Key Concepts - Nazism and the Rise of Hitler | Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Birth of the Weimar Republic |

|
| The Nazi Worldwide |

|
| Establishment of the Racial State |

|
| Youth in Nazi Germany |

|
| Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity |

|
Birth of the Weimar Republic
World War I Participation: Germany, alongside the Austrian Empire, fought against the Allies (England, France, Russia), with the U.S. joining later.
Impact of War on Europe: The war was lengthy, leading to significant resource depletion across Europe.
Defeat and Consequences: Germany was defeated in November 1918. The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties:
(i) Loss of overseas colonies.
(ii)Loss of 13% of territory to France, Poland, Denmark, and Lithuania.
(iii) Loss of 75% of iron and 26% of coal resources.
(iv) Demilitarisation of Germany to weaken its military capabilities.
(v)Imposition of the War Guilt Clause, making Germany responsible for the war and liable for reparations amounting to £6 billion.
(vi) Occupation of the Rhineland by Allied armies.Political Changes Post-War: The abdication of the emperor led to the establishment of the Weimar Republic with a democratic constitution and a federal structure. Universal suffrage was introduced, including voting rights for women.
Public Discontent: The Weimar Republic was unpopular primarily due to the terms of the Treaty of Versailles, viewed as humiliating and unjust by many Germans.
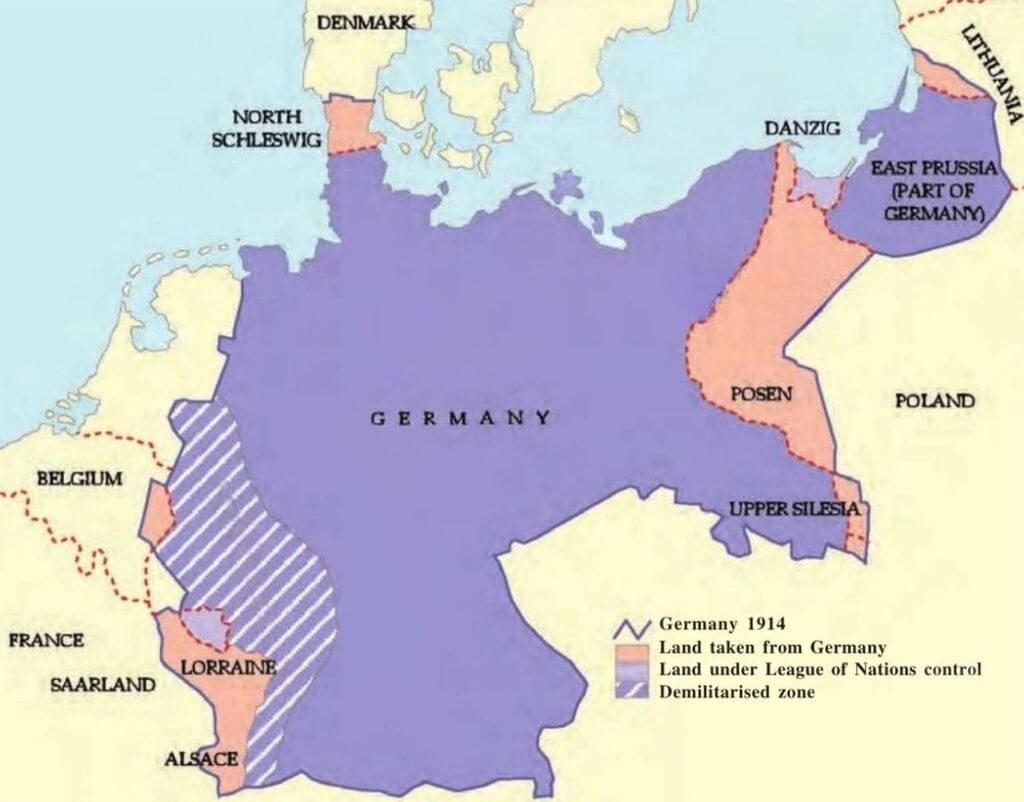 Germany after the Versailles Treaty
Germany after the Versailles Treaty
The Effects of the War
- Europe transitioned from creditor to debtor status post-WWI, profoundly affecting financial stability.
