Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Question Answers - Democratic Politics - I
Q1. How can you say that every government that holds an election is not a democracy? Give an example to prove your point. [Important]
Ans. It is true that every government that holds an election is not a democracy. In many dictatorships and monarchies, there are formally elected parliaments and governments but the real power is with those who are not elected. Pakistan under General Musharraf could not be called a democracy because people there elected their representatives to the national and provincial assemblies but the power to take final decision rested with army officials and with General Musharraf.
Q2. In China, elections are held after every five years. Inspite of this, China does not have a democratic government. Why?
Ans. In China, elections are regularly held after every five years for electing the country's Parliament. The Parliament has the power to appoint the President of the country. It has nearly 3,000 members elected from all over China. Some members are elected by the Army. Before contesting elections, a candidate needs the approval of the Chinese Communist Party. The government is always formed by the Communist Party.
Q3. In which way is the right to vote denied in Saudi Arabia and Fiji?
Ans. In Saudi Arabia women do not have the right to vote. In Fiji, the electoral system is such that the vote of an indigenous Fiji has more value than that of an Indian Fijian. In both the countries, the right to vote is denied as there is no political equality. In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote and each vote must have one value.
Q4. Why has India never had a famine of the level which occurred in China in 1958-61?
Ans.In China’s famine of 1958-61, nearly three crore people died. In those days India’s economic condition was not much better than China. Yet India did not have a famine of the kind China had. The reason was the difference in the economic policies of the two countries. Democratic government in India responded to the food shortage in a way that Chinese government did not. If China too had had multi-party elections, an opposition party and a press free to criticise the government, so many people would not have died in the famine.
 Fig. Children affected in famine
Fig. Children affected in famine
Q5. ‘Democracy is based on consultation and discussion.’ Explain.
Ans. Consultation and discussion help democracy prosper. A democratic decision always involves many persons, discussions and meetings. When a number of people put their heads together, they are able to point out possible mistakes in any decision. This reduces the chances of rash or irresponsible decisions. Thus democracy improves the quality of decision-making.
Q6. Why is it not possible for the people to rule directly but through elected representatives?
Ans. The people cannot rule directly but only through their elected representatives because, firstly, modern democracies involve such a large number of people that it is physically impossible for them to sit together and take a collective decision. Secondly, even if they could, the citizens do not have the time, the desire or the skill to take part in all the decisions.
Q7. Is it possible for any country to become a perfect democracy? Give reasons.
Ans. No country is a perfect democracy as every democracy has to realize the ideals of democratic decision-making. This cannot be achieved once and for all. This requires a constant effort to save and strengthen democratic forms of decision-making. What we do as citizens can make a difference to making our country more or less democratic.
Q8. Explain any three differences between democratic country and non-democratic country?
Ans. 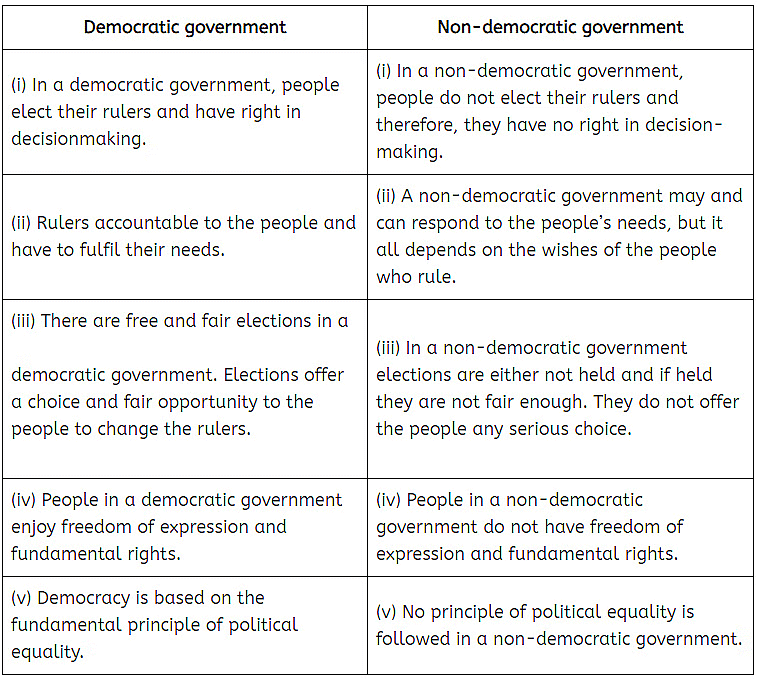
Q9. Why is Democracy considered the best form of government? Give three reasons.
