UPSC Exam > UPSC Notes > Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy > Forests in India - Indian Geography, UPSC, IAS
Forests in India - Indian Geography, UPSC, IAS | Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy PDF Download
Indian Forest
- Forest area is the area recorded as forest land irrespective of the existence of trees, while the actual forest is the area occupied by the forest with a canopy
- The Forest area is based on the record of the State Revenue Department.
- Forest area covers 23.28% of the total area of the country
- These forests supply a wide variety of resources.
- They provide structural timber and wood for making furniture and pulp, matchwood, wood for charcoal, gum, resins, canes, and fibers.
- Besides these, there are many other forest products such as leaves, fruits, tan dyes, medicinal herbs, beeswax, honey, turpentine oil, and lac.
Spatial variation
- Forest cover varies from state to state
- Lakshadweep has 0% forest area while A&N Islands have 86.93 %
- Most of the states with less than 10% of the forest area are: Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Delhi
- The NE states have more than 30% of the land under forest
Destruction of Forests and Measures for Conservation
- Overgrazing and forest fire often destroy forests.
- Reckless cutting of the trees causes forest destruction.
- Jhum cultivations destroy forest; it invites soil erosion.
- To preserve the forest, the Govt. of India has taken up a series of programmers:
- The forests are declared Reserved Forests.
- The government has chalked out a good program of ‘Van Mahatsov’.
- The Forest Research Institute has been set up at Dehra Dun for the promotion and preservation of the forests properly.
- The GoI adopted a forest policy in 1952 which was modified in 1988
Aims of Forest Policy
- Forest cover to be increased to 33%
- Maintain environmental stability
- Conserving the natural heritage of the country
- Checking soil erosion
- Increasing the productivity of the forests
- Creating a massive people movement
- Based on the forest conservation policy the following steps were initiated:
- Social forestry
- Wildlife conservation
- Biosphere Reserves
Social Forestry
- It means management and protection of forests and afforestation on barren lands with the purpose of helping in the environment, social and rural development
- National Commission on Agriculture has classified social forestry into- Urban forestry, Rural forestry & Farm forestry
Urban forestry
- It pertains to the raising & management of trees on public and privately owned lands in and around public centers such as green belts, parks, roadside avenues, etc.
Rural forestry
- It emphasizes Agroforestry and Community forestry
- Agro-Forestry is the raising of trees and agricultural crops on the same land inclusive of waste patches
- Community forestry involves the raising of trees on public or community lands
- Farm forestry: a process under which farmers grow trees for commercial & non-commercial purposes on their farmlands
Wildlife conservation
- In 1972 Wildlife Act was enacted with two main objectives-
- To provide protection to the endangered species
- To provide legal support to the conservation areas of the country classified as National Parks, sanctuaries, and closed areas
- There are 98 National Parks and 492 wildlife sanctuaries in India
Project Tiger
- Implemented in 1973
- The main objective is to ensure the maintenance of the viable population of tigers in India
- There are 27 Tiger reserves in 17 states
- The tiger population has increased from 1827 in 1972 to 3642 in 2001-02
Biosphere Reserves
A Biosphere Reserve is a unique and representative ecosystem of terrestrial and coastal areas.
- These are the areas where every plant and animal is protected in its natural habitat
- It aims at achieving: conservation, development, research & monitoring
List of Biosphere Reserves in India
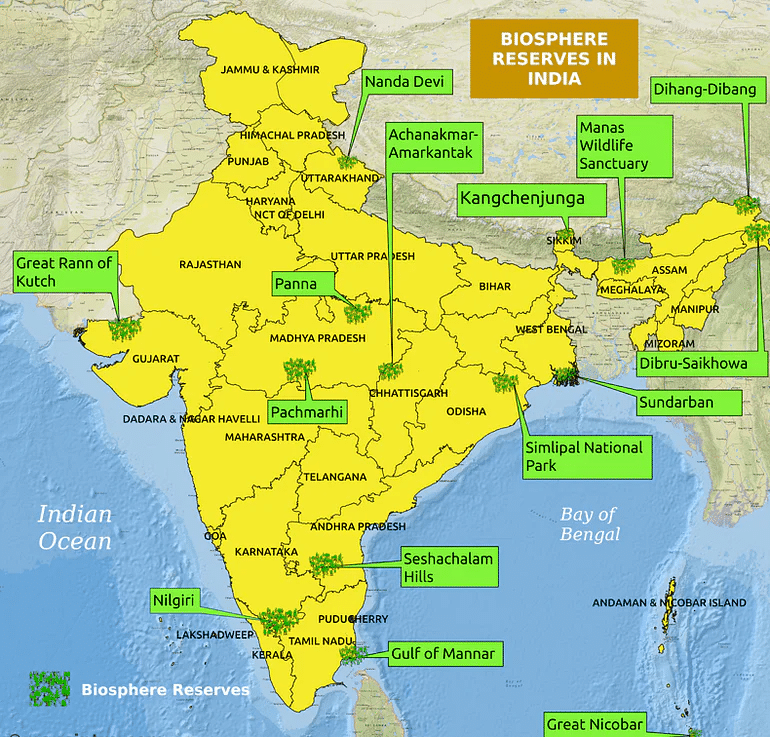
Biosphere reserves are announced by the state or central governments by notification. The Governments can nominate them under the UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme after its establishment as a biosphere reserve. There are 18 biosphere reserves in India.
