NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - How do Organisms Reproduce
| Table of contents |

|
| Page No. 128 |

|
| Page No. 133 |

|
| Page No. 140 |

|
| Page No. 141 |

|
Page No. 128
Q1: What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Ans: DNA copying has following importance in reproduction:
- It keeps the species’ traits: By copying DNA, the specific characteristics of a species are passed down to the next generation.
- Allows for variation: Sometimes small changes occur in DNA copying. These variations can lead to differences within a species, which can be important for adapting to new environments.
- Ensures healthy growth: DNA has all the instructions needed for an organism to develop properly. Accurate copying of DNA is key for this.
- Continuity of Life: Through accurate DNA replication, life continues from parents to offspring without interruption.
Q2: Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Ans:Variations are more beneficial to the species than the individual because sometimes, for a species, the environmental conditions change so drastically that their survival becomes difficult.
- Example: If the temperature of water increases suddenly, then most of the bacteria living in that water will die. Only a few variants that are resistant to heat would be able to survive.
- However, if these variants had not been present, then the entire species of bacteria would have been destroyed.
- Thus, these variants help in the survival of the species. However, not all variations are necessarily beneficial for individual organisms.
Page No. 133
Q1: How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Ans: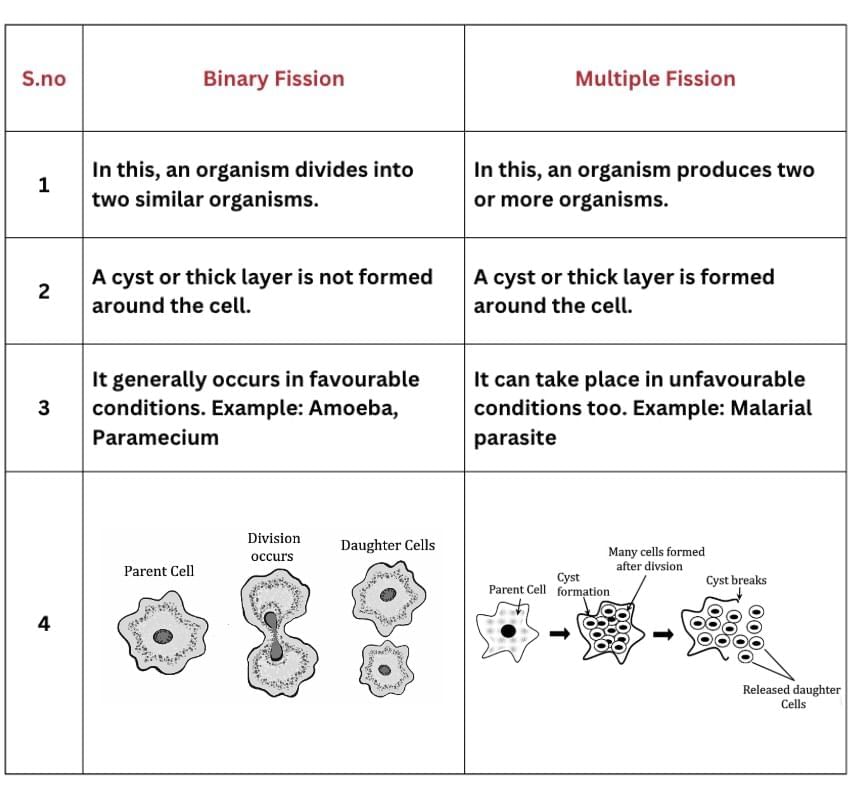
Ans: There are many advantages if an organism reproduces through spores.
Advantages of spore formation:
- Spores allow reproduction without needing a partner.
- Large numbers of spores are produced in one sporangium.
- Spores are distributed easily by air to far-off places to avoid competition in one place.
- Spores are covered by thick walls to prevent dehydration under unfavourable conditions.
Q3: Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Ans:
- Simple organisms such as Hydra and Planaria are capable of producing new individuals through the process of regeneration.
- The process of regeneration involves the formation of new organisms from their body parts.
- Simple organisms can utilize this method of reproduction as their entire body is made of similar kind of cells in which any part of their body can be formed by growth and development.
- However, complex organisms have an organ-system level of organization.
- All the organ systems of the body work together as an interconnected unit.
- They can regenerate their lost body parts such as skin, muscles, blood, etc. However, they cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration.
Q4: Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Ans: Advantages of vegetative propagation are:
Faster Flowering and Fruiting: Plants grown through vegetative propagation can produce flowers and fruits earlier than those grown from seeds.
Useful for Seedless Plants: This method helps in growing plants like banana, orange, rose, and jasmine that do not produce seeds anymore.
Same as Parent Plant: All plants produced are genetically identical to the parent. So, the same good qualities are passed on.
Desirable Traits are Retained: Useful features of the parent plant remain unchanged in the next generations.
Quick and Easy Method: It is a fast, cheap, and simple way to grow plants.
Helpful When Seeds Don’t Grow: It works well in areas where seed germination is difficult.
Preserves Good Quality: High-quality plant varieties can be maintained for a long time.
