Coding & Decoding | General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce PDF Download
What is Coding and Decoding?
Coding is a way of transmitting data between the sender and the receiver in an encrypted manner, i.e., without any other person knowing about it.
- Before transmission, the data is encoded, and when it is received, it is decoded in order to obtain the original data.
- This prevents the data from being intercepted or leaked.
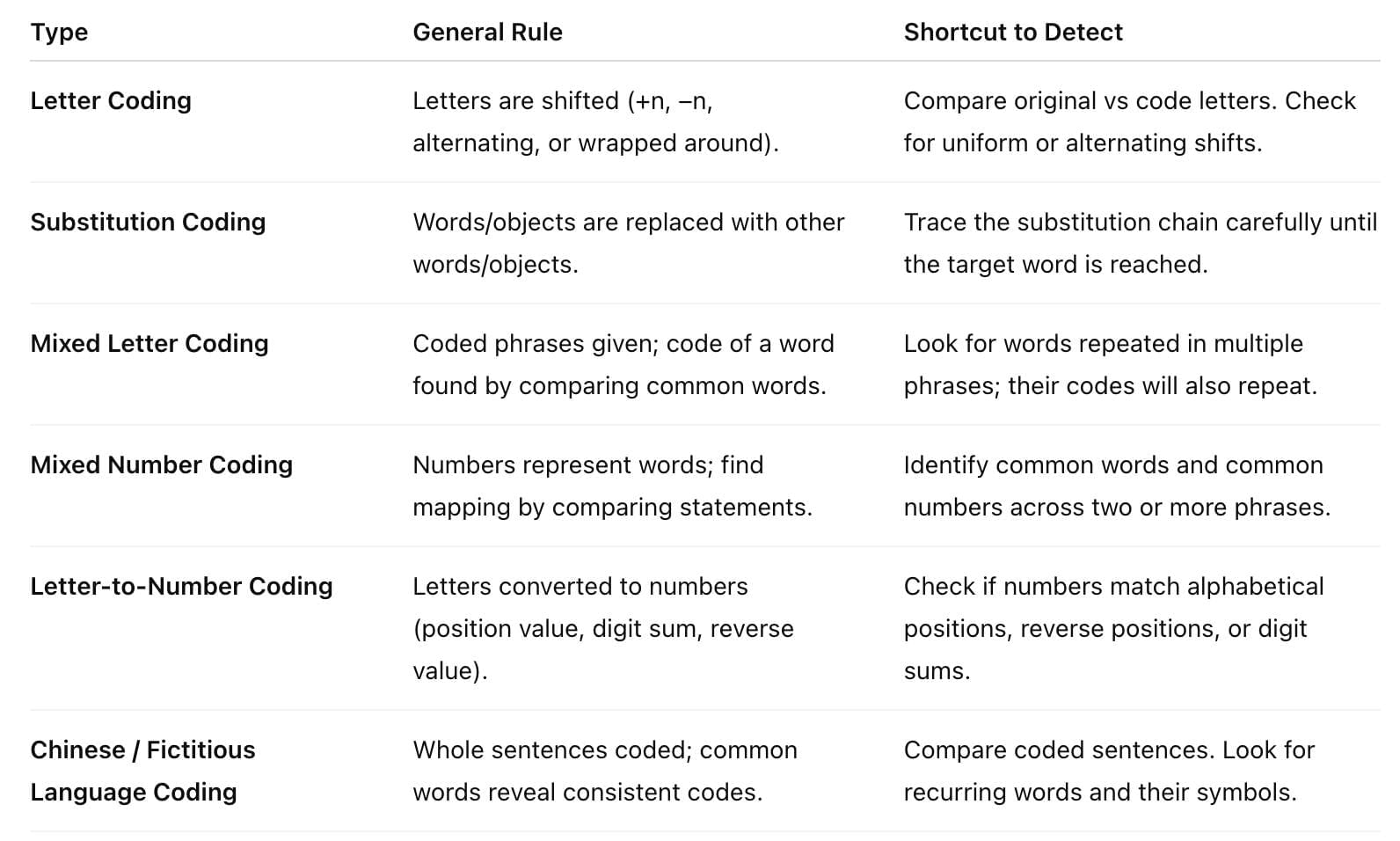
Types of Coding Decoding Questions
Let us see the various types of reasoning questions on coding and decoding one by one : 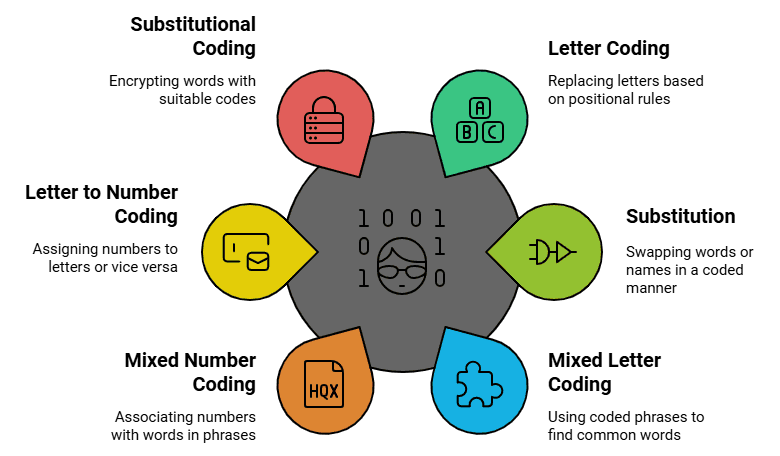 Types of Coding Decoding
Types of Coding Decoding
1. Letter coding
- In this type of question, the letters in a word are replaced by other letters according to a specific rule.