- The Weimar Republic, burdened by war guilt and reparations, faced severe financial and national humiliation.
- Supporters of the Weimar Republic were disparagingly called 'November criminals' by conservative nationalists.
- Media and politics emphasized aggression and masculinity; glorified trench life contrasted with the harsh realities soldiers faced.
- Popular support for democracy waned, fostering a rise in conservative dictatorships in interwar Europe.
Political Radicalism and Economic Crises
- The Weimar Republic's formation coincided with the Spartacist uprising, inspired by the Bolshevik Revolution.
- Soviets of workers and sailors were established, pushing for Soviet-style governance.
- Opposition from socialists, Democrats, and Catholics led to the formation of the democratic republic in Weimar.
- The Weimar Republic, with the aid of the Free Corps, suppressed the Spartacist uprising, leading to the foundation of the Communist Party of Germany.
- Communists and Socialists became irreconcilable, weakening their opposition against Hitler.
- The economic crisis of 1923 exacerbated political radicalisation; Germany struggled with war reparations and depleted gold reserves.
- The French occupation of the Ruhr in retaliation for non-payment of reparations and Germany's passive resistance led to hyperinflation.
- Hyperinflation peaked in 1923, with the German mark plummeting in value, leading to extreme price rises and economic instability.
- The Dawes Plan, introduced by the Americans, helped stabilise Germany by reworking the reparations terms, easing the financial crisis.
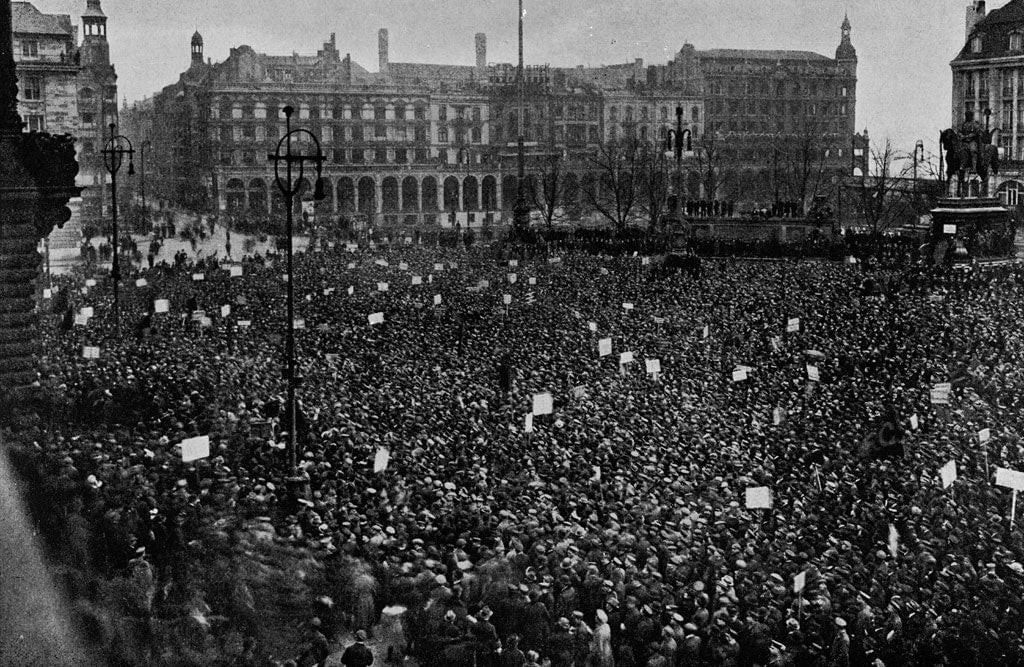 Spartacist uprising
Spartacist uprising
The years of Depression
- Economic Instability (1924-1928): The Weimar Republic experienced temporary stability, heavily reliant on short-term loans from the USA.
