Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 9 > Important Points & Differences: Climate
Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Climate
Important Points To Remember
1. Mango showers
- Pre-monsoon showers occurring in Kerala and coastal Karnataka.
- Help in the early ripening of mangoes.
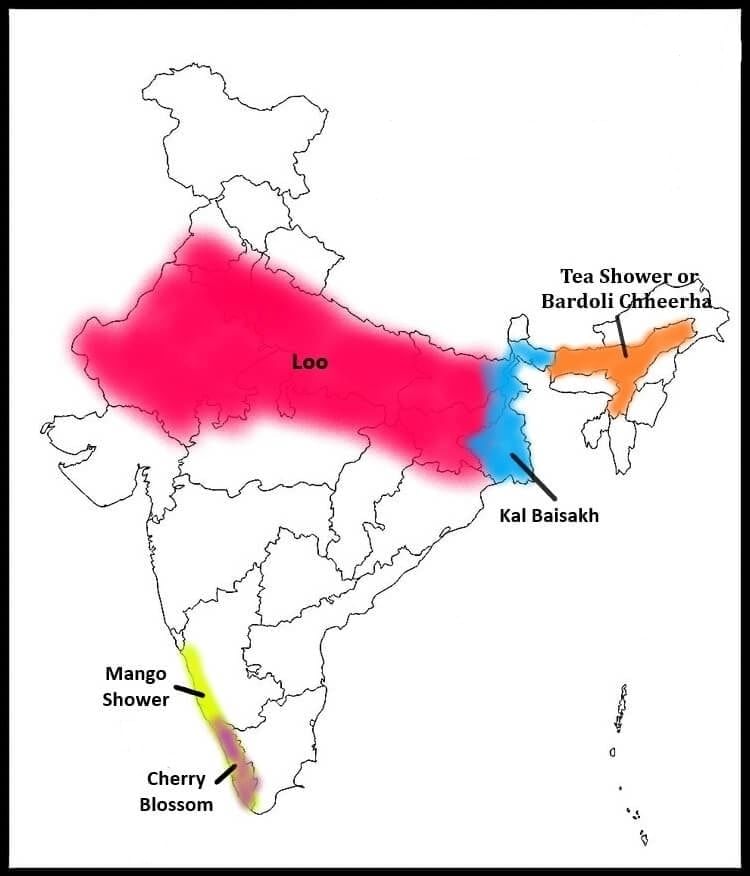 Regions of Mango Shower and Kal Baisakh
Regions of Mango Shower and Kal Baisakh
2. Kalbaisakhi
- Means violent black clouds in the month of Baisakh.
- Refers to north-westerly and northerly winds in Bengal and Assam.
- Causes heavy rainfall and destruction.
3. Chennai receives more rain in winter
- Northeast winds pick up moisture from the Bay of Bengal in winter.
- These winds bring onshore rainfall during winter.
- In summer:
1. Chennai lies in the rain-shadow of the Western Ghats.
2. Winds are offshore, leading to less rainfall.
Question for Important Points & Differences: ClimateTry yourself: Which region experiences mango showers?View Solution
4. Break or burst of the monsoon
- Sudden arrival of moisture-laden winds with violent thunder and lightning.
- Known as the "break" or "burst" of the monsoon.
- The first break occurs on the southwest coast of India around June 1st.
5. Southern Oscillation
- It is the interrelation between the pressure systems of the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- When pressure is high in the Pacific, it is low in the Indian Ocean, and vice versa.
- Winds shift across the equator with seasons, causing the Southern Oscillation.
