Alkynes: Nomenclature, Properties & Preparation | Chemistry Class 11 - NEET PDF Download
Alkynes
1. Introduction
A triple bond gives an alkyne four fewer hydrogen atoms than the corresponding alkane. There fore the triple bond contributes two degree of unsaturation (DU).
Alkynes are not as common in nature as alkenes, but some plants do use alkynes to protect themselves against disease or predators. Acetylene is by far the most important commercial alkyne. Acetylene is an important industrial feedstock but its largest use is as the fuel for the oxyacetylene welding torch.
2. Structure and Bonding in Alkynes
(1) Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon -carbon triple bond.
(2) Alkynes are also called acetylenes because they are derivatives of acetylene.
(3) The general formula is : CnH2n-2. (one triple bond)
(4) In alkyne C≡C bond length is 1.20 Å.
(5) Its bond energy is 192 kcal. mol-1
(6) The hybridization of carbon atoms having triple bond (C≡C) in alkynes is sp
(7) Overlapping of these sp hybrid orbitals with each other and with the hydrogen orbitals gives the sigma bond framework which is linear (180º) structure.
(8) Two p bonds result from overlap of the two remaining unhybridized p orbitals on each carbon atom. These orbitals overlap at right angles (90º) to each other, forming one p bond with electron density above and below the C - C sigma bond, and the other with electron density in front and in back of the sigma bond. This result in a cylindrical p electron cloud around s bonded structure
Note : Any type of stereoisomerism does not arise in acetylenic bond due to linearity of C º C bond.
Ex.1 Cis-trans isomerism is not possible in alkynes because of :
Ans. 180º bond-angle at the carbon-carbon triple bond.
Ex.2 Draw the geometrical isomers of hept -2-en-5-yne?
Ans.
Nomenclature of Alkynes
- Common system: According to the common system, different members of alkynes are named in the form of derivatives of acetylene.
- IUPAC System: According to the IUPAC system, the nomenclature of alkynes is very similar to the nomenclature of alkanes. Hence, the naming is similar just the suffix “yne” replaces the suffix “ane” of the corresponding alkanes. Moreover, the numbering of position starts with the first carbon having the triple bond.
3. Physical Properties of Alkynes:
(1) Alkynes are relatively nonpolar (w.r.t. alkyl halides and alcohols) and are nearly insoluble in water (but they are more polar than alkenes and alkanes). They are quite soluble in most organic solvents, (acetone, ether, methylene chloride, chloroform and alcohols).
(2) Acetylene, propyne, and the butynes are gases at room temperature, just like the corresponding alkanes and alkenes. In fact, the boiling point of alkynes are nearly the same as those of alkanes and alkenes with same number of carbon atoms.
4. Table
Name | Formula | M.p.,°C | B.P., °C | Relative density (at 20°C) |
Acetylene | HC = CH | - 82 | - 75 |
|
Propyne | HC=CCH3 | - 101.5 | - 23 |
|
1-Butyne | HC = CCH2CH3 | - 122 | 9 |
|
1-Pentyne | HC = C(CH2)2CH3 | - 98 | 40 | 0.695 |
2-Butyne | ch3c = cch3 | - 24 | 27 | 0.694 |
2-Pentyne | ch3c = cch2ch3 | - 101 | 55 | 0.714 |
3-Methyl-1-butyne | HC = CCH(CH3)2 |
| 29 | 665 |
5. TABLE - COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ALKANES, ALKENES, ALKYNES
Ex.3 Which has a longer carbon-methyl bond, 1-butyne or 2-butyne. Explain?
Ans. The bond from the methyl group in 1-butyne is to an sp3-hybridised carbon and so is longer than the bond from the methyl group in 2-butyne, which is to an sp-hybridised carbon.

Ex.4 Arrange the following bond-lengths in increasing order.
Ans. (d) < (b) < (c) < (e) < (a)
Q.3 Arrange C - H bond -lengths (a,b,g) in increasing order as shown : -
6. Laboratory Test of Alkyne
7. Laboratory test of terminal alkynes
When triple bond comes at the end of a carbon chain. The alkyne is called a terminal alkyne.