- Wall Street Crash (1929): The withdrawal of American loans after the 1929 Wall Street crash precipitated a global economic crisis, marking the onset of the Great Depression.
- Impact on the USA: The national income of the USA halved, with widespread factory closures, plummeting exports, and mass unemployment.
- Severe Effects in Germany: By 1932, German industrial output fell to 40% of its 1929 level; unemployment soared to 6 million.
- Social Desperation: Widespread unemployment led to high levels of poverty and despair, with many turning to criminal activities and others displaying signs of severe economic distress.
- Middle-Class Anxiety: The middle classes feared proletarianization due to diminishing savings and ruined businesses.
- Political Fragility: The Weimar Republic’s political system was unstable, characterized by proportional representation and frequent use of emergency powers under Article 48, which hindered effective governance and led to disillusionment with democracy.
- Constitutional Weaknesses: The Weimar constitution’s flaws, including difficulty in achieving majority rule and extensive presidential emergency powers, exacerbated political instability.
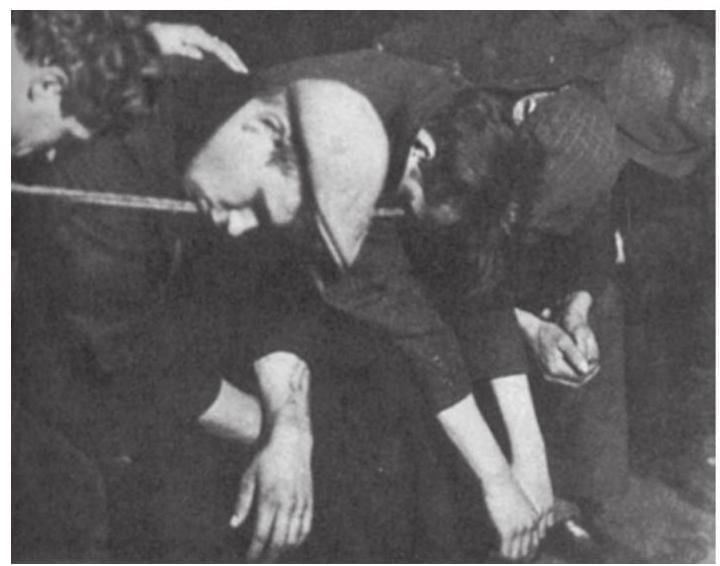 Sleeping on the line. During the Great Depression the unemployed could not hope for either wage or shelter. On winter nights when they wanted a shelter over their head, they had to pay to sleep like this.
Sleeping on the line. During the Great Depression the unemployed could not hope for either wage or shelter. On winter nights when they wanted a shelter over their head, they had to pay to sleep like this.
Hitler's Rise to Power
- Hitler's Background: Born in 1889 in Austria, he experienced poverty, served as a corporal in WWI.
- Political Start: Joined the German Workers' Party in 1919, transformed it into the Nazi Party.
- Failed Coup: 1923, attempted to seize Bavaria, arrested for treason.
- Nazism & Great Depression: Economic crisis helped Nazism become a mass movement; Nazi Party votes rose from 2.6% in 1928 to 37% in 1932.
- Propaganda and Promises: Hitler used strong speeches and propaganda to promise national restoration, economic recovery, and independence from foreign influence.
- Mass Mobilisation: Emphasised rituals and spectacles, used symbols like the Swastika and mass rallies to build unity and support.
- Saviour Image: Propaganda portrayed Hitler as a messiah figure rescuing Germany from despair.

Destruction of Democracy
- Hitler's Chancellorship: Appointed on January 30, 1933, by President Hindenburg.
- Power Consolidation: Hitler began dismantling democratic structures immediately after gaining power.
- Reichstag Fire: The February 1933 fire enabled Hitler to suspend civic rights under the Fire Decree.
- Targeting Communists: Post-fire, Communists were among the first detained and sent to concentration camps.
- Enabling Act (March 3, 1933): Granted Hitler dictatorial powers, allowing rule by decree and banning all political parties except the Nazi Party.
