NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 - Working of Institutions
Q1. If you are elected as the President of India which of the following decisions can you take on your own?
(a) Select the person you like as Prime Minister.
(b) Dismiss a Prime Minister who has a majority in Lok Sabha.
(c) Ask for reconsideration of a bill passed by both the Houses.
(d) Nominate the leaders of your choice to the Council of Ministers.
Ans: (c) Ask for reconsideration of a bill passed by both Houses.
As President of India, you can:
- Request that Parliament review a bill.
- Delay the bill's assent, but must sign it if passed again.
However, you cannot:
- Select a Prime Minister on your own.
- Dismiss a Prime Minister with a majority.
- Nominate leaders to the Council of Ministers independently.
Q2. Who among the following is a part of the political executive?
(a) District Collector
(b) Secretary of the Ministry of Home Affairs
(c) Home Minister
(d) Director General of Police
Ans: (c) Home Minister
The Home Minister is part of the political executive, while the others are part of the bureaucracy or civil services (administrative executive).
Q3. Which of the following statements about the judiciary is false?
(a) Every law passed by the Parliament needs the approval of the Supreme Court.
(b) Judiciary can strike down a law if it goes against the spirit of the Constitution.
(c) Judiciary is independent of the Executive.
(d) Any citizen can approach the courts if her rights are violated
Ans: (a) Every law passed by the Parliament needs the approval of the Supreme Court.
This statement is false because laws passed by Parliament do not require prior approval from the Supreme Court. However, the judiciary can review and strike down laws if they are found to be unconstitutional.
Q4. Which of the following institutions can make changes to an existing law of the country?
(a) The Supreme Court
(b) The President
(c) The Prime Minister
(d) The Parliament
Ans: (d) The Parliament
Only Parliament has the authority to make, amend, or repeal laws in the country. The other institutions can influence laws but cannot directly change them.

Q5. Match the ministry with the news that the ministry may have released:

Ans:
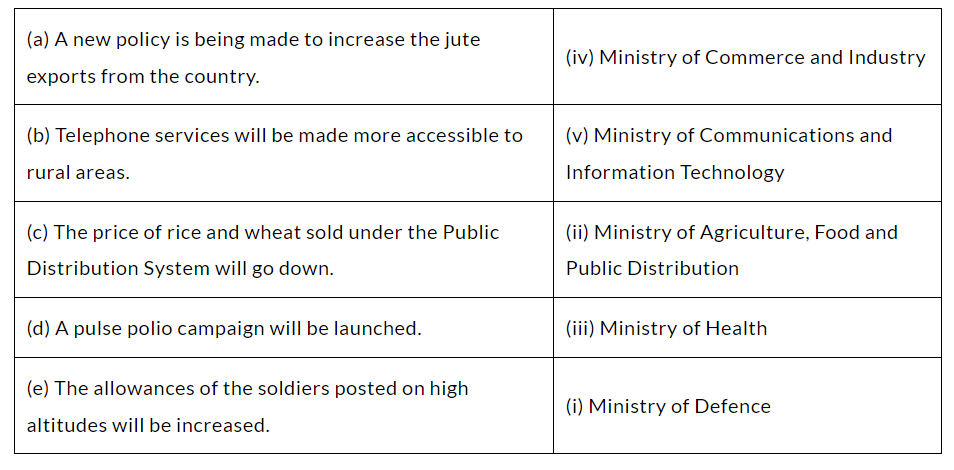
Q6. Of all the institutions that we have studied in this chapter, name the one that exercises the powers on each of the following matters.
(a) Decision on allocation of money for developing infrastructure like roads, irrigation etc. and different welfare activities for the citizens.
(b) Considers the recommendation of a Committee on a law to regulate the stock exchange.
(c) Decides on a legal dispute between two state governments.
(d) Implements the decision to provide relief for the victims of an earthquake.
Ans:
(a) Lok Sabha (The Finance Ministry) decides on the allocation of money for developing infrastructure, such as roads and irrigation, and for various welfare activities for citizens.
(b) The Parliament considers recommendations from a Committee regarding laws to regulate the stock exchange.
(c) The Supreme Court resolves legal disputes between two state governments.
(d) The Executive implements decisions to provide relief for victims of an earthquake.
Q7. Why is the Prime Minister in India not directly elected by the people?
Choose the most appropriate answer and give reasons for your choice.
(a) In a Parliamentary democracy only the leader of the majority party in the Lok Sabha can become the Prime Minister.
(b) Lok Sabha can remove the Prime Minister and the Council of Ministers even before the expiry of their term.
(c) Since the Prime Minister is appointed by the President there is no need for it.
(d) Direct election of the Prime Minister will involve lot of expenditure on election.
Ans: The most appropriate answer is (a). This is because:
- In a Parliamentary democracy, the Prime Minister is the leader of the majority party in the Lok Sabha.
- This ensures that the Prime Minister has the support of the majority, preventing them from becoming a puppet or a dictator.
- The Prime Minister works alongside a council of ministers, which promotes collaboration and accountability.
Q8. Three friends went to watch a film that showed the hero becoming Chief Minister for a day and making big changes in the state. Imran said this is what the country needs. Rizwan said this kind of personal rule without institutions is dangerous. Shankar said all this is a fantasy. No minister can do anything in one day. What would be your reaction to such a film?
Ans: Such a film is unrealistic and undemocratic. Key points include:
- The Chief Minister should be chosen through a fair election process.
- A personal rule without institutions is dangerous.
- Implementing reforms requires careful planning and time.
Q9. A teacher was making preparations for a mock parliament. She called two students to act as leaders of two political parties. She gave them an option: Each one could choose to have a majority either in the mock Lok Sabha or in the mock Rajya Sabha. If this choice was given to you. Which one would you choose and why?
Ans: I would choose to have a majority in the Lok Sabha, as the Lok Sabha is more powerful than the Rajya Sabha because:
- If any law is not passed by both the houses, the final decision is taken in the joint session in which members of both the houses sit together but because of the larger number of members, the view of the Lok Sabha is likely to prevail.
- The Lok Sabha exercises more powers in money matters too. Once the Lok Sabha passes the budget of the government or any other money-related law, the Rajya Sabha cannot reject it.
- Most importantly, the Lok Sabha controls the Council of Ministers. If the majority of the Lok Sabha members say they have no confidence in the Council of Ministers, it has to quit, whereas the Rajya Sabha does not have this power.
Q10. After reading the example of the reservation order, three students had different reactions about the role of the judiciary. Which view, according to you, is a correct reading of the role of judiciary?
(a) Srinivas argues that since the Supreme Court agreed with the government, it is not independent.
(b) Anjaiah says that judiciary is independent because it could have given a verdict against the government order. The Supreme Court did direct the government to modify it.
(c) Vijaya thinks that the judiciary is neither independent nor conformist, but acts as a mediator between opposing parties. The court struck a good balance between those who supported and those who opposed the order.
Ans: (b) Anjaiah’s view on the role of the judiciary is correct because:
- The judiciary is independent and impartial.
- It operates separately from the legislature and the executive.
- Judges do not follow the government's wishes or the ruling party's agenda.
- The Supreme Court's directive to modify the government order shows its ability to check governmental power.
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Civics Chapter 4 - Working of Institutions
| 1. What are the key institutions that make up the Indian political system? |  |
| 2. How does the Parliament function in India? |  |
| 3. What is the role of the President in the Indian political system? |  |
| 4. How does the Judiciary function as a check on the other institutions? |  |
| 5. What is the significance of local self-governments in the Indian political system? |  |

