1-Butyne, terminal alkyne
8. Acidity of Terminal Alkynes:
Terminal alkynes are much acidic than other hydrocarbons due to more electronegative sp hybridized carbon. The polarity (acidity) of a C - H bond varies with its hydridization, increasing with the increase in percentage's character of the orbitals.
sp3 < sp2 < sp
The hydrogen bonded to the carbon of a terminal alkyne is considerably more acidic than those bonded to carbons of an alkene and alkane (see section). The pKa values for ethyne, ethene & ethane illustrate this point
The order of basicity of their anions is opposite to that of their relative acidity:
Relative Basicity
CH3CH2: > H2C = CH:- > HC≡C:-
Relative acidity
pKa 15.7 16-17 25 38 44 50
Relative Basicity
9. General methods of preparation :
(I) By dehydro-halogenation of gem and vic dihalide:
General Reaction:
RCH = CHR + Br2 →
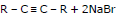
A vic - dibromide
The dehydrohalogenations occur in two steps, the first yielding a bromoalkene and the second alkyne.
Mechanism :
Step 1
Step 2
e.g. CH3CH2CH = CH2
CH3CH2C≡CH
e.g.
[CH3CH2C º CH]
CH3CH2C≡C!Na+
CH3CH2C≡C:-Na CH3CH2C≡CH + NH3 + NaCl
General Reaction
Ex.5 Give the structure of three isomeric dibromides that could be used as starting materials for the preparation of 3,3-dimethyl-1-butyne.
Sol. (I)
(II)
(III)
Ex.6 Show the product in the following reaction
?
Sol.
Q.4. 1,1-dibromopentane on reaction with fused KOH at 470 K gives 2-pentyne
1,1-dibromo pentane 2-pentyne
Give the mechanism of this rearrangement.
(II) By Dehalogenation of Tetrahaloalkane:
General Reaction
(III) Replacement of The Acetylenic Hydrogen atom of terminal Alkynes.
General Reaction
Sodium ethynide and other sodium alkynides can be prepared by treating terminal alkynes with sodium amide in liquid ammonia.
(R or R' or both may be hydrogen)
The following example illustrates this synthesis of higher alkyne homologues.
(R'-X must be an unhindered primary halide or tosylate)
The unshared electron pair of the alkynide ion attacks the back side of the carbon atom that bears the halogen atom and forms a bond to it. The halogen atom departs as a halide ion.
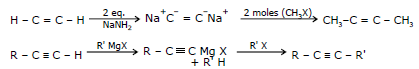
e.g.
Addition of acetylide ions to carbonyl groups
e.g.
Sodium Propanal 1-Pentyn-3-ol acetylide
e.g.
3-Methyl-1-butyne 4-Methyl-1-Phenyl pent-2-yne-1-ol
e.g.
Cyclohexanone 1-Ethynylcyclohexanol(3º)
Ex.7 Show how to synthesize 3-decyne from acetylene along with necessary alkyl halides.
Sol. H - C≡C - H H3C - (CH2)5 - C≡C - H
1-Octyne
H3C - (CH2)5 - C≡C - H CH3 - (CH2)5 - C≡C - CH2CH3
1-Octyne 3-Decyne
Q.5 Show how you would synthesize the following compound, beginning with acetylene and any necessary additional reagents.
(IV) By Kolble's Electrolytic synthesis.
(V) By Hydrolysis of carbides
CaC2 + 2HOH → C2H2 + Ca(OH)2
MgC2 + 2HOH → C2H2 + Mg(OH)2
Mg2C3 + 4HOH→ CH3 - C≡CH + 2Mg(OH)2
10. Chemical Properties of Alkyne
(i) Acidic Character Of Alkynes
Alkynes are one of the simplest hydrocarbons known to us. They have a general formula of CnH2n-2. Alkynes belong to the family of unsaturated hydrocarbons that is; they contain both sigma and pi bond linkages between carbon and hydrogen.