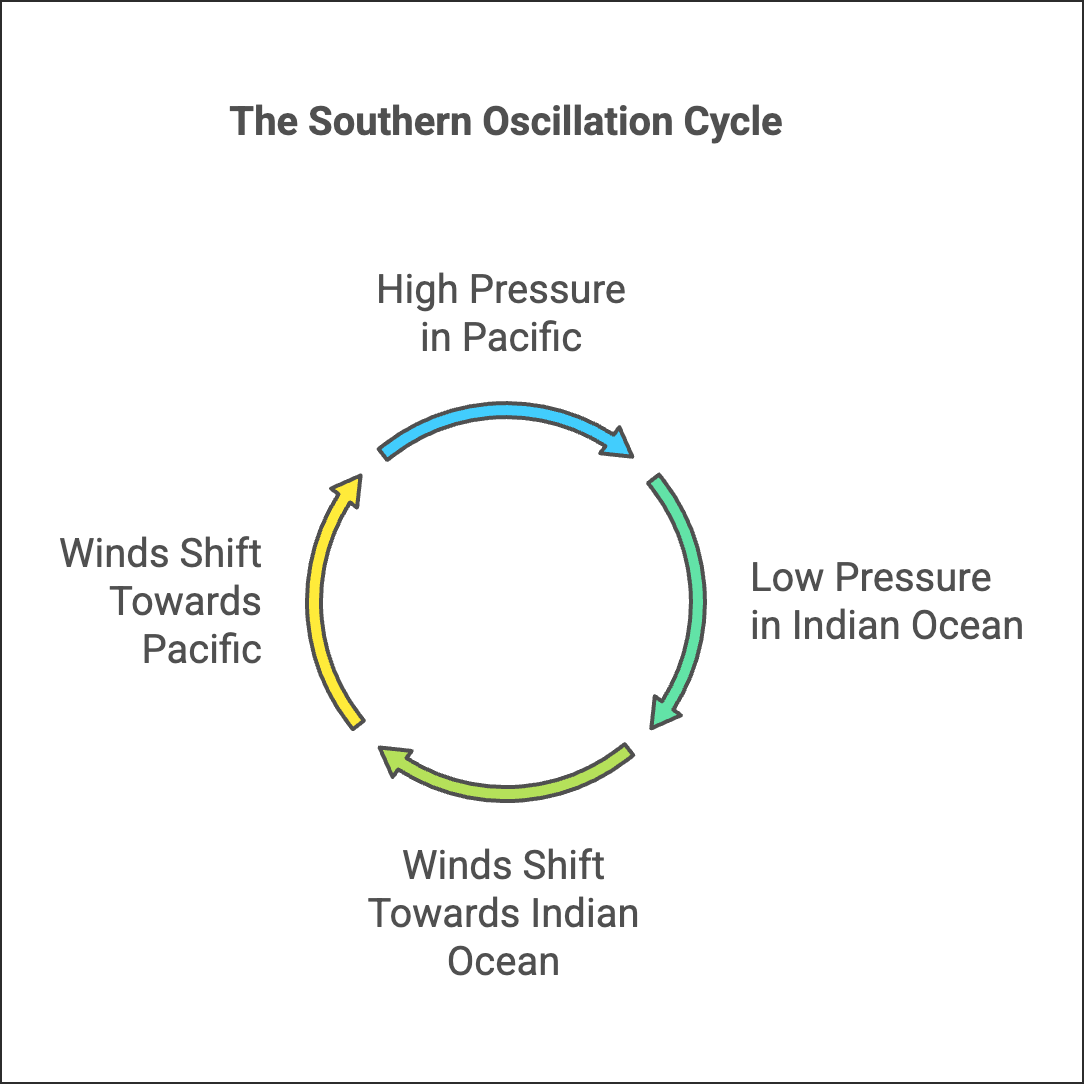
6. EI Nino Southern Oscillations
- El Niño is a warm ocean current that replaces the cold Peruvian current every 2 to 5 years.
- It is linked to pressure changes in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.
- This phenomenon is called El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO).
7. Mawsynram receives the highest rainfall in the world
- Located at the head of a funnel-shaped valley in the Khasi Hills.
- Unique topography and wind direction cause extreme rainfall, making it the wettest place on Earth.