- General Rule: Letters in a word are replaced with other letters based on a fixed shift (forward or backward) or alternation (+n, –n, etc.).
- Edge Cases:
- When shifting goes beyond Z, wrap around to A. Example: Y → A with +2.
- Sometimes vowels and consonants may be shifted differently.
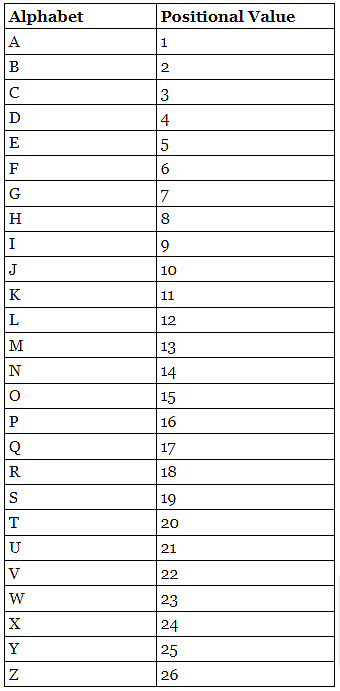
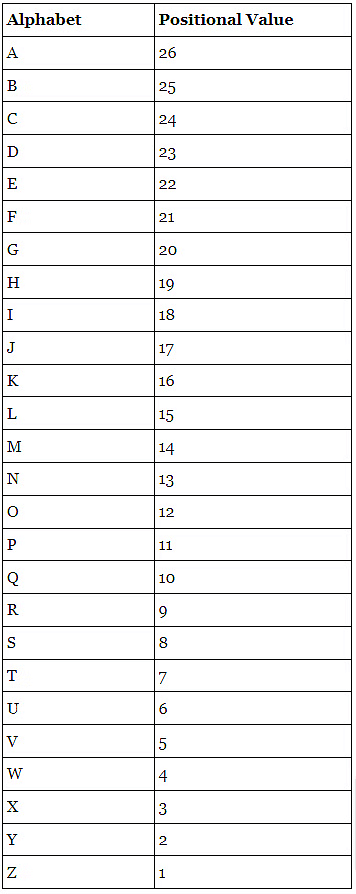
- To solve the coding-decoding reasoning questions, first of all, it is necessary to remember the positions of all alphabetical letters, both in forward and backward order, which is given below.
Positional Value of Alphabets in the forward direction
Positional Value of Alphabets in the backward direction
Example: In a certain code, “PARKING” is written as “RYTIKLI”. How will FLOWERS be written in that code?
Sol: Find out the pattern by comparing the 1st letter of PARKING with the 1st letter of RYTIKLI.
We observe that P is converted to R. R is two positions after P.
Now A is converted to Y. So, we can conclude that A is two positions before Y.
So, PARKING is coded as +2 and -2 alphabets in an alternate manner.
Using the same logic, FLOWERS is coded as ‘HJQUGPU’.The correct answer is ‘HJQUGPU’.
2. Substitution
- General Rule: In such questions, one word or object is substituted with another word/object. The challenge is to trace the substitution correctly.
- Edge Cases: Ensure the substitution chain is traced carefully; students often stop too early without careful verification.
Example: If ‘Parrot’ is known as ‘Peacock’, ‘Peacock’ is known as ‘Swallow’, ‘Swallow’ is known as 'Pigeon', and ‘Pigeon’ is known as ‘Sparrow’, what would be the name of the national bird?
Sol: We know ‘peacock’ is the national bird of India. But in the given question, ‘Peacock’ is coded as ‘Swallow’. So ‘Swallow’ is the correct answer.
3. Mixed Letter Coding
- In this type of question, three to four phrases are given in coded language, and the code for a particular word is asked.
- General Rule: Phrases are written in coded language. The code for a particular word is found by comparing common words across statements.
- Edge Cases:
Words can have similar-looking codes; double-check across multiple statements.
Be careful when two words are common but only one matches across different statements.