Q5: Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Ans: DNA copying is essential part of the process of reproduction so that the characteristics of the parent organisms are transmitted to its offspring and at the same time some occasional variations are also produced in the offspring. The changes in the copy of DNA provide an organism the capability to survive in changing conditions.
Page No. 140
Q1: How is the process of pollination different from fertilization?
Ans:
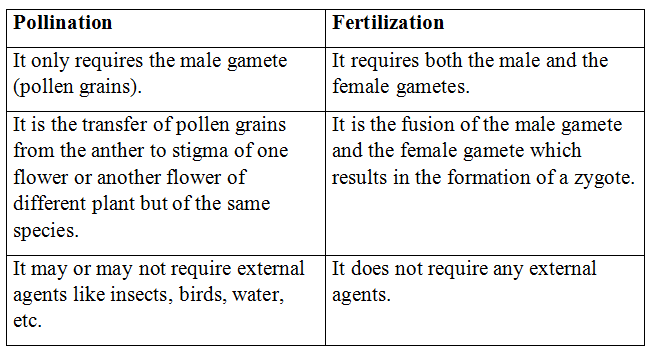 Q2: What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Q2: What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Ans: The secretions from seminal vesicles and prostate glands lubricate the sperms and provide a fluid medium for easy transport of sperms. Their secretion also provides nutrients in the form of fructose, calcium, and some enzymes.
Q3: What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Ans: Secondary sexual characteristics in girls:
- Increase in breast size and darkening of the skin of the nipples present at the tips of the breasts.
- The appearance of hair in the genital area.
- The appearance of hair in other areas of skin like underarms, face, hands, and legs.
- Increase in the size of the uterus and ovary.
- The hips broaden.
- Beginning of menstrual cycle.
- More secretion of oil from the skin, which results in the appearance of pimples.
Q4: How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Ans: The embryo develops inside the mother’s body for about nine months. Inside the uterus, the outer tissue surrounding the embryo develops finger-like projections called villi. These villi are surrounded by uterine tissue and maternal blood. They provide a large surface area for the exchange of oxygen and nutrients. Also, the embryo gets nourishment inside the mother’s body through the placenta. The placenta is an organ that connects the mother’s blood supply to the embryo through the umbilical cord. It delivers oxygen and nutrients from the mother to the embryo and removes waste products from the embryo’s blood. This process ensures the embryo grows and develops properly during pregnancy.
Q5: If a woman is using a copper−T, will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Ans: No. Using a copper-T will not provide protection from sexually transmitted diseases, as it does not prevent the entry of semen. It only prevents the implantation of the embryo in the uterus.
Page No. 141
Exercises
Q1: Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in
(a) amoeba
(b) yeast
(c) plasmodium
(d) leishmania
Ans: (b) Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in yeast.
Yeast reproduces asexually by budding. A small bud forms on the parent cell, receives a part of the nucleus, and then separates to become a new cell. This may form a chain of buds. The parent cell is smaller than the daughter cell.
Q2: Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
(a) Ovary
(b) Uterus
(c) Vas deferens
(d) Fallopian tube
Ans:(c) Vas deferens is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings.
Vas deferens is a part of the male reproductive system. It is a long, muscular tube travelling from the epididymis into the pelvic cavity. It is behind the bladder. Its function is to transport the mature sperm to the urethra. It also carries urine outside of the body.
Q3: The anther contains
(a) sepals
(b) ovules
(c) pistil
(d) pollen grains
Ans:(d) The anther contains pollen grains.
The stamen are male reproductive organs. They contain anther, which is a site of pollen development. Inside the anther, the male sporogenous cell differentiates and undergoes meiosis to produce microspores that develop into pollen grains.
(a) Stamen
(b) 3-D Cut-section of an Anther
Q4: What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Ans: Advantages of sexual reproduction:
- In sexual reproduction, more variations are produced. Thus, it ensures the survival of species in a population.
- The newly formed individual has the characteristics of both parents.
