Taxonomy: Identification, Nomenclature & Classification | Biology Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Taxonomy? |

|
| I. Hierarchical Classification System |

|
| II. Binomial Nomenclature System |

|
| Rules of Binomial Nomenclature |

|
| Previous Year Questions (PYQs) on this Topic Asked in NEET |

|
The world is an interesting place and earth is considered home to 8.7 million species. Wouldn’t it be interesting to know the types of species of plants and animals with the help of well devised systems. Thus, EduRev is providing effectively planned notes of “Taxonomy” under which you will study about identification, nomenclature and classification of the species.
What is Taxonomy?
Taxonomy is a science that deals with the naming, describing, and classification of all living organisms according to their similarities and differences .
Example: Plants, Animals
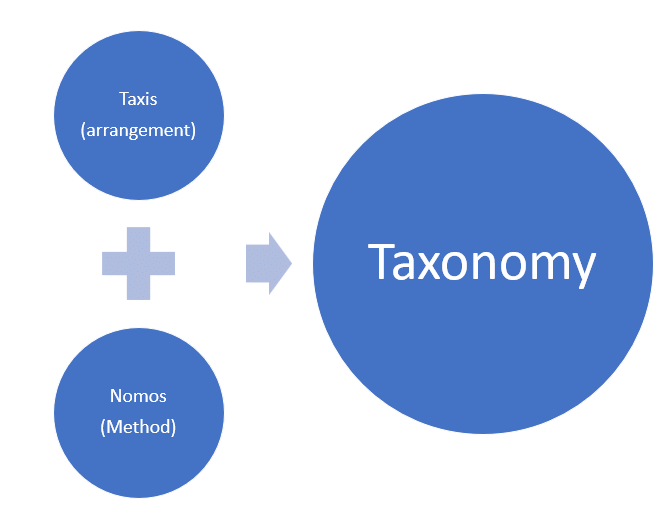
- The word “Taxonomy” is derived from a Greek word – “taxis”, meaning arrangement or division, and “nomos”, meaning method.
- Taxonomy deals with Characterization, Identification, and Classification. It helps us understand the diversity of life on Earth and how different organisms are related to each other.
- The process of taxonomy is based on description, genetic variation, recognition and defining taxa in the ecosystem.
- Carolus Linnaeus is considered the Father of Taxonomy. He is the one who developed the procedure to name and organize species. Even today this procedure is being followed.
His contributions to taxonomy were:
(i) Hierarchical Classification System
(ii) Binomial nomenclature system
History of Taxonomy
Carolus Linnaeus [1707 - 1778]
- He is known as the Father of Taxonomy, Father of Plant Taxonomy, and Father of Animal Taxonomy.
- Linnaeus gave the Two kingdom system classification. He grouped plants and animals into kingdom Plantae and kingdom Animalia, respectively.
- Linnaeus wrote many books. The most important publication is Systema Naturae.
To learn more about the History of the Taxonomy, Watch this video: Introduction to Taxonomy
Taxonomy includes the study of the following:
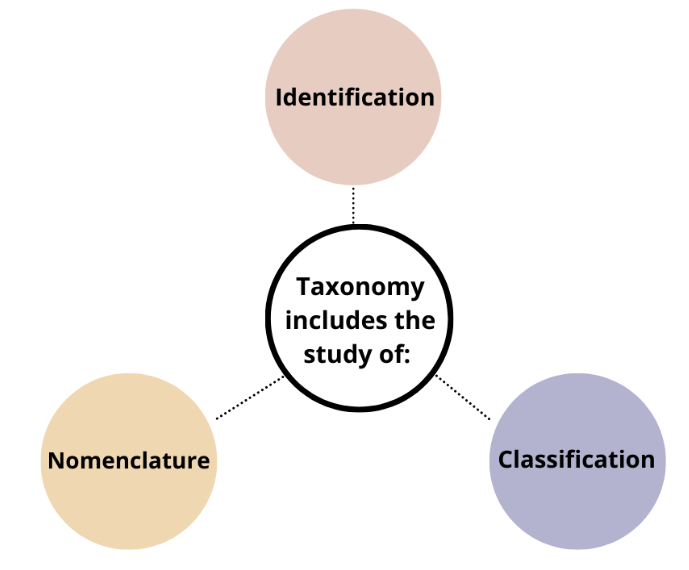
- Identification: Identification of living organisms.
- Nomenclature: Naming of living organisms.
- Classification: Classification of living organisms in groups.