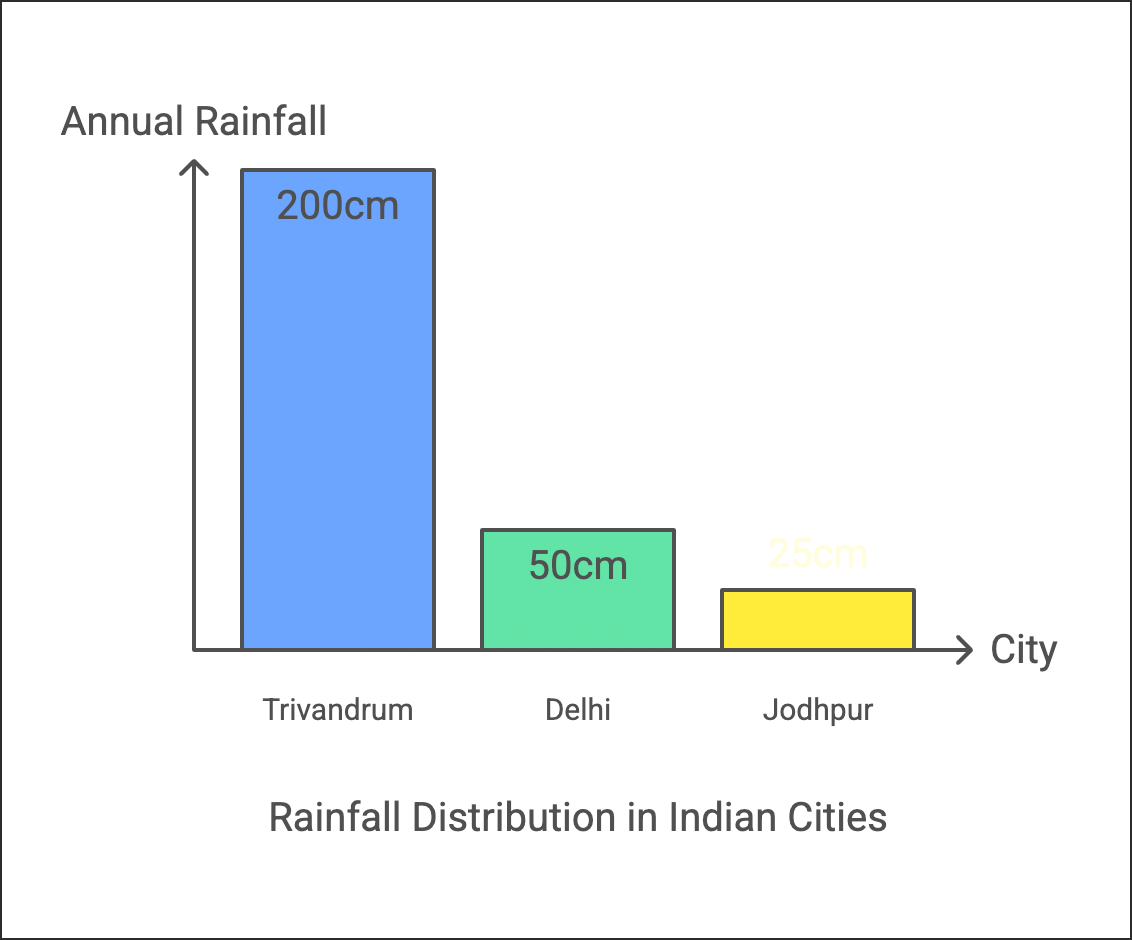
8. The rainfall decreases from South to North
- Southwest Monsoons originate from the Indian Ocean and split into branches due to the shape of the Indian Peninsula.
- Trivandrum receives over 200 cm of rainfall.
- Delhi, being inland, gets only around 50 cm.
- Arabian Sea branch:
1. Hits the Western Ghats, causing heavy rainfall.
2. Flows parallel to the Aravallis, leading to low rainfall in Jodhpur (less than 25 cm).
9. The Western Ghats receive more rain from the southwest monsoons than the Eastern Ghats because:
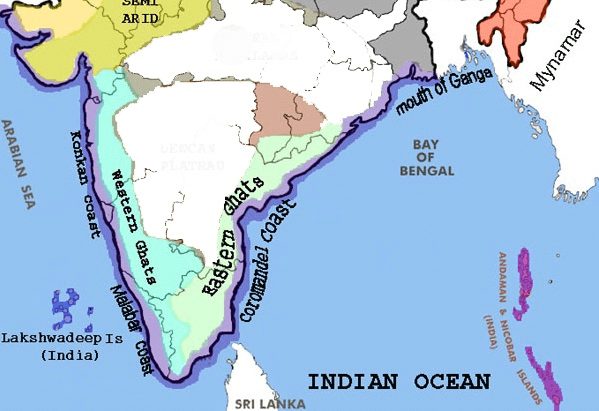 Map showing the position of Western and Eastern Ghats
Map showing the position of Western and Eastern Ghats
- The Arabian Sea branch of the monsoon is onshore.
- These winds are forced to rise and cause heavy rains.
- By the time these winds reach the east coast, most of the moisture is lost.
- The winds are offshore, so they are given less rain.
- The Eastern Ghats lies on the leeward/rain-shadow area, hence it gets less rain.