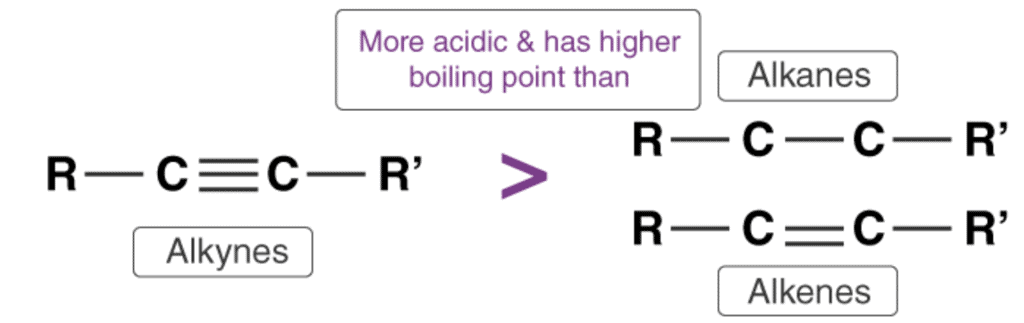
Relative Acidity of Alkynes
- The acidity of alkynes is due to their ability to lose hydrogen atom to form alkynideions. Thus, alkynes act as Brønsted-Lowry acids. The triple bonded carbon atom in alkynes is “sp” hybridized. Due to the high percentage of “s” character (50%) in alkynes, the “sp” hybridized orbitals of carbon atom in alkynes exhibit high electronegativity. These attract the C-H bond of alkynes to a great extent. Thus, alkyne molecules can easily lose hydrogen atom forming alkynide ions. Hence, we can say that the hydrogen atom attached to the triply bonded carbon atom is acidic in nature.
- The acidity of alkynes is greater than the acidity of alkanes and alkenes as the carbon atom in alkanes and alkenes are “sp3” and “sp2” hybridized respectively. Hence, these molecules contain a smaller percentage of “s” character in comparison to alkynes. Thus, the electronegativity of the carbon atom in these cases is lesser than alkynes. Hence, alkanes and alkenes don’t show the reactions with bases to liberate hydrogen gas. It can further be noted that only hydrogen atom attached to a triply bonded carbon atom are acidic not the other hydrogen atoms in the alkyne chain. The general trend in acidity is seen as:
HC≡CH > H2C=CH2 > CH3–CH3
HC≡CH > CH3–C≡CH >> CH3–C≡C–CH3
(ii) Addition of dihydrogen
Alkynes react with dihydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as Pt/Pd/Ni in order to form alkenes. The alkenes formed, further react with dihydrogen to form alkanes. It has been observed that in most reactions triple bond is converted into a double bond and a double bond is then converted into a single bond due to the addition reaction with dihydrogen.
The catalyst that is involved in the case of rhodium, nickel, palladium, and platinum. Hydrogenation is a step-by-step process in which initially an alkene is formed. After which it undergoes further hydrogenation to form an alkane
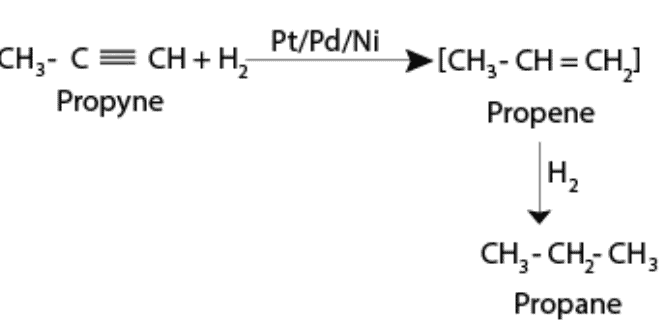
Slowing down the reaction in the intermediate stage is actually quite impossible as the whole reaction is really smooth. But some alkenes are isolated with the use of poisoned catalysts. One such example of a poisoned catalyst is the Lindlar catalyst.
Lindlar catalyst
Lindlar catalyst is the combined form of palladium which is coated with quinoline and absorbed on calcium carbonate.
(iii) Addition of Halogen (X2=Cl2, Br2)
General Reaction R - C º C - R' R - CX = CX - R'
(Anti-addition)
Ex.9 Explain why alkynes are less reactive than alkenes toward addition of Br2.