- State Control: Nazis seized control of the economy, media, army, and judiciary.
- Security Forces Expansion: Creation of the Gestapo, SS, and other forces to enforce Nazi ideologies.
- Police Powers: Extended powers led to widespread abuse including detentions, deportations, and arrests without due process, establishing Nazi Germany as a feared criminal state.
Reconstruction
- Hjalmar Schacht was responsible for economic recovery, focusing on full employment and production, resulting in the construction of German superhighways and the Volkswagen.
- Hitler withdrew from the League of Nations in 1933, reoccupied the Rhineland in 1936, united Austria and Germany in 1938, and annexed Czechoslovakia.
- England tacitly supported Hitler's actions, considering the Versailles Treaty too severe.
- Despite Schacht’s advice against extensive rearmament due to deficit financing, Hitler dismissed him and escalated military spending to prepare for territorial expansion.
- Germany invaded Poland in September 1939, triggering war with France and England.
- In September 1940, Germany, Italy, and Japan signed a pact, bolstering Hitler’s international stance.
- By 1940, Hitler had installed puppet regimes across Europe and reached the peak of his power.
- In June 1941, Hitler’s invasion of the Soviet Union ultimately led to significant German losses at Stalingrad and a retreat pushed by the Soviet Red Army.
- Initially resistant, the USA entered the war after Japan, allied with Hitler, attacked Pearl Harbor in December 1941.
- The war ended in May 1945 with Hitler’s defeat and the US's atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
The Nazi Worldwide
- Nazi Ideology: Founded on Hitler’s belief in a racial hierarchy, placing "Aryan" Germans at the top and Jews at the lowest.
- Racial Superiority: Influenced by Darwin’s theory of evolution and Spencer's concept of survival of the fittest, misapplied to justify racial dominance.
- Lebensraum: Aimed at territorial expansion for resource gain and uniting Germans geographically.
- Implementation: Poland was used as a testing ground for these expansionist and racial policies
Establishment of the Racial State
- Nazi Racial Ideology: Aimed to create a pure Germanic race by eliminating those deemed ‘undesirable’, including Jews, Gypsies, blacks, Russians, and Poles.
- Euthanasia Programme: Targeted Germans considered mentally or physically unfit, condemning them to death.
- Persecution of Minorities: Gypsies and blacks were persecuted as racial ‘inferiors’, while Russians and Poles were treated as subhuman.
- Jewish Suffering: Jews faced extreme persecution due to Nazi beliefs amplified by traditional anti-Semitic stereotypes.
- Nazi Measures Against Jews:
- 1933-1938: Jews were terrorized and segregated, encouraged to emigrate.
- 1939-1945: Jews were concentrated in ghettos and exterminated in gas chambers in Poland.
The Racial Utopia
- Nazi Genocide Strategy: Integrated genocide with warfare, particularly evident in occupied Poland.
- Annexation and Displacement: Northwestern Poland annexed, Poles displaced for German resettlement.
- General Government Zone: Eastern Poland designated for 'undesirables', serving as a harsh containment area.
- Intellectual Suppression: Polish intelligentsia targeted and killed to prevent resistance.
- Racial Selection of Children: Aryan-looking Polish children either Germanized or left to perish in orphanages.
- Holocaust Centers: General Government housed major ghettos and gas chambers for executing Jews.
Youth in Nazi Germany
- Youth Indoctrination: Hitler prioritized shaping the youth, believing that instilling Nazi ideology early was crucial for a strong Nazi society.
- School 'Cleansing': Jewish and politically unreliable teachers dismissed. Schools segregated by race, with 'undesirable' children (Jews, handicapped, Gypsies) eventually expelled and many sent to gas chambers.
- Nazi Schooling and Curriculum: Textbooks rewritten to include racial science, promoting stereotypes about Jews and emphasizing loyalty to Hitler.
- Ideological and Physical Training: Sports aimed at fostering violence and aggression; curriculum designed to glorify war and instill hatred towards Jews and democracy.