Indian would have been an arid land or dessert if there had been no phenomena of monsoons :
- Indian receives 75 to 90% of the rainfall from the monsoons.
- These monsoons winds occur due to the uneven heating of land and sea.
- The mighty Himalayas check the two branches of southwest monsoons, the Arabian Sea branch and the Bay of Bengal branch.
- These, cover the whole of India thus preventing it from becoming a desert.
Question for Important Points & Differences: ClimateTry yourself:What is the primary factor responsible for the formation of monsoon winds in India?
View Solution
Important Differences Between:
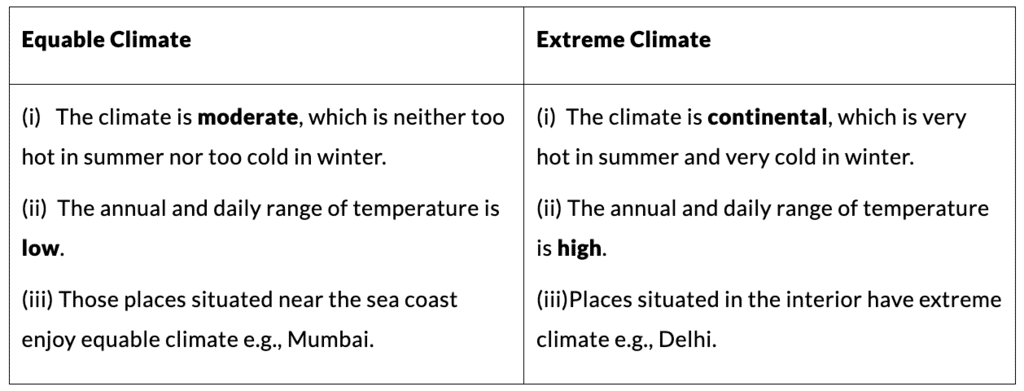
1. Equable Climate & Extreme Climate
