Hydrogen Peroxide: Structure, Preparation, Properties & Uses | Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced PDF Download
Hydrogen Peroxide [H2O2]
H2O2 was discovered by J.L. Thenard in 1818. It is an important compound used in pollution control treatment of domestic and industrial effluents.
Structure of H2O2
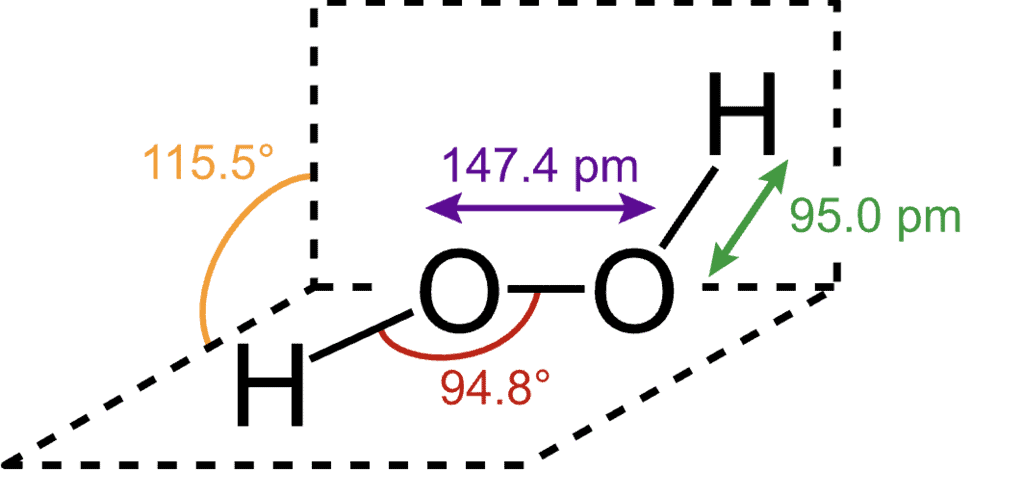
It has a non-planar open book (skew) structure. The 0-H bond length is 95 pm and O-O bond length is 147•5 pm. The H-O-O bond angle is 94•8 and the dihedral angle (angle between the planes containing the H-O-O group) is 111.5° in the gas phase. The bond lengths and angles are slightly changed in liquid and solid phases due to hydrogen bonding. The bond angle between the two planes reduces to 90•2° in the crystalline state.
The structure of H2O2 can also be explained on the basis of valence bond theory where both the oxygen atoms are sp-hybridized. Two of these hybrid orbitals on each oxygen are occupied by lone pairs of electrons. The third hybrid orbital overlaps with the s-orbital of a hydrogen atom to form an O-H sigma bond while the fourth one forms a sigma bond with the half-filled hybrid orbital of the second oxygen atom.
Methods of Preparation:
Strength of Hydrogen Peroxide:
The most common method to express the strength of H2O2 is in terms of the volume (in mL) of oxygen liberated at NTP by decomposition of 1 mL of that sample of H2O2. A solution of H2O2 labelled as ’10 volume’ actually means “1 mL of such a solution of H2O2 on decomposition by heat produces 10 mL of oxygen at NTP”.
(i) Strength of H2O2 in terms of normality:
(68 x X/22.4) = 17 x N ⇒ X = 5.6 x N
where, X is volume strength of H2O2.
(ii) % strength = (17/56) x volume strength
(iii) X = 11.2 x molarity.
Storage of Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2):
It is stored in the presence of traces of alcohol, acetanilide or sodium pyrophosphate which slows down the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide.
Chemical Properties of H2O2:
(i) Acidic nature- It is weakly acidic in nature and pure hydrogen peroxide turns blue litmus red.
(ii) Oxidising agent- It acts as a strong oxidising agent in acidic as well as in basic medium.
e.g., oxidising action of H2O2 is:
(iii) Reducing agent-
(a) In acidic medium
(b) In basic medium
(iv) Bleaching properties- Its bleaching action is due to oxidation by atomic oxygen and permanent.
H2O2 → H2O + [O]
dye + [O] → dye is oxidised and bleached.
Physical Properties of Hydrogen Peroxide
- Hydrogen Peroxide is an almost clear, pale blue liquid in its pure state
- It has an odour similar to that of nitric acid
- Hydrogen peroxide has a viscosity higher than water. It is about 40% denser than water
- The pure concentrated form boils around 150°C. However, at this temperature, it undergoes thermal decomposition and has an explosive reaction. This is why hydrogen peroxide is generally stored in an aqueous form. Also to avoid it reacting with the light we store it in dark color containers. It must be remembered that we have no practical knowledge of hydrogen peroxide’s boiling point. It is only a theoretical assumption. This is because it explodes before reaching its boiling point.
- It is miscible in water, i.e. it forms a homogeneous solution when mixed with water.
Uses of Hydrogen Peroxide:
1) The most important industrial use of hydrogen peroxide is as a bleaching agent for delicate materials like Silk, wool, paper pulp, straw, oils and fats.
2) It is used as a hair bleach and as a mild disinfectant.
3) It is extensively used to manufacture inorganic chemicals like sodium perborate and percarbonate which are important constituents of good quality detergents.
4) In the production of epoxides, propylene oxide and polyurethane.
5) Hydrogen peroxide is also used in the synthesis of hydroquinone, pharmaceuticals like cephalosporin and food products.
6) It is increasingly being used in Environmental chemistry to control pollution by treatment of domestic and industrial effluents, oxidation of cyanide and restoration of aerobic conditions to sewage waste.
7) It is used as an antiseptic under the name perhydrol for washing wounds, teeth and ears.
8) It is used for restoring the colour of lead paint which have blackened due to action of H2S present in the air on lead paints.
9) It is used in laboratory for detecting the presence of chromium, titanium and vanadium salts with which it yields peroxides of characteristic colours.
10) 93% hydrogen peroxide solution is used as an oxidant for rocket fuel and as a propellant.
11) It is used as antichlor in textile industry to remove excess of chlorine after bleaching operations.
12) A mixture of hydrazine hydrate and hydrogen peroxide with copper catalyst is used as a rocket propellant.
|
334 videos|651 docs|300 tests
|
FAQs on Hydrogen Peroxide: Structure, Preparation, Properties & Uses - Chemistry for JEE Main & Advanced
| 1. What is the chemical structure of hydrogen peroxide? |  |
| 2. How is hydrogen peroxide prepared? |  |
| 3. What are the properties of hydrogen peroxide? |  |
| 4. What are the common uses of hydrogen peroxide? |  |
| 5. Is hydrogen peroxide safe to use? |  |

















