Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answers - Minerals and Energy Resources
Q1. Name the two varieties of iron ore in India that have a high content of iron. Mention the names of places in India which have the richest iron ore deposits. Explain two effects on our economy due to the export of good quality ores in large quantities.
Ans: The two varieties of iron ore in India with high iron content are magnetite and hematite.
Rich deposits of iron ore are found in several regions of India:
- Odisha-Jharkhand belt: High-grade hematite in Badampahar (Mayurbhanj and Keonjhar districts) and Gua and Noamundi in Singhbhum district, Jharkhand.
- Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt: Located in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra, features super-high-grade hematite in the Bailadila range of hills in Bastar district.
- Maharashtra-Goa belt: Includes Ratnagiri and Chandrapur in Maharashtra, and Bicholim and Pali in Goa.
About half of India's iron ore production is exported, mainly to Japan, Korea, and European countries, through ports like Paradip, Vishakhapatnam, Mangalore, and Marmagao.
The export of high-quality iron ore has two significant effects on the economy:
- Positive effect: It generates substantial foreign exchange, essential for development activities.
- Negative effect: It hampers domestic industrial production, as the country struggles to produce enough iron and steel despite having ample iron ore reserves.
Q2. What are the differences between hydro-electricity and thermal electricity? What is nuclear electricity?
Ans: 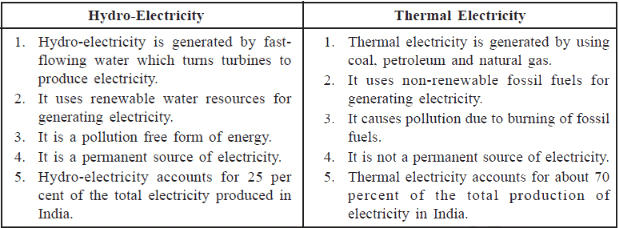
Nuclear electricity, also known as atomic energy, is produced by changing the structure of atoms in elements like uranium and thorium. This alteration releases a significant amount of energy in the form of heat, which is then used to generate electric power.
Q3. Name the ore from which aluminium is obtained. Why is aluminium considered to be an important metal? Name the areas which have rich deposits of the ore of aluminium.
Ans: Aluminium is primarily obtained from bauxite. Although several ores contain aluminium, bauxite is a reddish-brown, clay-like substance from which alumina and subsequently aluminium are extracted. Bauxite deposits form through the decomposition of various rocks rich in aluminium silicates.
Aluminium is important due to its:
- Strength: It combines the strength of metals like iron with extreme lightness, making it ideal for manufacturing aircraft and transport vehicles.
- Malleability: Its great malleability allows it to be used in construction for doors, windows, rods, and utensils.
- Conductivity: Aluminium is a good conductor of electricity, which makes it suitable for electrical conductors.
Rich deposits of bauxite are mainly found in:
- Amarkantak Plateau
- Maikal Hills
- Bilaspur-Katni Plateau region in Madhya Pradesh and Chhattisgarh
Additionally, Odisha is the leading producer, accounting for about 45% of India's total bauxite production, with the Panchpatmali deposits in Koraput being particularly significant.
Q4. State the facts about coal found in India with reference to the following :
(a) their total reserves
(b) its importance as a source of energy and as a source of raw material
(c) its main varieties
(d) distribution of coal in India
Ans: Coal is the most abundantly available and important fossil fuel in India.
(a) Total reserves of coal: India has approximately 214,000 million tonnes of coal reserves. These reserves are found in two main geological ages:
- Gondwana: Over 200 million years old.
- Tertiary: About 55 million years old.
(b) Importance as a source of energy and raw material:
- Coal is the primary source of power generation in India.
- It meets a significant portion of the nation's energy needs for industries and households.
- Essential for manufacturing iron and steel.
- Used as a raw material in the chemical industry.
(c) Main varieties of coal:
- Anthracite: Highest quality hard coal with over 80% carbon content.