Sol. The three memebered ring bromonium ion fromed from the alkyne (A) has a full double bond causing it to be more strained and less stable than the one from the alkene (B).
(A) (B)
(A) less stable than (B)
Also, the C's of A that are part of the bormonium ion have more s-character than those of B, further making A less stable than B.
(iv) Addition of Hydrogen halides (Were HX = HCl, HBr, HI)
General Reaction
R - C≡C - R'
e.g.
e.g. CH3-C≡C - CH2CH3 HBr →
e.g. H - C≡C - CH2CH2CH3
(v) Addition of water
Alkynes are immiscible in water. They do not react with water under normal conditions. Alkynes may react with water in the presence of dilute sulphuric acid and mercuric sulphate at a temperature of 333K. This results in the formation of carbonyl compounds.
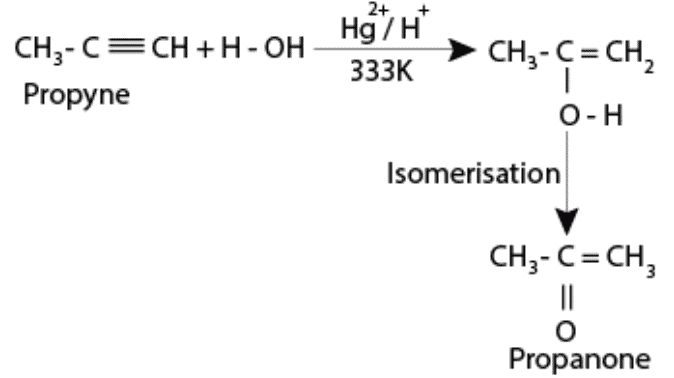
(vi) Polymerisation
(a) Linear polymerisation: Under suitable conditions, linear polymerisation of ethyne takes place to produce polyacetylene or polyethyne which is a high molecular weight polyene containing repeating units of (CH = CH – CH = CH ) and can be represented as —( CH = CH – CH = CH)n— Under special n conditions, this polymer conducts electricity
Thin-film of polyacetylene can be used as electrodes in batteries. These films are good conductors, lighter and cheaper than metal conductors.
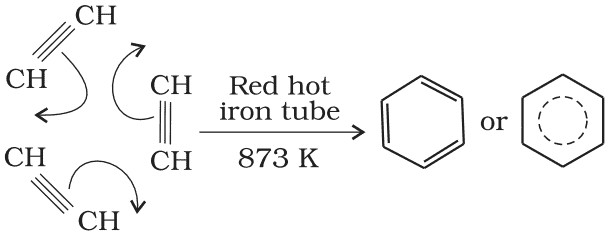
(b) Cyclic polymerisation: Ethyne on passing through a red hot iron tube at 873K undergoes cyclic polymerization. Three molecules polymerise to form benzene, which is the starting molecule for the preparation of derivatives of benzene, dyes, drugs and large a number of other organic compounds. This is the best route for entering from aliphatic to aromatic compounds as discussed below:
(vii) Reduction to alkenes
(a) By Lindlar's reagent
General Reaction
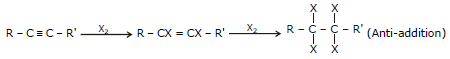
(b) By Brich reduction
General Reaction R - C º C - R' (anti addition)
e.g.
(c) By hydroboration reduction
General Reaction R - C º C - R'
Ex.8 Identify (X) and (Y) in the following reaction
CH3-CH2 - C º CH
Ans. (X) : (Y) :
|
114 videos|263 docs|74 tests
|
FAQs on Alkynes: Nomenclature, Properties & Preparation - Chemistry Class 11 - NEET
| 1. What is the nomenclature of alkynes? |  |
| 2. What are the properties of alkynes? |  |
| 3. How can alkynes be prepared? |  |
| 4. What are the uses of alkynes? |  |
| 5. How do alkynes differ from alkenes and alkanes? |  |






















