Dispersion of Light | Science Class 10 PDF Download
Refraction of Light through a Prism
What is a Prism?
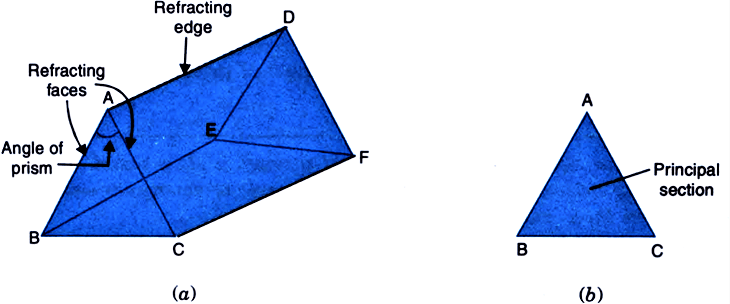 (a) A 3-D view of a Glass Prism, (b) Principal Section of a Glass Prism
(a) A 3-D view of a Glass Prism, (b) Principal Section of a Glass Prism
A prism is a transparent refracting medium bound by two plane surfaces inclined to each other at a certain angle (commonly 60° or 45°).
- The faces ABED and ACFD are refracting surfaces of the prism.
- The face BEFC is the base of the prism. The angle ∠ BAC is the prism angle.
- The line of intersection of the two refracting surfaces is called the refracting edge (the line AD in the diagram) of the prism.
- The face ABC is the principal section of the prism. The principal section of a prism is perpendicular to its refracting edge.
How does Light get Refracted by a Prism?
The incident ray suffers a deviation (or bending) through an angle d due to refraction through the prism. The angle d is called the angle of deviation.
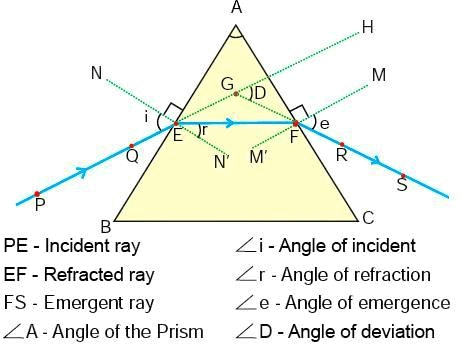 Refraction through a Triangular Glass Prism
Refraction through a Triangular Glass Prism
Note:
The prism is in the position of the minimum deviation when, angle of emergence = angle of incidence or ∠e = ∠i.
The refractive index of the material of prism is given as:
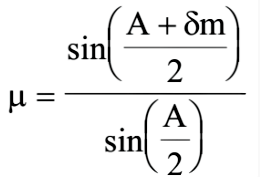
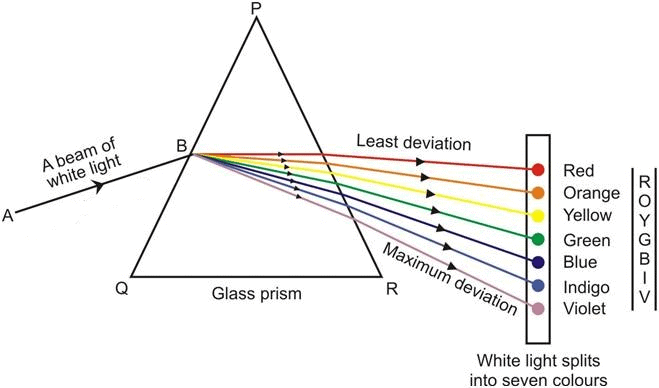
Dispersion of White Light by a Glass Prism
What is meant by the Dispersion of Light?
The process of splitting of white light into its seven constituent colours is called dispersion of white light.
The band of seven colours formed on a screen due to the dispersion of white light is called the spectrum of visible light or the spectrum of white light.
What causes Dispersion of White Light?
Dispersion of white light into seven colours occurs because the light of different colours has different wavelength. 
- In this band of seven colours, red light has the longest wavelength and violet has the shortest.
- Lights of all colours travel at the same speed in vacuum. But, in any transparent medium, such as glass or water, the lights of different colours travel with different speeds.
- Due to difference in their speeds, the lights of different colours bend through different angles. In any transparent medium, the red light travels the fastest, and the violet light the slowest of all the seven colours. Therefore, the red light bends the least, and the violet light bends the most.
- Thus, dispersion of white light into seven colours occurs because the lights of different colours bend through different angles while passing through a glass prism.
What is meant by Monochromatic and Polychromatic Light?
The light of one single colour, or of one single wavelength is called monochromatic light (chrome means colour).
- Sodium light is golden yellow in colour. So, sodium light is monochromatic light.
- The light made up of many colours, or light consisting of radiations of many wavelengths is called polychromatic light.
- White light is made up of seven colours. So, white light (or sunlight) is polychromatic light.
How is the Dispersed White Light Recomposed?
Recombination of the seven colours of the dispersed white light to get white light is called recomposing of the dispersed white light.
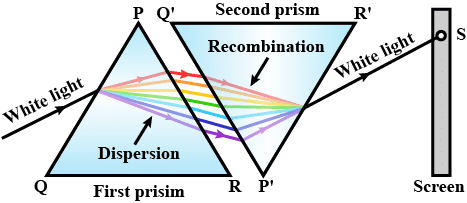
How does a Rainbow Form?
Rainbow is an example of the dispersion of white light.
- Just after the rain, a large number of small droplets of water remain suspended in the air.
- Each drop acts like a small prism.
- When sunlight falls on these drops, the white light splits into seven colours.
- The dispersed light from a large number of drops forms a continuous band of seven colours. This coloured band is called a rainbow.
- Thus, a rainbow is produced due to the dispersion of white light by small raindrops hanging in the air after the rain.
The rainbow is seen when the sun is behind the observer.
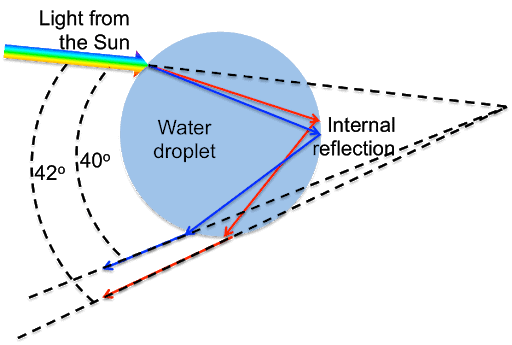 Refraction of Sunlight by a Spherical Raindrop leading to the formation of the Rainbow
Refraction of Sunlight by a Spherical Raindrop leading to the formation of the Rainbow
|
80 videos|569 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Dispersion of Light - Science Class 10
| 1. What is the process of refraction of light through a prism? |  |
| 2. How does a prism cause the dispersion of white light? |  |
| 3. What role does the angle of the prism play in refraction and dispersion? |  |
| 4. How does a rainbow form in the sky? |  |
| 5. Why do we see a spectrum of colors in a rainbow? |  |

















