |






