1. Identification
- Identification is the recognition of the essential character of an organism.
- The procedure of nomenclature or naming is only possible if the organism is properly characterised and we know what organism the name refers to.
2. Nomenclature
- There are millions of plants and animals in the world; we know the plants and animals in our own area by their local names.
- Even within a country, these regional names might differ from place to place and create confusion while communicating.
- As a result, it is necessary to standardise the naming of living organisms so that they are known by the same name all over the world. This is referred to as Nomenclature.
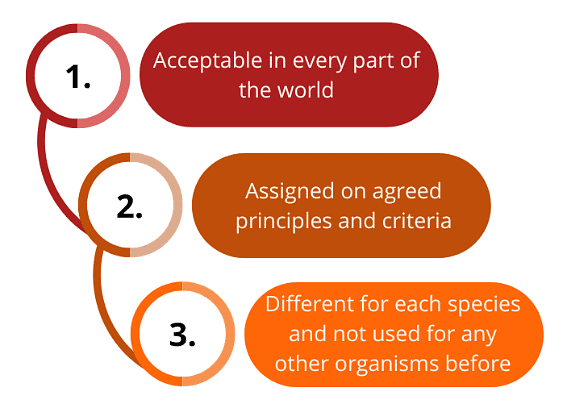
These names represent a particular organism in every part of the world. The scientific names must be:
To accomplish the uniformity, certain international codes have been established:
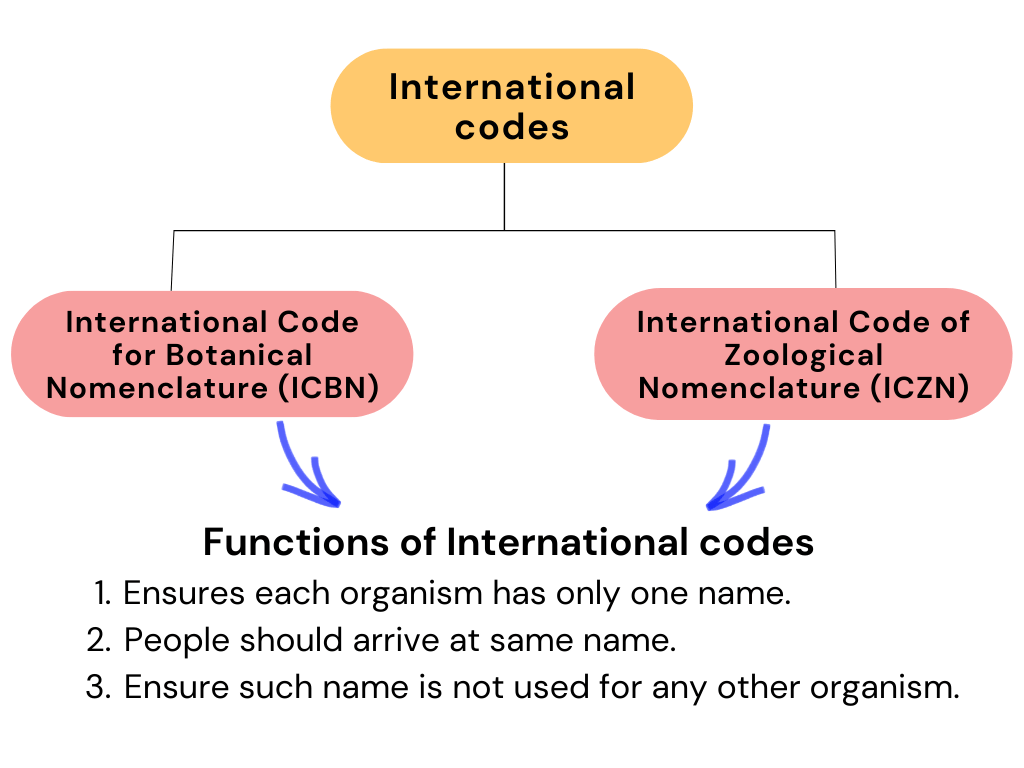
3. Classification
- The process of categorising things based on their characteristics is known as classification.
- When organisms share similarities, they are grouped together.