Example: In a certain code language,
‘new banking system’ means ‘ss tp na’
‘officer in uniform’ means ‘or mu at’
‘new bank officer’ means ‘or bk na’
‘systems in bank’ means ‘bk at ss’
(a) What is the code for ‘in’?
Sol: In statements (2) and (4), the common code word is ‘in’ and the common code is ‘at’.
(b) What does the code ‘bk’ stand for?
Sol: In statements (3) and (4), the common code word is ‘bk’ and the common word for that is ‘bank’.
4. Mixed Number Coding
- General Rule: In this type, numbers are used to represent words in phrases. By comparing statements, the number corresponding to each word is identified.
- Edge Cases:
Watch out for reuse of the same number for different words (rare but possible in advanced exams).
If multiple words remain, carefully eliminate step by step.
Example: In a certain code,
‘467’ means ‘leaves are green’,
‘485’ means ‘green is good’
‘639’ means ‘they are paying’.
What is the number code for ‘leaves’?
Sol: In statements 1 and 2, the common word is ‘green’ and the common number is ‘4’. So, ‘4’ is for ‘green’. Now, in statements 1 and 2, ‘are’ is common and ‘6’is common. So, ‘6’ stands for ‘are’.
In statement 1, only ‘leaves’ and ‘7’ are remaining, therefore ‘leaves’ corresponds to ‘7’.
5. Letter to Number Coding
- General Rule: In this type of question, each letter is replaced by its alphabetical position. If position > 9, digits are added until a single-digit number is obtained.
- Edge Cases:
Always check if “reverse positions” (27 – position) are being used instead of forward positions.
Some exams use a digital product or alternating sum instead of digit sum.
Example: If ‘EXAMINATION’ is coded as 56149512965, how is ‘GOVERNMENT’ coded?
Options:
(a) 7645954552
(b) 7654694562
(c) 7645965426
(d) 7654964526.
Sol: EXAMINATION (E=5, X=24, A=1, M=13, I=9, N=14, A=1, T=20, I=9, O=15, N=14) and code 56149512965:
- If position > 9, sum digits (e.g., X=24→2+4=6, M=13→1+3=4).
- If position ≤ 9, use position (e.g., E=5→5, A=1→1).
- Apply to GOVERNMENT (G=7, O=15, V=22, E=5, R=18, N=14, M=13, E=5, N=14, T=20):
- G=7→7, O=15→1+5=6, V=22→2+2=4, E=5→5, R=18→1+8=9, N=14→1+4=5, M=13→1+3=4, E=5→5, N=14→1+4=5, T=20→2+0=2.
- Code: 7645954552.
- Option (a) is the correct answer.
6. Chinese Coding
- General Rule: Sentences are coded with symbols or codes. Common words across sentences reveal their codes.
- Edge Cases:
Sometimes two words may share similar symbols. Validate by cross-checking across all statements.
Trick questions may introduce filler words that don’t appear elsewhere—avoid guessing.
Example: In a code:
- ‘he is smart’ is ‘#a $b %c’
- ‘she is clever’ is ‘@d $b &e’
- ‘he loves her’ is ‘#a *f @d’
What is the code for ‘is’?
Sol: Compare:
- Phrases 1 and 2 share ‘is’ and code ‘$b’. Thus, ‘is’ = ‘$b’.
- Verify: Phrase 1 (he=#a, smart=%c), Phrase 2 (she=@d, clever=&e), Phrase 3 (he=#a, loves=*f, her=@d). Therefore, the code is correct.
Tips and Tricks to Solve Coding Decoding Questions
Candidates can find various tips and coding decoding reasoning tricks from below for solving the questions related to this section.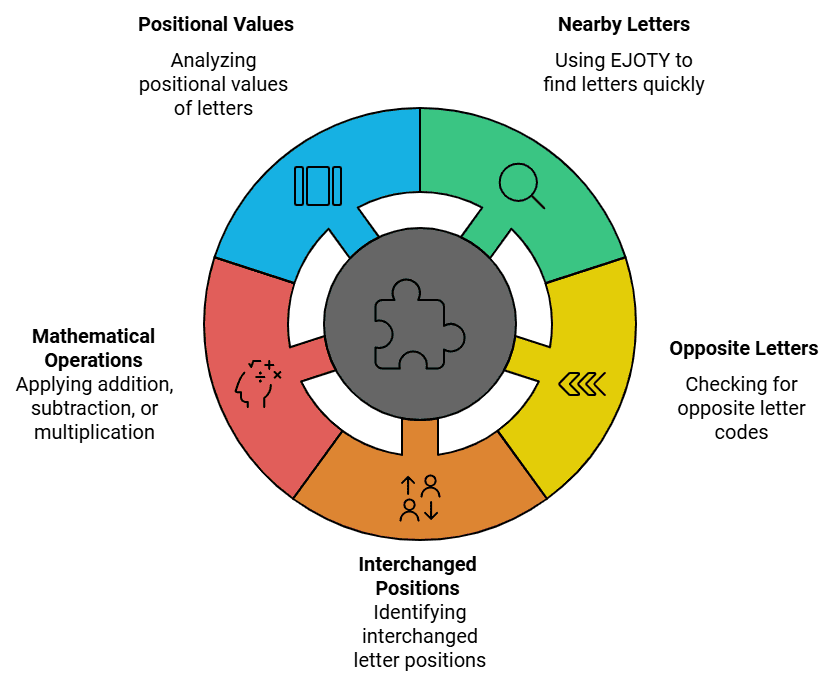 Tip # 1: Remembering EJOTY helps recall the positions of letters that are multiples of 5 (E=5, J=10, O=15, T=20, Y=25). This can also help find nearby letters quickly and thus speed up coding-decoding calculations.
