AC, DC Current & Domestic Circuits | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Domestic Electric Circuits
 Supply from Power Stations: Electricity is generated at power station. In our homes, we receive the supply of electric power either supplied through overhead poles or underground cables using two thick aluminium wires.
Supply from Power Stations: Electricity is generated at power station. In our homes, we receive the supply of electric power either supplied through overhead poles or underground cables using two thick aluminium wires.
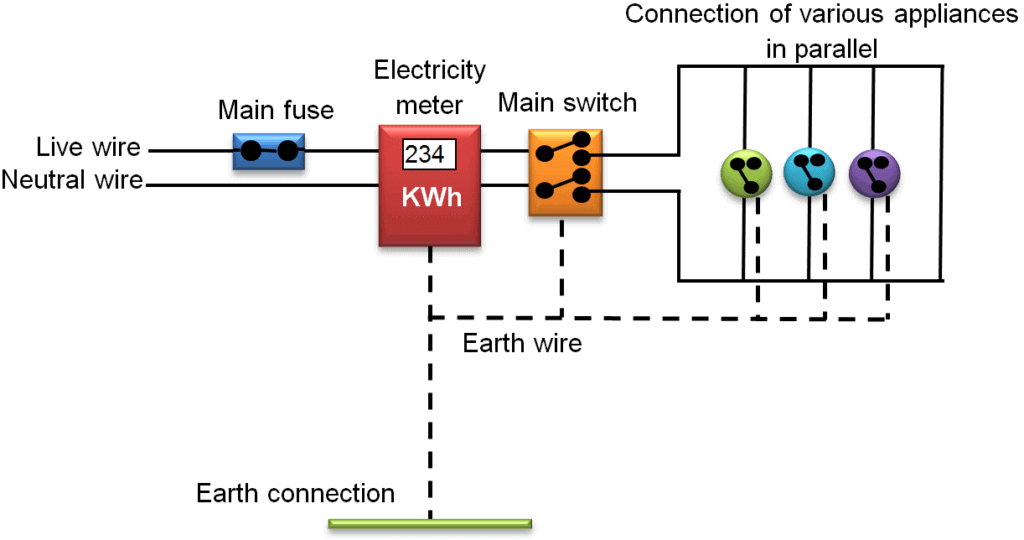
Main board: It is provided outside the building under a covered place (varandah or poarch). It contains the meter (energy-meter) and the main switch. (Fig.)
From the street electric pole, a thick rubber insulated cord reaches the main board. It contains two thick copper or aluminium wires, one covered with red and the other covered with black (or brown) plastic covering.Main board outside the building.
They form the live line wire (L) and neutral line wire (N) respectively.
Live line wire has a potential of 220 V whereas the neutral wire has zero potential (with respect to the earth). They enter the main board and are connected to the meter.
Wiring ahead is provided by the house owner himself. These wires are also red and black plastic covered.
From the meter the wires enter the main switch. In the main switch, a fuse F is provided in the path of live wire.
From outside the main switch, the wires become free to be used inside the building as required.
A third wire is a thick bare wire of copper, called earth wire E. It is connected to an earth connection which consists of a thick copper plate P buried deep inside the moist earth.
Inside the building: It is a well known fact that inside the house, connections to all the devices are made in parallel, each having independent switch and fuse (if necessary). Thus, whenever some fault occurs in circuit of one particular device in one room, devices in other rooms do not suffer.
Circuit inside the building.
As shown in Fig., connection to low power devices like bulb B and fan F are made with lines N and L only, putting switch in line L. For devices of more power and with whom the body remains in contact (like electric press or refrigerator), we use connections through a 3 pin plug socket (shoe) system.
A three pin plug P and three pin socket S are shown in Fig.. The three points of the socket are connected to the three lines as shown in the diagram. A fuse F is also introduced to avoid damage to the appliance.
The three pin plug uses a three wire cord which has three plastic wires inside a single rubber insulating cover. The wires are coloured : red, black (or brown) and green respectively to serve as an extension of live, neutral and earth wires for the appliance. The three wires are connected to the three holes in the socket as shown in Fig.. When the plug is inserted in the socket, proper lines get connected to the appliance.
Electric Fuse: An electric fuse is a safety device used to save the electrical appliances like electric bulbs, electric tubes, T.V. etc. from burning when large current flows in the circuit. Electric fuse is a wire made of copper or aluminium or tin-lead alloy. The melting point of the material of which the electric fuse wire is made should be low.
Suppose a fuse is not connected in the path of a live wire of the circuit. In such case, the circuit may be over heated if the curent in the circuit exceeds the safe limit. There is a change of short circuiting of the circuit which causes the fire. So to avoid short circuiting of the circuit, a fuse must be put in the path of the circuit.
Function of earth wire : Due to the long use, some covered wires inside the appliance may become bare and may make contact with metallic body of the appliance. In such a case the appliance gives a shock if not earthed. The earth wire keeps the potential of the appliance zero and shock is avoided.
Use of Switch : All electrical appliances are provided with separate switches. All switches are connected with live wire as well as with neutral wire. When we switch off an appliance, then it gets disconnected from the live wire. Now if one touches the metallic body of the appliance there is no danger of electric shock.
But, if connections to the switch are in such a way that on switching off the appliance, neutral wire gets disconnected but not live wire, then there is danger of electric shock.
Short Circuit
When the live wire and the neutral wire come into direct contact. This occurs when the insulation of wires is damaged or there is a fault in the appliance. In such a situation, the current in the circuit abruptly increases. This is called short-circuiting. When short circuiting occurs, the resistance of the circuit becomes very small and hence huge amount of current flows through it. Large amount of current in the circuit produces large amount of heat which raises the temperature of the circuit to very high value. As a result of this, the circuit catches fire.
Overloading : means flow of large amount of current in the circuit beyond the permissible value of current. It occurs when many electrical appliances of high power rating like geyser, heater, refrigerator, motor etc. are connected in a single socket or in a single circuit. High current flowing in the circuit due to overloading causes fire.
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on AC, DC Current & Domestic Circuits - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the difference between AC and DC current in domestic electric circuits? |  |
| 2. How are AC and DC currents used in household appliances? |  |
| 3. Can AC and DC currents be used interchangeably in domestic circuits? |  |
| 4. What safety precautions should be taken when working with domestic electric circuits? |  |
| 5. How can one identify if a circuit in their home is AC or DC? |  |

