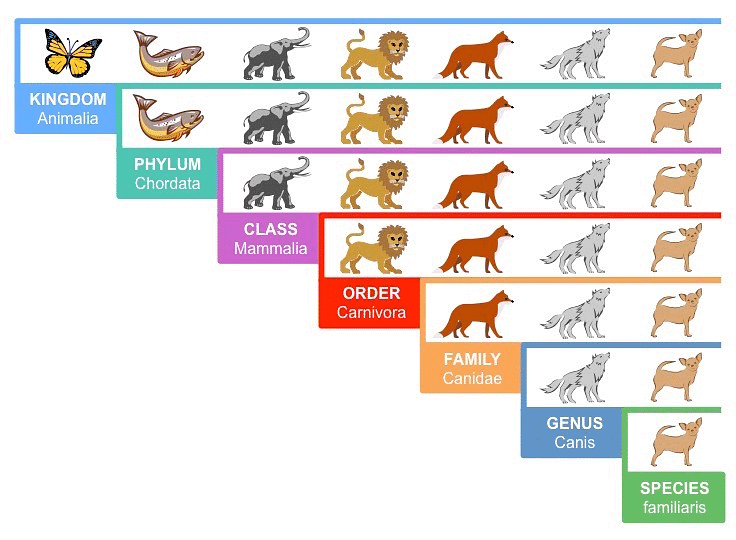
- Kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, and species are the seven levels of classification for living organisms.
Additional information
Taxonomy is divided into two categories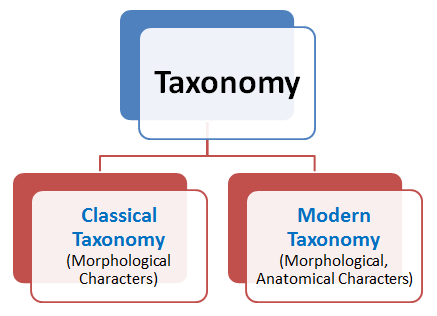
1. Classical Taxonomy
- Classical taxonomy is based on recognizable morphological characters of normal individuals assumed to be the same appearance while their differences are inexpressible.
- Classical taxonomy originated with Plato followed by Aristotle (Father of Zoology). Theophrastus (Father of Botany) up to Linnaeus (Father of Taxonomy) and his contemporaries.
Features of Classical taxonomy:
(i) Species are specified on the basis of morphological characters.
(ii) Only few characters are studied for classification.
(iii) It does not include the evolutionary relationship of organisms.
(iv) A few individuals or their preserved specimens are used for the study. This study is known as the typological concept.
(v) Species are believed to be static or unchanging.
(vi) Species is the centre stage of the study, its sub-units are not important.
2. New Systematics or Modern Taxonomy
- The term new systematics was coined by Julian Huxley (1940).
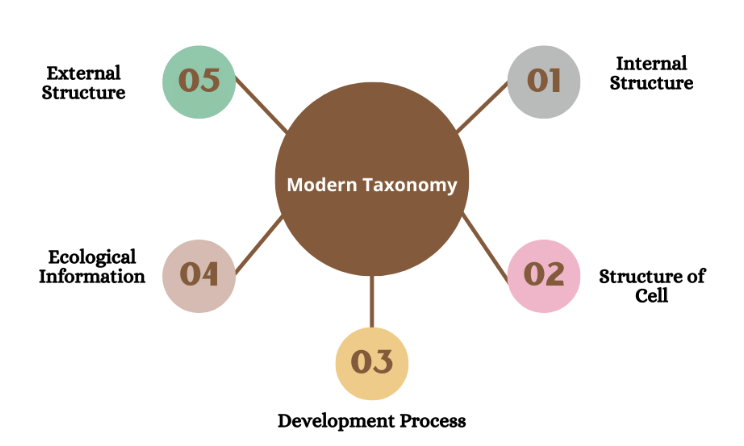
- New systematics is the study that takes into consideration of all types of characters including characters from classical morphology and anatomy such as:
- Cytology (study of cells)
- Physiology (functioning of living organisms)
- Biochemistry (study chemical reactions at a molecular level)
- Ecology (interaction of organisms with environment )
- Genetics (study of genes and heredity)
- Embryology ( formation and development of an embryo and fetus )
- Behaviour etc, of the whole population instead of a few typological specimens.
- In contrast to classical systematics, New Systematics strives to bring out evolutionary relationships amongst organisms. It also called population systematics and biosystematics.
- In Modern taxonomy, large number of individuals are studied.
Features of Modern Taxonomy:
(a) New systematics is based on the study of all types of variations in the species.
(b) Modern taxonomy deals with the study of genetic constituents, cellular structure, phylogenetic relationship, mode of nutrition, reproduction along with morphological characters.
(c) Specifying boundaries of species is carried out on the basis of all types of biological traits. It is also called biological delimitation of species.