Tip # 1: Remembering EJOTY helps recall the positions of letters that are multiples of 5 (E=5, J=10, O=15, T=20, Y=25). This can also help find nearby letters quickly and thus speed up coding-decoding calculations.
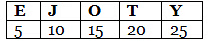
Tip # 2: To solve the Letter-to-Letter coding and decoding questions quickly, candidates need to check if the opposite letters are given in the code. Then, candidates need to check if the position of letters is interchanged. Finally, check if operations like addition or subtraction are applied.
Tip # 3: To solve the letter-to-number type coding and decoding reasoning questions quickly, candidates first need to check if the positional values of letters are given in the code. Then check if the positional values of letters are interchanged. Check if the positional values of letters are reversed alphabetical series. Finally, check if operations like addition, subtraction, or multiplication are applied.
Checklist: Identifying the Coding Pattern
Before attempting to solve, quickly check what kind of coding is used. Use the following checklist:
- Compare the original word and its code: Are letters in the same position, reversed, or shifted?
- Check vowels and consonants: Are they treated differently (e.g., vowels shifted +2, consonants –1)?
- Look for alternating patterns: Do the shifts change (+2, –2, +2, –2, etc.)?
- Numbers and letters: Are positions converted into numbers or interchanged between them?
- Multiple coded statements: If more than one coded phrase is given (Chinese coding), look for common words and their corresponding codes.
- Numeric codes: Check if the numbers represent the sum of letter positions, reverse positions (27 – position), or digital sums.
Basic points you need to remember before solving any question of this topic.
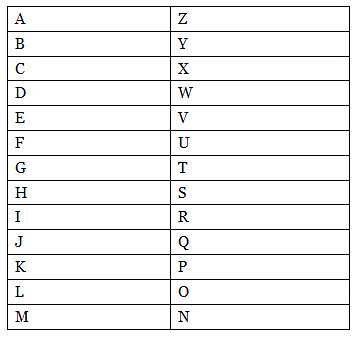
- Alphabets’ positions (A=1, B=2,……,Y=25, Z=26)
- Opposite position of alphabet (A=26, B=25,……, Z=1)
- Opposite of each alphabet (A is opposite to Z, B is opposite to Y and so on)
Sample Coding Decoding Questions
Example 1: In the following questions, find out the alternatives which will replace the question mark.
ENGLISH : FOHNHRG :: SCIENCE : ?
Sol: Here ENGLISH is written as follows.
If we follow the same principle for SCIENCE then we get the word TDJGMBD. Hence, it is the correct answer.
Example 2: In a certain code language, if “FRIEND” is written as “UIRVMW”, then how will “TRADER” be written in that code language?
Sol: The pattern used in this question is opposite to that letter such as
Therefore, TRADER will be coded as GIZWVI.
Example 3:If LANGUAGE is coded as 31573175, how is GRAMMAR coded?
(a) 7914419
(b) 7924419
(c) 7914549
(d) 7814419
Sol: Option (a)
Write each letter of GRAMMAR with its position:
G = 7, R = 18, A = 1, M = 13, M = 13, A = 1, R = 18.Convert positions > 9 to single digits by summing digits:
R (18) → 1 + 8 = 9
M (13) → 1 + 3 = 4
(A = 1 and G = 7 remain the same.)Replace letters with final digits in order:
G → 7, R → 9, A → 1, M → 4, M → 4, A → 1, R → 9.
→ 7914419.Hence, option A is the correct answer.
|
164 videos|798 docs|1153 tests
|
FAQs on Coding & Decoding - General Test Preparation for CUET UG - CUET Commerce
| 1. What is Coding-Decoding in reasoning tests? |  |
| 2. What are the common types of Coding-Decoding questions? |  |
| 3. What are some tips to solve Coding-Decoding questions effectively? |  |
| 4. How can I practice Coding-Decoding questions for competitive exams? |  |
| 5. Are Coding-Decoding questions difficult to understand? |  |