- Bituminous: Most commonly used coal, containing 60-80% carbon.
- Lignite: Low-grade brown coal with high moisture content (about 60% carbon).
- Peat: Formed from decaying plants, with less than 50% carbon and low heating capacity.
(d) Distribution of coal in India:
- Coal is primarily found in the eastern part of India.
- Major resources of Gondwana coal are in the Damodar Valley (West Bengal, Jharkhand), including Jharia, Raniganj, and Bokaro.
- Other coal deposits are located in the Godavari, Mahanadi, Son, and Wardha valleys.
- Tertiary coal deposits are found in the northeastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh, and Nagaland.
Q5. How is petroleum an important source of both energy and raw material? Mention the names of the areas which have rich petroleum deposits.
Ans: Petroleum, also known as mineral oil, is a vital energy source in India. Its significance lies in the following areas:
- Provides fuel for heating and lighting.
- Powers vehicles, including automobiles, trains, aeroplanes, and ships.
- Generates thermal electricity, which is crucial for commercial power.
Additionally, petroleum is a key raw material for various industries. Byproducts obtained from its fractional distillation include:
- Chemical fertilisers
- Insecticides
- Plastics
- Raw materials for synthetic textiles and rubber.
In India, major petroleum production areas include:
- Mumbai High and Bassien in the Arabian Sea, contributing 63% of production.
- Gujarat, accounting for 18%, with important oilfields like Ankaleshwar and Kalol.
- Assam, the oldest oil-producing state, contributed 16%. Key fields include Digboi, Naharkatiya, and Sibsagar.
- Other regions with discoveries include the Kaveri, Krishna, and Godavari basins, as well as Jawalamukhi in Himachal Pradesh.
Q6. Why do we need to conserve our mineral resources? Explain any three methods of conservation of minerals.
Ans: Minerals are essential for various aspects of life, including agriculture, industry, and domestic use. However, we are depleting these resources, which took millions of years to form, at an alarming rate. The natural processes that create minerals are incredibly slow, making their replenishment negligible compared to current consumption rates. As these resources are finite and non-renewable, their rapid exploitation leads to lower quality and higher extraction costs. Therefore, it is crucial to conserve our mineral resources for future generations.
Here are three methods to conserve minerals:
- Minimise waste during mining and processing.
- Develop advanced technologies to utilise low-grade ores cost-effectively.
- Implement a recycling and reuse policy for minerals, using scrap metals and alternatives to reduce the need for new deposits.
Q7. In recent years, the use of which fuel for transport vehicles is gaining popularity? What development has provided impetus to India’s gas production?
Ans: In recent years, the use of Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) for transport vehicles is gaining popularity. It is replacing liquid fuels like petrol and diesel due to several advantages:
- Environmental benefits: CNG produces less pollution compared to traditional fuels.
- Cost-effective: As petroleum resources deplete, CNG offers a more economical alternative.
- Government initiatives: In cities like Delhi, CNG is promoted for cleaner air and reduced emissions.
Development in gas production: The 1,700 km Hazira-Bijapur-Jagdishpur (HVJ) cross-country gas pipeline has significantly boosted India’s gas production. This pipeline:
- Links Mumbai High and Bassein gas fields with various industrial complexes.
- Facilitates the easy transportation of natural gas from production areas to markets.
- Supports the growing demand for gas in the fertiliser and power sectors.
Overall, the expansion of gas infrastructure is crucial for meeting energy needs and promoting cleaner fuel options.
|
90 videos|815 docs|79 tests
|
FAQs on Class 10 Geography Chapter 5 Question Answers - Minerals and Energy Resources
| 1. What are the different types of minerals and their uses? |  |
| 2. How are energy resources classified? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of mineral resources for economic development? |  |
| 4. What are the environmental impacts of exploiting mineral and energy resources? |  |
| 5. How can we promote sustainable use of minerals and energy resources? |  |

