(d) Inter-relationships are brought out between primary & advanced species.
(e) Species are considered dynamic.
Contributions in taxonomy by Carolus Linneus:
I. Hierarchical Classification System
A system of classifying organisms into different hierarchical levels is known as hierarchical classification. It includes the sequence of categories from kingdom to species in decreasing or increasing order, and vice versa.
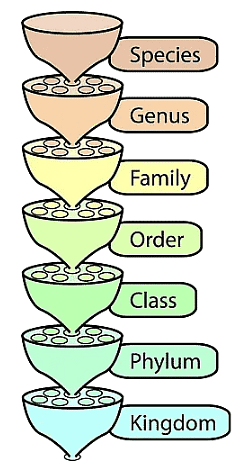 Hierarchical Classification System
Hierarchical Classification System
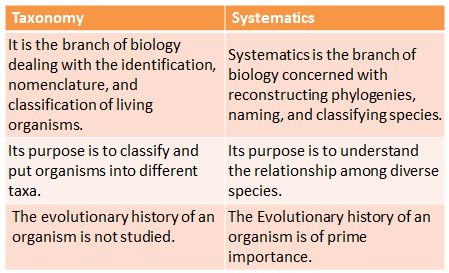
What is Systematics?
Systematics is a branch of biology that deals with classifying plants, animals, and other organisms into categories that can be named, remembered, compared, and studied.
- It deals with the evolutionary relationships between organisms.
- The study of only one organism of a group provides sufficient information about that group's remaining members.
- Linnaeus proposed the term "Systematics".
- It includes a description of the morphological characters of plants or living organisms.
 Systematics in Animals
Systematics in Animals
Basis of Systematic Study
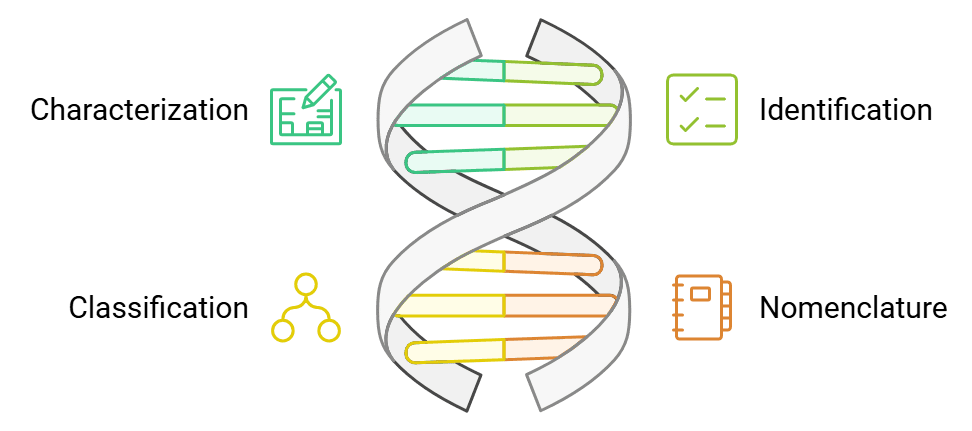 Basis of Systematic Study
Basis of Systematic Study
- Characterization: The organism to be studied is described on the basis of its morphological and other characteristics.
- Identification: Based on characterization, the organism's identification is carried out to know whether it is similar to any known taxa group.
- Classification: The organism is now classified based on its resemblance to different taxa. It is possible that the organism may not resemble any known taxa or groups to accommodate that a new group or taxon is raised.
- Nomenclature: After placing the organism in various taxa, its correct name is determined. If the organism is new to systematics, it is given a new name based on nomenclature rules and conventions.
Difference between Taxonomy & Systematics
II. Binomial Nomenclature System
Binomial nomenclature is the system of providing distinct and appropriate names to organisms, each consisting of two words, first generic name {i.e., name of genus) and second specific epithet (i.e., name of species).
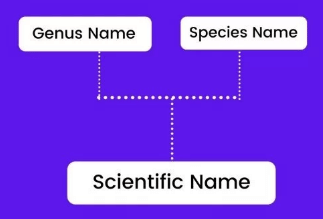
- For example, the Scientific name of Mango is written as Mangifera indica.
In this name, Mangifera represents the genus and indica is a particular species or specific epithet.

- All scientific names for animals under binomial nomenclature were given by Linnaeus in the tenth edition of his book Systema Naturae (1758).
Note: The information provided above about “Binomial Nomenclature” is important with respect to the NEET exam.