- Variations are more successful in sexual reproduction than in asexual reproduction. This is because, in asexual reproduction, the new DNA has to work within the same old cell machinery, which may not support the changes properly.
Q5: What are the functions performed by the testes in human beings?
Ans: The testes are the male reproductive organs that are located outside the abdominal cavity within a pouch called the scrotum.
Functions of testes:
- Produce sperms.
- Produce a hormone called testosterone, which brings about secondary sexual characteristics in boys.
Q6: Why does menstruation occur?
Ans: Menstruation is a process in which blood and mucous flows out every month through the vagina.
- This process occurs every month because one egg is released from the ovary every month and at the same time, the uterus (womb) prepares itself to receive the fertilized egg.
- Thus, the inner lining of the uterus gets thickened and is supplied with blood to nourish the embryo.
- If the egg does not get fertilized, then the lining of the uterus breaks down slowly and gets released in the form of blood and mucus from the vagina.
Q7: Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Ans:
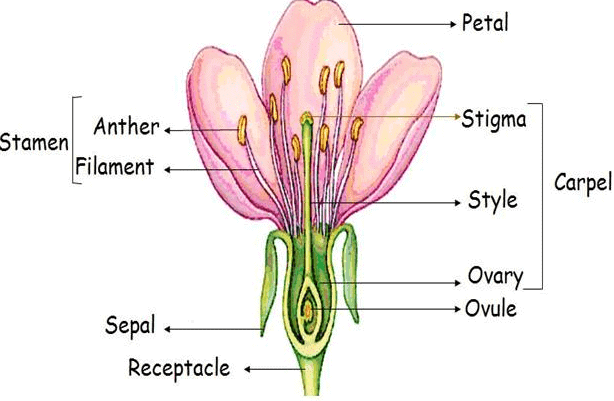 Longitudinal Section of a Flower
Longitudinal Section of a Flower
Q8: What are the different methods of contraception?
Ans: The contraceptive methods can be broadly divided into the following types:
1. Natural Method
- It involves avoiding the chance of meeting the sperm and ovum.
- In this method, the sexual act is avoided from the 10th to the 17th of the menstrual cycle because, during this period, ovulation is expected, and therefore, the chances of fertilization are very high.
2. Barrier Method
- In this method, the fertilization of the ovum and sperm is prevented with the help of barriers.
- Barriers are available for both males and females.
- Condoms are barriers made of thin rubber that are used to cover the penis in males and the vagina in females.
3. Oral Contraceptives
- In this method, tablets or drugs are taken orally.
- These contain small doses of hormones that prevent the release of eggs, and thus, fertilization cannot occur.
4. Implants and Surgical Methods
- Contraceptive devices such as the loop or Copper-T are placed in the uterus to prevent pregnancy.
- Some surgical methods can also be used to block the gamete transfer. It includes the blocking of the vas deferens to prevent the transfer of sperm, known as vasectomy.
- Similarly, the fallopian tubes of the females can be blocked so that the egg will not reach the uterus, known as tubectomy.
Q9: How are the modes of reproduction different in unicellular and multicellular organisms?
Ans:
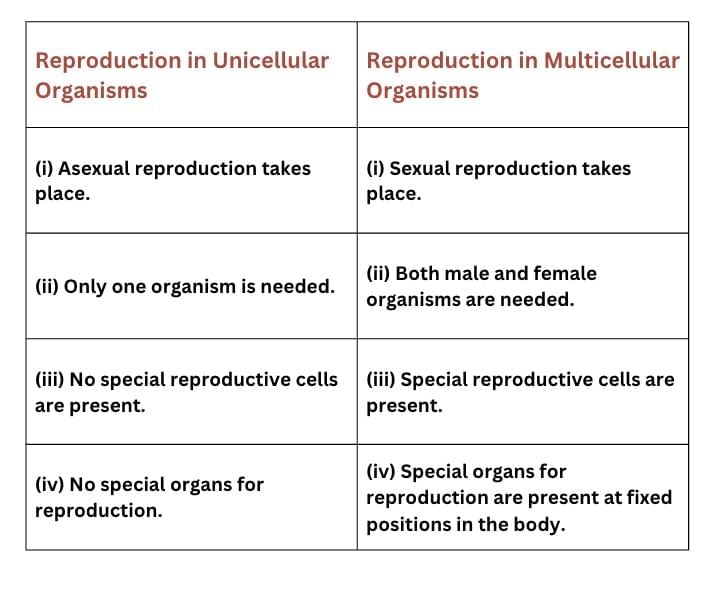
Q10: How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Ans:
- Living organisms reproduce for the continuation of a particular species.
- It helps in providing stability to the population of species by producing a new individual that resembles the parents. For example, cats give birth to only cats or dogs give birth to only dogs.
- Therefore, reproduction provides stability to populations of dogs or cats or any other species.
Q11: What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Ans: Contraceptive methods are mainly adopted because of the following reasons:
- To prevent unwanted pregnancies.
- To control population rise or birth rate.
- To prevent the transfer of sexually transmitted diseases.
|
82 videos|677 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Science Chapter 7 - How do Organisms Reproduce
| 1. What is reproduction? |  |
| 2. What are the different modes of reproduction? |  |
| 3. What are the advantages of sexual reproduction? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of asexual reproduction? |  |
| 5. Can all organisms reproduce both sexually and asexually? |  |
















