Chemical Properties of Carbon & its Compounds | Science Class 10 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Combustion |

|
| Reduction and Oxidation |

|
| Addition Reactions |

|
| Substitution Reactions |

|
All carbon compounds show some common characteristic properties. As most of the fuels we use are either carbon or its compounds. Some properties are described here:
Combustion
Combustion is a chemical process in which carbon compounds on burning produce heat and light (in the form of flame)
Combustion of Carbon
Carbon (or charcoal) burn in air or oxygen to give CO2 producing heat and light.
Combustion of Hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbons burn to produce carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H2O) and heat and light.
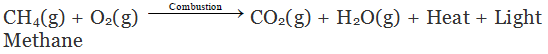
Note: Natural gas and biogas contain methane. So, burning of natural gas and biogas are also called combustion reactions.
Burning of LPG (Butane) produces CO2, H2O heat and light.

Combustion of Cellulose
Combustion of cellulose (like wood, cotton cloth and paper) gives CO2, H2O heat and light. Cellulose is a carbohydrate and can be described by the formula (C6H10O5)n.
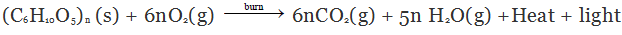
Combustion of alcohol
Ethanol and oxygen (in air)
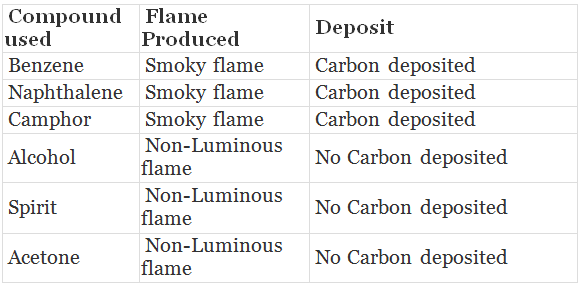
Activity: To observe the combustion of given organic compounds.
Materials: Benzene, naphthalene, Camphor, alcohol (ethanol). Spirit, acetone.
Procedure:
1. Take each compound on iron spatula and burn them in bunsen burner.
2. Record the type of flame produced.
3. Put a metal plate above the flame and observe whether or not there is black carbon deposition.
Observation:
Conclusion:
Benzene, naphthalene, camphor burn with smoky flame and carbon particles get deposited. They undergo incomplete combustion due to excess of carbon content.
- Alcohol, spirit and acetone burn with non-Luminous flame and no carbon gets deposited. They undergo complete combustion, therefore produce more heat.
Combustion and the nature of flame:
(i) Saturated hydrocarbons such as, methane, ethane, propane, butane and natural gas and LPG burn with a blue flame in the presence of sufficient / excess of air / oxygen.
(ii) In the presence of limited amount of air / oxygen, saturated hydrocarbons such as methane, butane. etc give smoky flame.
(iii) Unsaturated hydrocarbons such as ethene, ethyne etc. burn with a luminous / yellow smoky flame.
(iv) The gas / kerosene stove used at home has inlets for air so that a sufficiently oxygen rich mixture is burnt to give a clean blue flame. If you carefully observe the bottoms of vessels getting blackened, it is a clear indication that the air holes are blocked and the fuel is getting wasted.
(v) Fuels, such as coal and petroleum, have some amount of nitrogen and sulphur in them. Combustion of coal and petroleum results in formation of oxides of sulphur and nitrogen (such as sulphur dioxide, nitric oxide, nitrogen peroxide) which are major pollutants in the environment.
Formation of Coal and Petroleum:
Coal and petroleum have been formed from biomass which has been subjected to various biological and geological processes.
Coal is a naturally occurring black mineral and is a mixture of free carbon and compounds of carbon containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and sulphur. It is not only a good fuel but is also a source of many organic compounds. It is found in coal mines deep under the surface of earth.
Coal is believed to be formed from fossils which got buried inside the earth during earthquakes and volcanoes which occurred about 300 million years ago. Due to huge pressure and temperature inside the earth and in the absence of air, the fossil fuels (vegetable matter or wood, etc.) were converted into coal. The slow chemical processes of the conversion of wood into coal is called carbonisation. Since coal is formed by slow carbonisation of plants and fossils, it produces many important carbonisation products like peat, lignite, bituminous and anthracite etc. and is itself known as fossil fuel. Coal is also a non-renewable source of energy.
Petroleum is a complex mixture containing various hydrocarbons (compounds of carbon and hydrogen) in addition to small amounts of other organic compounds containing oxygen, nitrogen, and sulphur. It is a dark coloured, viscous and foul smelling crude oil. The name petroleum is derived from latin words : "petra" meaning rock and "oleum" meaning oil. Since petroleum is found trapped between various rocks, it is also known as rock oil.
Oxidation
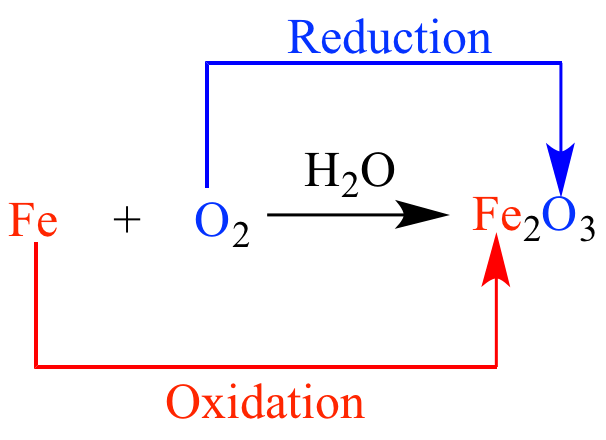
Reduction and Oxidation
Carbon and its compounds can be easily oxidised on combustion (or burning). During combustion / burning, the compounds gets oxidised completely to different products, depending upon the nature of the oxidising agents.
Carbon gives carbon monoxide or carbon dioxide depending upon the oxygen available.