Rules of Binomial Nomenclature
The rules framed by Linnaeus and by the above codes are as follows:
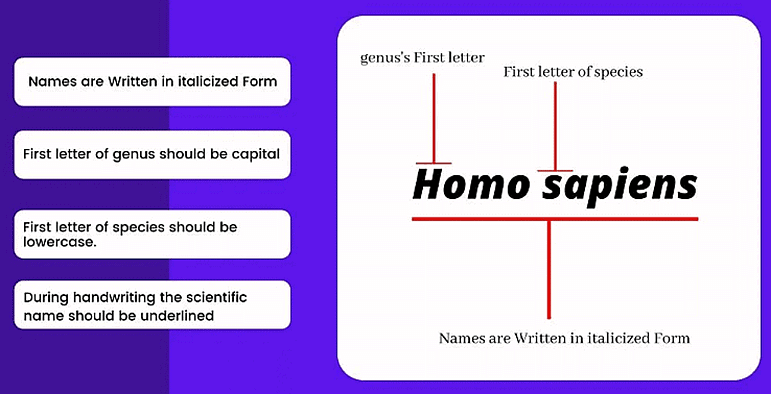
- Each organism is given only one name consisting of two words, generic and specific epithet.
- Both the words in a biological name, when handwritten, are separately underlined, or printed in italics to indicate their Latin origin.
- The generic name is written first. It is followed by a specific epithet and then the name of the discoverer in full or in abbreviation.
- The specific epithet begins with a small letter.
- The scientific name is printed or written in italics. They are Latinised or derived from Latin irrespective of their origin.
Learn this topic in depth through this video: Detailed Overview: Taxonomy & Nomenclature
In this document you have learnt the following points:
- Taxonomy is a science that deals with the naming, describing, and classification of all living organisms .
- Taxonomy includes the study of Identification, Nomenclature & Classification.
- Taxonomy is based on recognizable morphological characters of normal individuals whereas new taxonomy is the study that takes into consideration of all types of characters including characters from classical morphology and anatomy.
- Systematics is the branch of study related to the identification, classification and nomenclature of organisms. It deals with the evolutionary relationships between organisms.
- Rules of binomial nomenclature framed by Linnaeus.
- Binomial nomenclature is the system of providing distinct and appropriate names to organisms, each consisting of two words, first generic name and second specific epithet.
- For example, the Scientific name of Mango is written as Mangifera indica.
Previous Year Questions (PYQs) on this Topic Asked in NEET
Q1: Which of the following is against the rules of ICBN? [NEET 2019]
(a) Handwritten scientific names should be underlined.
(b) Every species should have a generic name and a specific epithet.
(c) Scientific names are in Latin and should be italicized when printed.
(d) Generic and specific names should be written starting with small letters.
Correct Answer is Option (d)
According to the international code for botanical nomenclature (ICBN), the first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter while the specific epithet starts with a small letter.
Q2: Select the correctly written scientific name of Mango, which was first described by Carolus Linnaeus. [NEET 2019]
(a) Mangifera Indica
(b) Mangifera Indica Car. Linn
(c) Mangifera indica Linn
(d) None
Correct Answer is Option (c)
- According to Binomial Nomenclature, the first word denoting the genus starts with a capital letter while the specific epithet starts with a small letter
Example: Scientific name of mango is Mangifera indica.- The author's name appears after the specific epithet, i.e., at the end of the biological name, and is written in an abbreviated form.
Example: Mangifera indica Linn. which indicates this species was first described by Linnaeus.
Q3: Nomenclature is governed by certain universal rules. Which one of the following is contrary to the rules of nomenclature? [NEET 2016]
(a) Biological names can be written in any language.
(b) The first word in a biological name represents the genus name, and the second is a specific epithet.
(c) The names are written in Latin and are italicized when printed.
(d) When written by hand, the names are to be underlined.
Correct Answer is Option (a)
Binomial nomenclature (also known as binary nomenclature) is a formal system for naming living things that consists of two parts (Genus & Species), both of which should be written in Latin grammatical forms.
Example: Homo sapiens
|
150 videos|399 docs|136 tests
|
FAQs on Taxonomy: Identification, Nomenclature & Classification - Biology Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the definition of taxonomy in biology? |  |
| 2. What is the hierarchical classification system in taxonomy? |  |
| 3. What are the rules of binomial nomenclature? |  |
| 4. How does binomial nomenclature help in the classification of organisms? |  |
| 5. Why is taxonomy important in the field of biology? |  |