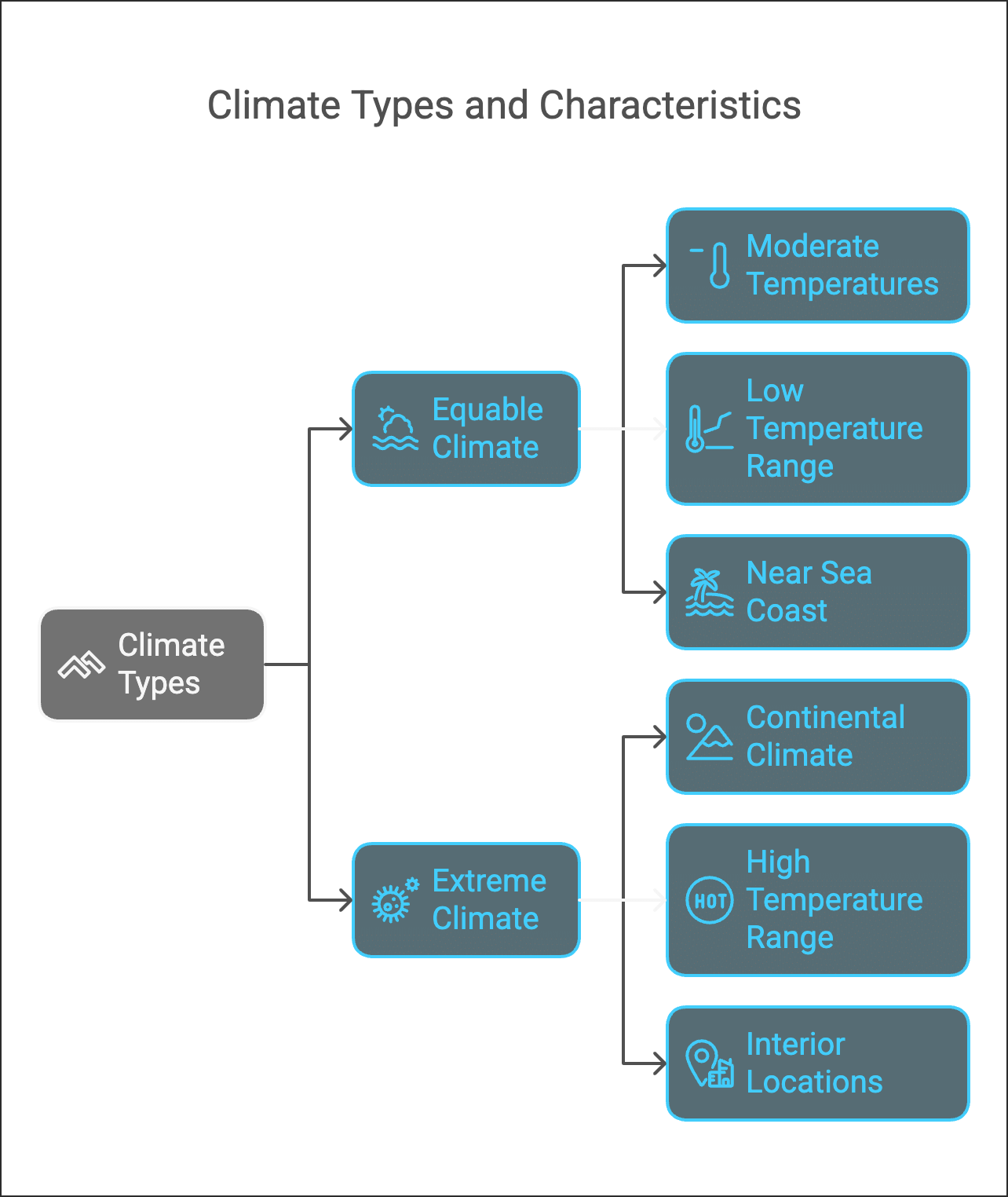
2. Rainfall and Precipitation
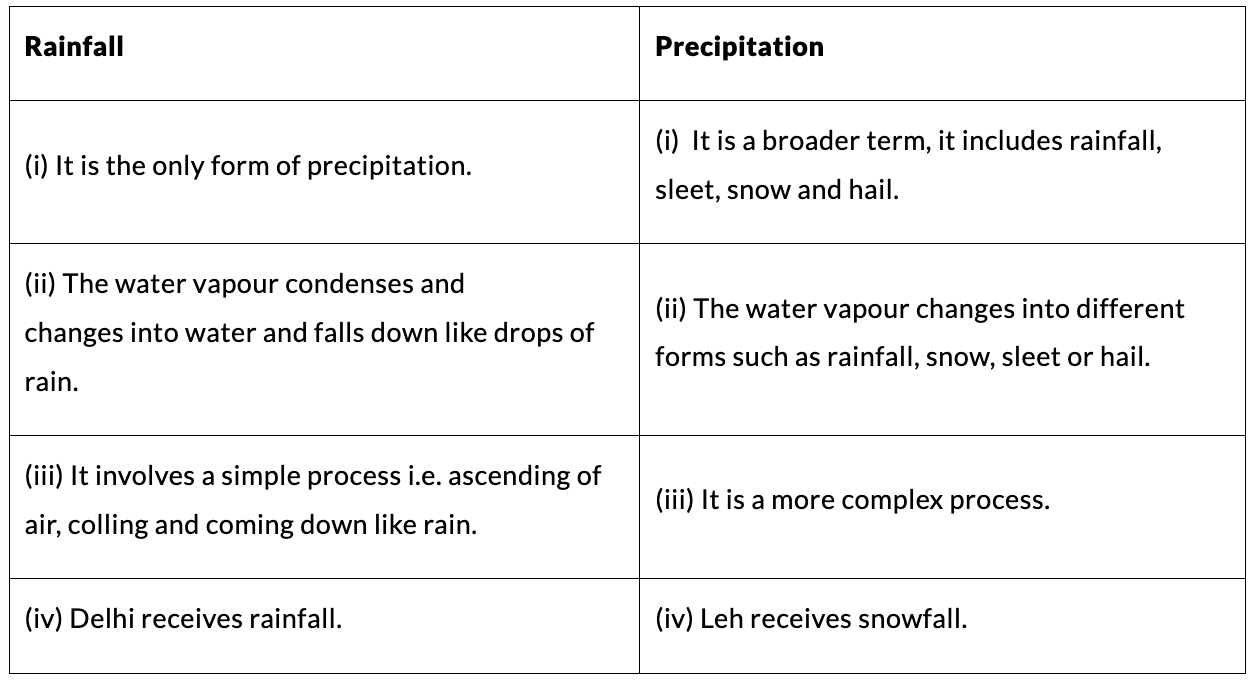
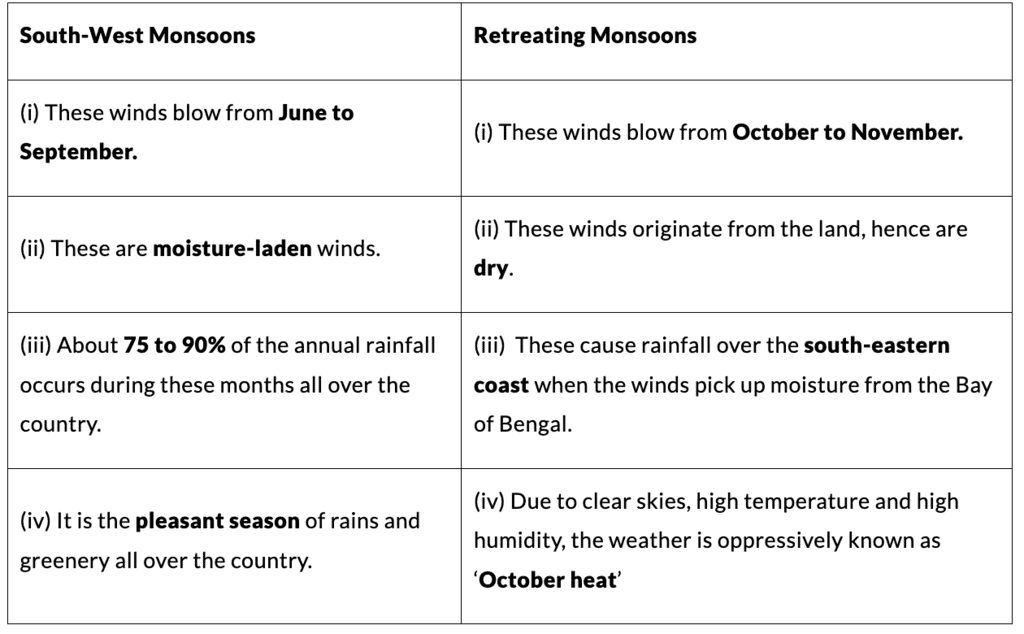
3. South-West Monsoons and Retreating Monsoons
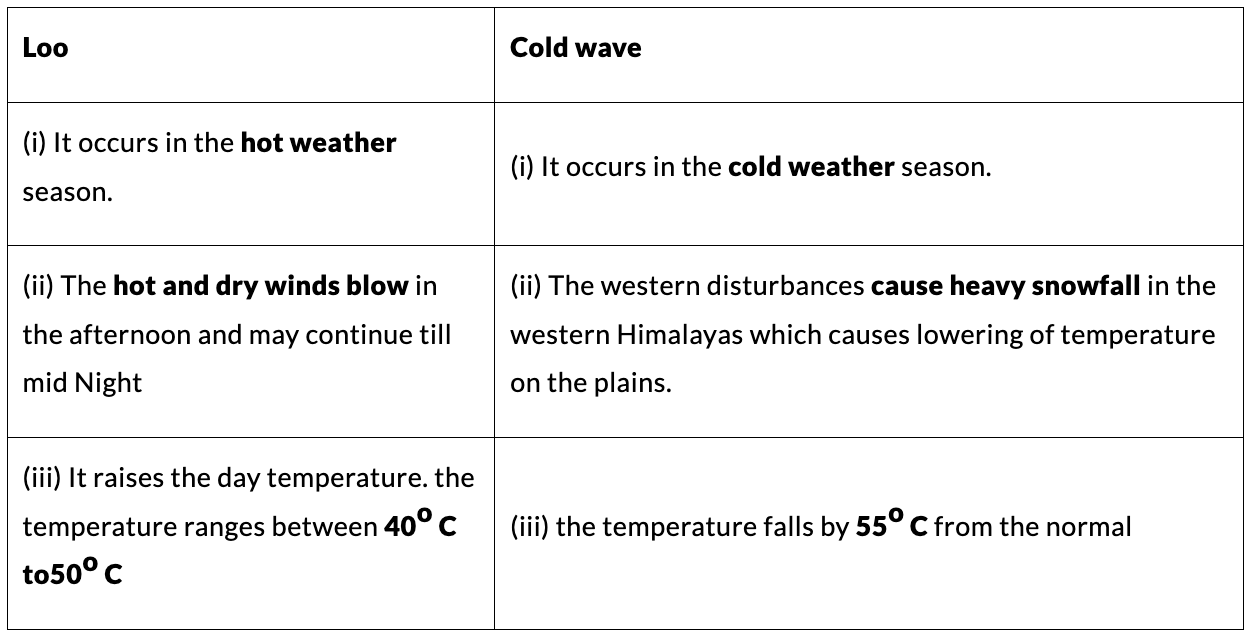
4. Loo and Cold Wave
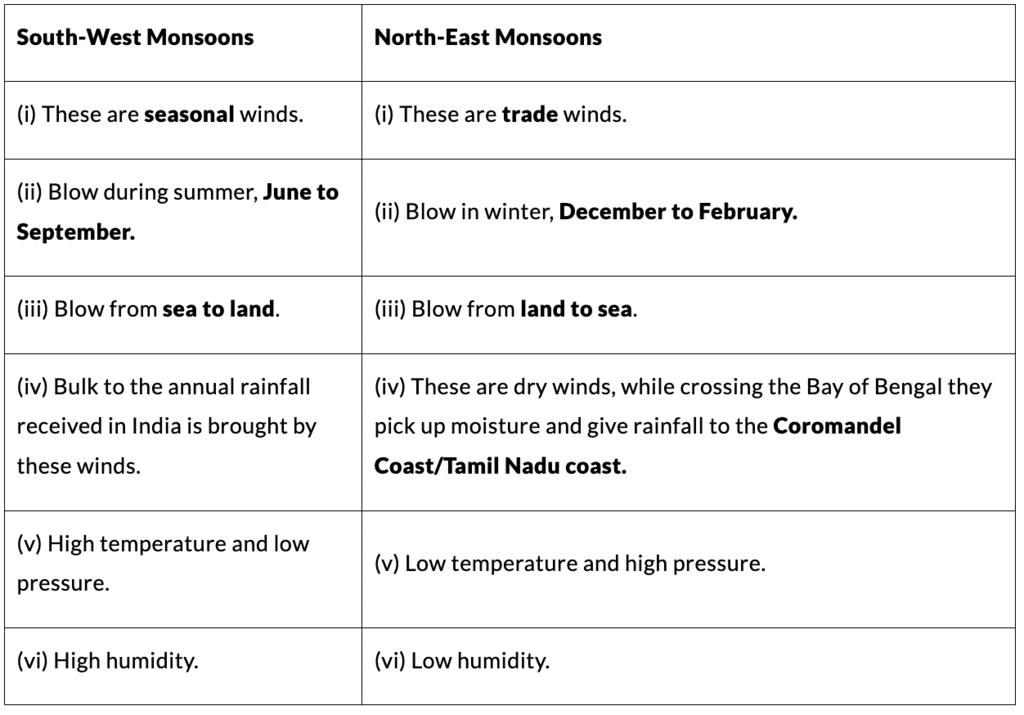
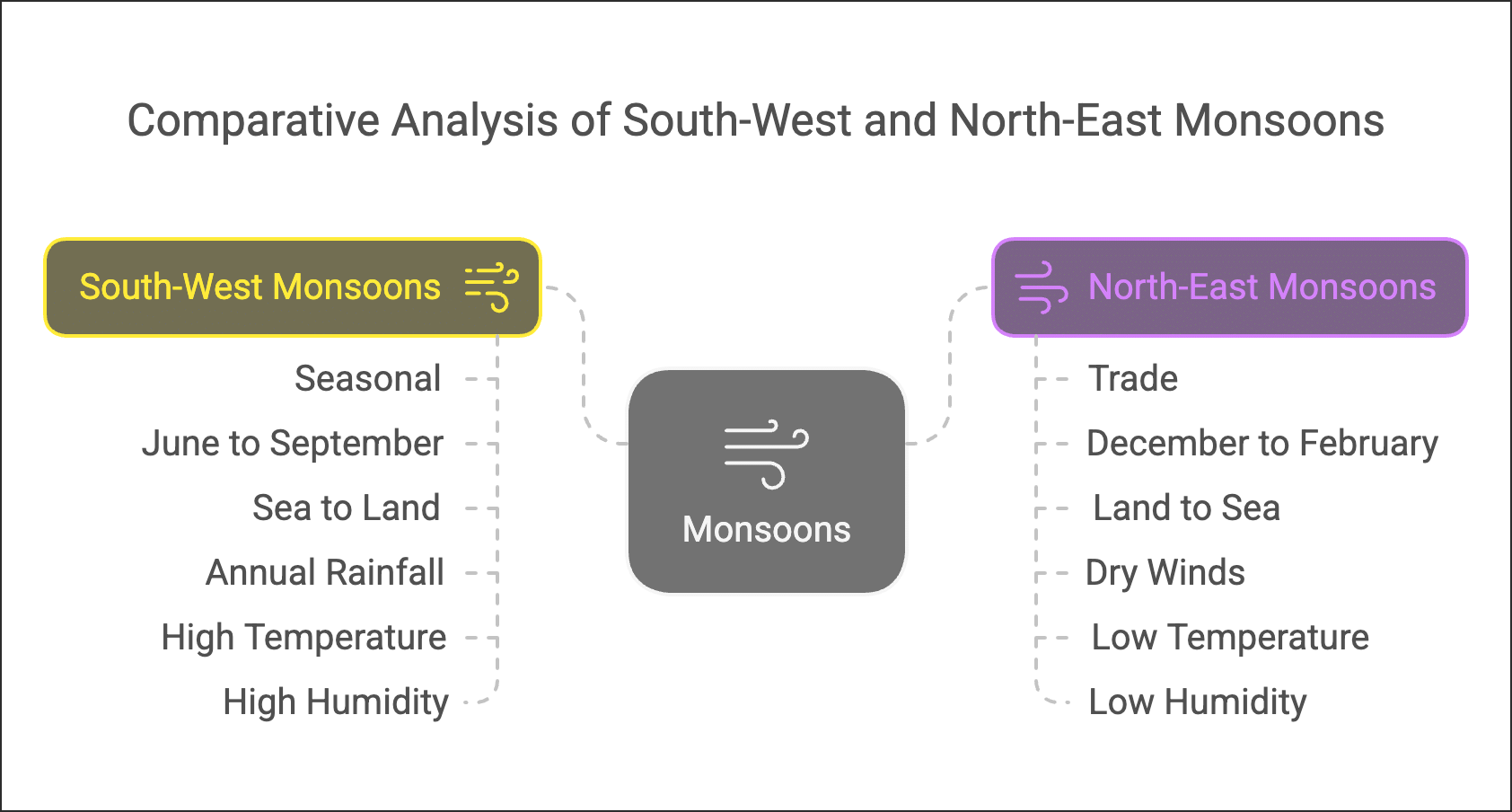
5. South-West Monsoons and North-East Monsoons
Question for Important Points & Differences: ClimateTry yourself:Which of the following is a significant difference between South West Monsoons and Retreating Monsoons?
View Solution
The document Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Climate is a part of the Class 9 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