| No. | Name of Biosphere Reserve | Year of Notification | Location (States) |
| 1 | Nilgiri | 1986 | Part of Wayanad, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Madumalai, Nilambur, Silent Valley, and Siruvani hills (Tamil Nadu, Kerala and Karnataka). |
| 2 | Nanda Devi | 1988 | Part of Chamoli, Pithoragarh, and Bageshwar districts (Uttarakhand). |
| 3 | Nokrek | 1988 | Part of Garo Hills (Meghalaya). |
| 4 | Great Nicobar | 1989 | Southernmost islands of Andaman And Nicobar (A&N Islands). |
| 5 | Gulf of Mannar | 1989 | The Indian part of the Gulf of Mannar between India and Sri Lanka (Tamil Nadu). |
| 6 | Manas | 1989 | Part of Kokrajhar, Bongaigaon, Barpeta, Nalbari, Kamprup, and Darang districts (Assam). |
| 7 | Sunderbans | 1989 | Part of the delta of Ganges and Brahmaputra river system (West Bengal). |
| 8 | Simlipal | 1994 | Part of the Mayurbhanj district (Orissa). |
| 9 | Dibru-Saikhowa | 1997 | Part of Dibrugarh and Tinsukia Districts (Assam). |
| 10 | Dehang-Dibang | 1998 | Part of Siang and Dibang Valley in Arunachal Pradesh. |
| 11 | Pachmarhi | 1999 | Parts of Betul, Hoshangabad, and Chindwara districts of Madhya Pradesh. |
| 12 | Khangchendzonga | 2000 | Parts of Khangchendzonga hills and Sikkim. |
| 13 | Agasthyamalai | 2001 | Neyyar, Peppara, and Shendurney Wildlife Sanctuaries and their adjoining areas in Kerala. |
| 14 | Achanakamar – Amarkantak | 2005 | Covers parts of Anupur and Dindori districts of M.P. and parts of Bilaspur districts of Chhattishgarh State. |
| 15 | Kachchh | 2008 | Part of Kachchh, Rajkot, Surendra Nagar, and Patan Civil Districts of Gujarat State. |
| 16 | Cold Desert | 2009 | Pin Valley National Park and surroundings; Chandratal and Sarchu & Kibber Wildlife Sanctuary in Himachal Pradesh. |
| 17 | Seshachalam Hills | 2010 | Seshachalam Hill Ranges covering parts of Chittoor and Kadapa districts of Andhra Pradesh. |
| 18 | Panna | 2011 | Part of Panna and Chhattarpur districts in Madhya Pradesh. |
UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserves – International Status
Recently, Panna Biosphere Reserve was also given the International status of UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserve.
- The status was given in the year 2020, and prior to that, the Khangchendzonga Biosphere Reserve from India was also included in this list in 2018.
- With the addition of the two Biosphere Reserves, 12 of the 18 biosphere reserves in the country have become part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves which is based on the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme list.
The UNESCO Protected Biosphere Reserves list in India are given below:
| YEAR | NAME | STATES |
| 2000 | Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 2001 | Gulf of Mannar Biosphere Reserve | Tamil Nadu |
| 2001 | Sundarbans Biosphere Reserve | West Bengal |
| 2004 | Nanda Devi Biosphere Reserve | Uttarakhand |
| 2009 | Pachmarhi Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
| 2009 | Nokrek Biosphere Reserve | Meghalaya |
| 2009 | Simlipal Biosphere Reserve | Odisha |
| 2012 | Achanakmar-Amarkantak Biosphere Reserve | Chhattisgarh |
| 2013 | Great Nicobar Biosphere Reserve | Great Nicobar |
| 2016 | Agasthyamala Biosphere Reserve | Kerala and Tamil Nadu |
| 2018 | Kanchenjunga Biosphere Reserve | Part of North and West Sikkim districts |
| 2020 | Panna Biosphere Reserve | Madhya Pradesh |
- The World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) covers globally chosen protected areas. It consists of a vibrant and interactive network of sites of distinction.
- It promotes the harmonious assimilation of people and nature for sustainable development in different ways.
- If one country declares one area as a biosphere reserve, it can nominate the same to under the UNESCO’s Man and Biosphere (MAB) Programme. If UNESCO accepts the proposal of the government, the biosphere reserve will enter into the World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR).
The document Forests in India - Indian Geography, UPSC, IAS | Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy is a part of the UPSC Course Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy.
All you need of UPSC at this link: UPSC
|
12 videos|182 docs|155 tests
|
FAQs on Forests in India - Indian Geography, UPSC, IAS - Geography (Prelims) by Valor Academy
| 1. What is the concept of social forestry in India? |  |
Ans. Social forestry is a concept implemented in India to involve local communities in the management and protection of forests. It aims to meet the needs of the people and promote environmental conservation through the active participation of individuals and communities.
| 2. What are the aims of forest policy in India? |  |
Ans. The aims of forest policy in India are to ensure environmental stability and ecological balance, conserve natural heritage, enhance forest cover, and meet the socio-economic needs of local communities through sustainable forest management practices.
| 3. How does wildlife conservation contribute to the conservation of Indian forests? |  |
Ans. Wildlife conservation plays a crucial role in the conservation of Indian forests as it helps maintain the biodiversity and ecological balance of the forest ecosystem. By protecting wildlife species, their habitats are also safeguarded, which in turn contributes to the overall health and sustainability of the forests.
| 4. What are biosphere reserves in India and why are they important for forest conservation? |  |
Ans. Biosphere reserves in India are designated areas that aim to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable development, and provide opportunities for scientific research and education. They play a crucial role in forest conservation by protecting and managing representative ecosystems, including forests, and promoting the sustainable use of natural resources.
| 5. What is the international status of UNESCO protected biosphere reserves in India? |  |
Ans. UNESCO protected biosphere reserves in India hold international recognition and are considered important sites for conservation and sustainable development. These reserves are listed under the UNESCO Man and the Biosphere (MAB) Programme, which promotes the harmonious relationship between humans and the environment.
Related Searches






