Ans. Democracy is a more accountable form of government.
(i) It improves the quality of decision-making
(ii) It enhances the dignity of citizens.
(iii)It allows us to correct its own mistakes.
Q10. What is the role of citizen in promoting democracy?
Ans. Every citizen should be able to play equal role in decision-making. For this a citizen not only needs an equal right to vote but also needs to have equal information, basic education, equal resources.
Q11. Is China a democratic country or not? Give two arguments in favor of your answer.
Ans. China is not a democratic country.
(i) Only those who are members of the Chinese Communist Party or eight smaller parties allied to it are allowed to contest elections;
(ii) Before contesting elections a candidate needs the approval of the Chinese Communist Party.
Q12. Explain any three features of democracy.
Ans. According to a Democracy—
(i) Rulers elected by the people take all the major decisions.
(ii) Elections offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the current rulers.
(ii) This choice and opportunity is available to all the people on an equal basis.
Q13. Why is Zimbabwe not considered a democratic country?
Ans. It is ruled by ZANU-PF, the party that led the freedom struggle. Its leader, Robert Mugabe has been ruling the country since independence. Elections are held regularly but always won by the ZANU-PF. President Mugabe uses unfair means in the elections. He has changed the constitution several times to increase the power of the president. Radio and TV are controlled by the government.
Q14. How does democracy in a country enhance the diginity of an individual? State three points.
Ans. Fig. Statue of dignity(i) Democracy is based on the principal of political equality on recognising that the poorest and the least educated has the same status as the rich and the educated.
Fig. Statue of dignity(i) Democracy is based on the principal of political equality on recognising that the poorest and the least educated has the same status as the rich and the educated.
(ii) People are not subjects of a ruler they are the rulers themselves.
(iii) Even when they make mistakes, they are responsible for their conduct.
Q15. ‘‘Elections in China do not represent people verdict.’’ Explain.
Ans. In China the elections do not offer the people any serious choice. They have to choose the ruling party and the candidates approved by it. Can it be called a choice? There is only are political party and people have to vote for its candidates.
Q16. ‘‘Democracy allows people to correct their own mistakes’’. Support the given statement with three points.
Ans. The advantage in a democracy is that mistakes made by a government cannot be hidden for long. There is a space for public discussion on these mistakes and there is room for correction. Either the rulers have to change their decisions or they can be changed.
Q17. Explain any three major political changes that took place recently in India's neighbourhood?
Ans.
(i) Pakistan–General Musharaff led a military coup.
(ii) Nepal–In 2005 the new king dismissed the elected government.
(iii) Iraq–Sadaam Hussain's regime was overthrown.
Q18. What does ‘one person, one vote, one value’ mean? Name the countries who deny the equal right to vote.
Ans: The principle of one person, one vote, one value is rooted in the concept of universal adult franchise. This means that every adult citizen, regardless of gender, race, religion, or socioeconomic status, has the right to vote and participate in the democratic process.
However, some countries deny equal voting rights:
- Saudi Arabia: Women were not allowed to vote until 2015.
- Estonia: Citizenship rules disadvantage the Russian minority, making it hard for them to obtain voting rights.
- Fiji: The electoral system gives more value to the votes of indigenous Fijians compared to Indian-Fijians.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Civics Chapter 1 Question Answers - Democratic Politics - I
| 1. What are the key features of democracy? |  |
| 2. Why is democracy considered important for a country? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages and disadvantages of democracy? |  |
| 4. How does democracy differ from other forms of government? |  |
| 5. What role does the constitution play in a democracy? |  |

