- Youth Organizations: Mandatory participation in Nazi youth groups like Jungvolk and Hitler Youth, which taught warfare glorification and racial hatred.
- Centralization of Youth: By 1926, all German youth movements were consolidated under the Hitler Youth to ensure uniform Nazi indoctrination.
The Nazi Cult of Motherhood
- Distinct Gender Roles: Nazi ideology promoted sharply different roles for men and women, opposing democratic gender equality.
- Female Indoctrination: Girls were taught to be mothers, focusing on rearing Aryan children and upholding Nazi home values.
- Motherhood in Nazi Policy: Hitler emphasised the mother's role; however, treatment varied based on the racial desirability of children.
- Incentives for Mothers: Rewards such as Honour Crosses given for multiple children; bronze for four, silver for six, gold for eight.
- Punishments for Non-compliance: Women associating with non-Aryans faced public shaming, loss of civic honour, and familial separation.
The Art of Propaganda
- Euphemistic Language: Nazis avoided terms like "kill" or "murder," using "special treatment" and "final solution" instead.
- Media Control: Utilised films, radio, and posters to disseminate propaganda and reinforce their agenda.
- Deceptive Descriptions: Gas chambers disguised as "disinfection-areas" with fake showerheads.
- Propaganda Tactics: Enemies stereotyped in media as threats; Jews depicted as vermin to dehumanise them.
- Manipulative Outreach: Nazis targeted all societal segments, claiming they alone could resolve national problems.
Ordinary People and the Crimes Against Humanity
- Varied Responses: Common people in Nazi Germany had mixed reactions to Nazism. Some embraced it, others passively witnessed, and a few actively resisted.
- Adoption of Nazi Views: Many Germans internalised Nazi propaganda, leading to widespread hatred towards Jews and other targeted groups.
- Participation in Persecution: Ordinary citizens often assisted in identifying and marking Jews, driven by a belief in Nazi promises of prosperity.
- Resistance and Apathy: While some Germans actively opposed Nazism, facing severe repercussions, the majority remained passive, fearful of repercussions for dissenting.
- Silence and Compliance: Pastor Niemoeller highlighted the prevalent silence and inaction among Germans during escalating Nazi atrocities, encapsulated in his reflective poem about the sequential persecution of various groups.
- Psychological Impact on Jews: Jews internalised negative stereotypes, evidenced by Charlotte Beradt’s documentation of their dreams reflecting Nazi-propagated imagery, showing deep psychological distress even before physical harm.
Knowledge about the Holocaust
- Delayed Awareness: The full extent of Nazi atrocities, known as the Holocaust, became widely recognized only after WWII ended and Germany was defeated.
- German Focus: Post-war, Germans were primarily concerned with their own recovery from the devastation of the war.
- Jewish Testimonies: Jews sought to ensure that the world remembered the horrors they endured, with many survivors expressing a strong desire to share their experiences.
- Documentation Efforts: Inhabitants of ghettos and concentration camps often wrote diaries, kept notes, and even created archives to document their experiences despite extreme conditions.
- Destruction of Evidence: As defeat loomed, Nazi officials were ordered to destroy all incriminating evidence of their genocidal practices.
- Lasting Memory: The Holocaust is remembered and studied through various forms including memoirs, fiction, documentaries, poetry, and in museums worldwide, serving as a tribute to victims and survivors, a reminder of collaboration, and a warning against apathy.
|
743 videos|1444 docs|633 tests
|
FAQs on Key Concepts - Nazism and the Rise of Hitler - Famous Books for UPSC Exam (Summary & Tests)
| 1. What were the main factors that led to the birth of the Weimar Republic? |  |
| 2. How did the Nazi Party rise to power in Germany? |  |
| 3. What were the key components of the racial state established by the Nazis? |  |
| 4. How did the youth in Nazi Germany experience indoctrination? |  |
| 5. How did ordinary people in Germany respond to the crimes against humanity committed by the Nazis? |  |
