55 videos|525 docs|78 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 4 Notes - Climate
| 1. What are the main differences between weather and climate? |  |
Ans. Weather refers to the short-term atmospheric conditions in a specific place at a specific time, including factors like temperature, humidity, precipitation, and wind. Climate, on the other hand, describes the long-term average of weather patterns over a significant period, typically 30 years or more, for a particular region.
| 2. How does climate change impact the environment? |  |
Ans. Climate change leads to various environmental impacts, including rising global temperatures, increased frequency and intensity of extreme weather events (such as hurricanes and droughts), melting ice caps, rising sea levels, and disruptions to ecosystems. These changes can threaten biodiversity and lead to habitat loss.
| 3. What are the different types of climates found around the world? |  |
Ans. The main types of climates include tropical, arid (desert), temperate, continental, polar, and highland climates. Each type is characterized by specific temperature ranges, precipitation patterns, and seasonal variations, influencing the types of vegetation and wildlife found in those regions.
| 4. How can individuals contribute to combating climate change? |  |
Ans. Individuals can help combat climate change by reducing energy consumption, using public transportation or carpooling, recycling and reducing waste, supporting renewable energy sources, and advocating for policies that protect the environment. Small lifestyle changes can collectively make a significant impact.
| 5. What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change? |  |
Ans. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide, trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect. This natural process is essential for life, but human activities, such as burning fossil fuels and deforestation, have increased the concentration of these gases, intensifying climate change and global warming.
Related Searches






