Hydrocarbon when oxidised give different products as follows :


Alcohols also give different products on oxidation depending upon the reaction conditions.
Example:
Alcohols on oxidation with certain oxidising agents such as chromic anhydride in acetic acid, yield corresponding aldehydes, whereas on oxidation with alkaline potassium permanganate (or acidified potassium dichromate) corresponding carboxylic acid is formed, as given below:

Addition Reactions
Addition Reactions
All unsaturated hydrocarbons react with molecules like H2, X2, H2O etc. to form other saturated compounds. These reactions are called addition reactions. Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as nickel or palladium to give saturated hydrocarbons.
Note: Catalysts are substances that cause a reaction to occur or proceed at a different rate without the reaction itself being affected.
 Fig: Addition of hydrogen to ethene
Fig: Addition of hydrogen to ethene

- The addition of hydrogen to an unsaturated carbon compound is called hydrogenation reaction.
- Certain vegetable oils such as ground nut oil, cotton seed oil and mustard oil, contain double bonds (C = C) and are liquids at room temperature.
- Because of the unsaturation, the vegetable oils undergo hydrogenation, like alkenes, to form saturated products called vanaspati ghee, which is semi-solid at room temperature.
Vegetable oils (Unsaturated oil) + Hydrogen Vanaspati Ghee (Saturated ghee)
Vanaspati Ghee (Saturated ghee)
[Intext Question]
Substitution Reactions
Substitution Reactions
The reactions in which one or more hydrogen atoms of a hydrocarbon are replaced by some other atoms or groups are called substitution reactions.
Example:
Methane reacts with chlorine (or bromine) in the presence of sunlight and undergoes a substitution reaction. It is called a photochemical reaction because it takes place in the presence of sunlight.




|
83 videos|438 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Chemical Properties of Carbon & its Compounds - Science Class 10
| 1. What is combustion and how does it relate to carbon and its compounds? |  |
| 2. What are reduction and oxidation reactions? How do they occur in carbon compounds? |  |
| 3. How do addition reactions occur in carbon compounds? |  |
| 4. What are substitution reactions and how do they occur in carbon compounds? |  |
| 5. How do the chemical properties of carbon and its compounds contribute to their significance? |  |























